We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 823
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
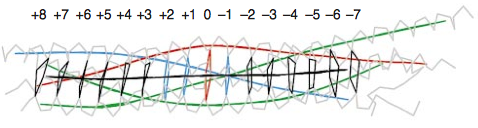
[[Image:Layers.png|thumbnail||1100 px||left| '''Topology of the 16 layers of the SNARE complex''']] | [[Image:Layers.png|thumbnail||1100 px||left| '''Topology of the 16 layers of the SNARE complex''']] | ||
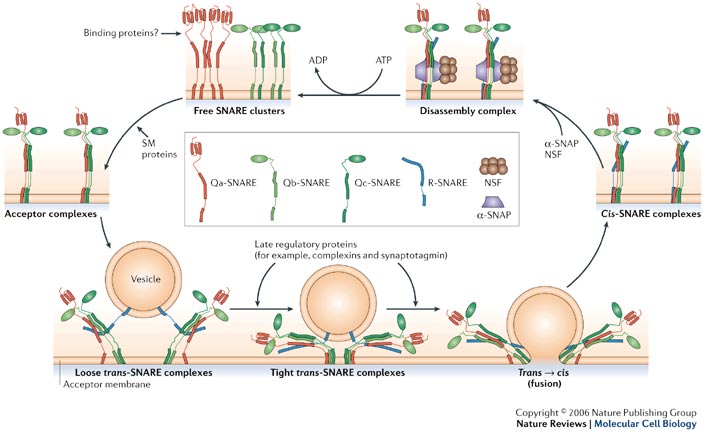
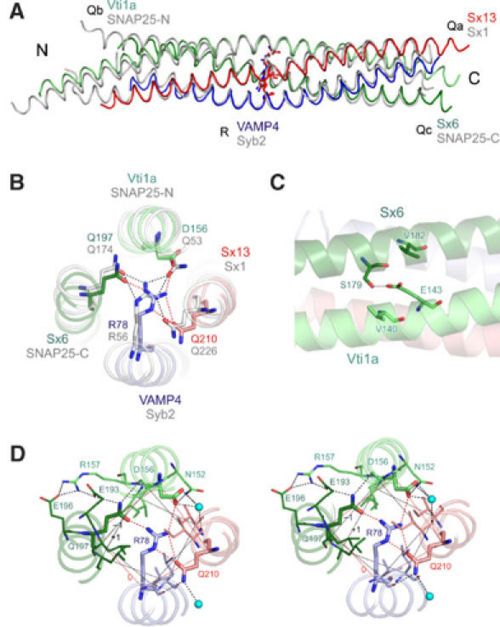
| - | The centre of the four-helix bundle is constituted of '''16 layers'''. These layers are composed of <scene name='56/568021/Hydrophobis_side_chains/ | + | The centre of the four-helix bundle is constituted of '''16 layers'''. These layers are composed of <scene name='56/568021/Hydrophobis_side_chains/2'>hydrophobic side chains</scene>, which are perpendicular to the axis of the four-helix bundle, except for the central '''“0”-layer'''. This last one consists of '''three glutamine (Q)''' and '''one arginine (R)''' highly conserved residues. Those highly conserved residues have led to a new classification of SNAREs into '''Q- and R-SNAREs'''. <ref> PMID: 9861047 </ref> Almost all membrane fusion reactions require one R-SNARE and three Q-SNAREs: Qa, Qb and Qc.<ref> PMID: 11237004 </ref><ref> PMID: 11001046 </ref> In many cases, the R-SNARE is in the vesicle, and the three Q-SNAREs are in the target membrane. For the early endosomal SNARE complex, syntaxin 13, vti1a, syntaxin 6, and VAMP4 were respectively classified as Qa-, Qb-, Qc- and R-SNAREs. |
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
The early endosomal SNARE complex forms a four-helix bundle with a '''left-handed superhelical twist'''. The position of the Qa-, Qb-, Qc-, and R-SNAREs is the same in the neuronal and late endosomal complexes.<ref name="sutton" /><ref name="anto" /> As mentioned above, an unconventional layer of hydrophilic residues – the “0”-layer – constituted of three glutamines and one arginine, characterizes the center of all SNARE complexes. However, in vti1a an '''aspartate residue''' substitutes the glutamine. The aspartate occupies the '''same position''' as the glutamine in the neuronal and late endosomal complexes, and is involved in a '''similar organization of hydrogen bonds''' with the other layer of amino acids. Moreover, in vti1a, <scene name='56/568021/Asp_156/5'>D156</scene> of the ‘0' layer also interacts with <scene name='56/568021/Asn_152/3'>N152</scene> at the surface of the vti1a helix and with a '''water molecule'''. Also, <scene name='56/568021/Gln_197/4'>sx6 Q197</scene> interacts with the <scene name='56/568021/D156/2'>backbone of vti1a D156</scene> and with <scene name='56/568021/Sx6_e193/2'>sx6 E193</scene> that in turn interacts with <scene name='56/568021/Vti1a_r157/3'>vti1a R157</scene>. Concerning <scene name='56/568021/Vti1a_r157/3'>vti1a R157</scene>, it interacts with <scene name='56/568021/Sx6_e196/2'>sx6 E196</scene>. This network of interactions resembles that observed in the neuronal complex.<ref> PMID: 12496247 </ref> The structure of the other layers is '''generally similar''' to that of the neuronal and late endosomal complexes. Indeed, slightly differences can be noted: in layer 6, the Qc-SNARE syntaxin 6 contains a valine, whereas the late endosomal Qc-SNARE syntaxin 8 contains a glutamate, which is involved in interactions with surface residues. Such interactions are absent in the early endosomal and the neuronal complexes. | The early endosomal SNARE complex forms a four-helix bundle with a '''left-handed superhelical twist'''. The position of the Qa-, Qb-, Qc-, and R-SNAREs is the same in the neuronal and late endosomal complexes.<ref name="sutton" /><ref name="anto" /> As mentioned above, an unconventional layer of hydrophilic residues – the “0”-layer – constituted of three glutamines and one arginine, characterizes the center of all SNARE complexes. However, in vti1a an '''aspartate residue''' substitutes the glutamine. The aspartate occupies the '''same position''' as the glutamine in the neuronal and late endosomal complexes, and is involved in a '''similar organization of hydrogen bonds''' with the other layer of amino acids. Moreover, in vti1a, <scene name='56/568021/Asp_156/5'>D156</scene> of the ‘0' layer also interacts with <scene name='56/568021/Asn_152/3'>N152</scene> at the surface of the vti1a helix and with a '''water molecule'''. Also, <scene name='56/568021/Gln_197/4'>sx6 Q197</scene> interacts with the <scene name='56/568021/D156/2'>backbone of vti1a D156</scene> and with <scene name='56/568021/Sx6_e193/2'>sx6 E193</scene> that in turn interacts with <scene name='56/568021/Vti1a_r157/3'>vti1a R157</scene>. Concerning <scene name='56/568021/Vti1a_r157/3'>vti1a R157</scene>, it interacts with <scene name='56/568021/Sx6_e196/2'>sx6 E196</scene>. This network of interactions resembles that observed in the neuronal complex.<ref> PMID: 12496247 </ref> The structure of the other layers is '''generally similar''' to that of the neuronal and late endosomal complexes. Indeed, slightly differences can be noted: in layer 6, the Qc-SNARE syntaxin 6 contains a valine, whereas the late endosomal Qc-SNARE syntaxin 8 contains a glutamate, which is involved in interactions with surface residues. Such interactions are absent in the early endosomal and the neuronal complexes. | ||
| - | Regarding the SNARE motifs, they are not only connected by the central interacting layers, but also '''by surface interactions''' that often involve side chains with complementary charges. As an example, an interaction between the helices of '''syntaxin 6''' and '''vti1a''' involves a <scene name='56/568021/Aspser/2'>hydrogen bond between E143 (vti1a) and S179 (sx6)</scene>. At a similar position in the late endosomal complex, a '''salt bridge''' is observed between <scene name='56/568021/D157r164/ | + | Regarding the SNARE motifs, they are not only connected by the central interacting layers, but also '''by surface interactions''' that often involve side chains with complementary charges. As an example, an interaction between the helices of '''syntaxin 6''' and '''vti1a''' involves a <scene name='56/568021/Aspser/2'>hydrogen bond between E143 (vti1a) and S179 (sx6)</scene>. At a similar position in the late endosomal complex, a '''salt bridge''' is observed between <scene name='56/568021/D157r164/2'>D157 (vti1b) and R164 (sx8)</scene>.<ref name="anto" /> It has to be noted that all these side chains are '''highly conserved''' between the respective SNAREs of ''Drosophila'' and mammals. Many other surface interactions connect the SNARE motifs. However, the role of these surface interactions in the stability of the whole complex is still unknown. |
Current revision
Introduction
| |||||||||||
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |