Sandbox Reserved 815
From Proteopedia
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| - | A prion is an infectious agent composed of protein in a misfolded form. The name prion, is derived from the words protein and infectious. Prions are responsible for the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in mammals .In humans, prions cause [http:// | + | A prion is an infectious agent composed of protein in a misfolded form. The name prion, is derived from the words protein and infectious. Prions are responsible for the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in mammals .In humans, prions cause [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Creutzfeldt%E2%80%93Jakob_disease Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease](CJD), [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fatal_familial_insomnia Fatal Familial Insomnia] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kuru_%28disease%29 kuru]. |
The 3haf structure results from a work leaded by Lee S. in 2010, in which they have characterized seven variants of the human prion. The structure was determined by XRAY diffraction in a 2.26-Angstrom resolution. | The 3haf structure results from a work leaded by Lee S. in 2010, in which they have characterized seven variants of the human prion. The structure was determined by XRAY diffraction in a 2.26-Angstrom resolution. | ||
Revision as of 18:24, 8 January 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||
| 3haf, resolution 2.26Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , | ||||||||
| Gene: | PRNP, PRIP, PRP (Homo sapiens) | ||||||||
| Related: | 3hak | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Contents |
Introduction
A prion is an infectious agent composed of protein in a misfolded form. The name prion, is derived from the words protein and infectious. Prions are responsible for the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in mammals .In humans, prions cause Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease(CJD), Fatal Familial Insomnia and kuru.
The 3haf structure results from a work leaded by Lee S. in 2010, in which they have characterized seven variants of the human prion. The structure was determined by XRAY diffraction in a 2.26-Angstrom resolution.
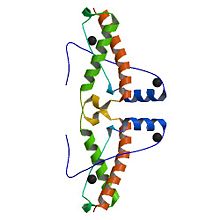
3haf is a domain of the Major prion protein. This domain is between the residue 120 and the 225 of the entire prion .This structure is a succession of helix and sheet beta. The domain contains sites of glycolisation. It can be noticed a mismatch precisely at the residue 129, where a Valin substitutes a Methionin, influencing the susceptibility of the formation of the prion.
Structure
Secondary Structure
The secondary structure is a succession of helix and beta sheet:
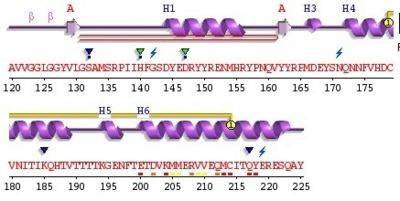
Alpha helix (112-135) _ coil_ alpha helix (144-153)_coil_3/10 helix (165-169)_coil_ alpha helix_ coil_ alpha helix (200-227)
The proportion of each structure is 43% of alpha helical (6helix, 62 residues) and 2% of beta sheet (2strands, 4 residues). There are also 2 glycosylation site and the C-ter domain is higher conserved.
3 residues can have a contact with metals; S132, H140 and D147 The structure shows also a hairpin structure at the N-ter domain. A lot of empty structures (not in the secondary structure) are present between helix. One structure is called 3/10 helix. The entire 3haf domain can interact with GRB2 (Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2), ERI3 (exoribonuclease 3) and SYN1 (Synapsin I).
Ligand:
This protein binds copper (II) ions with high affinity: Cd2+ (cadnium ions) and Cl- (chloride ion). But, this protein can also binds a Cu2+ ions on this NH2 tail and this bond can induce conformational change with a lot of unknown effect.
In fact, the 3haf domain is only one chain with 2 binding sites or residues CD (H40 and D147)
and 1 binding domains for CL S132.
Polymorphism:
The common Methionine/Valine polymorphism residue in 129 in the PrP influences disease… A mutation on the valine 129 can have an effect on some disease. If this Valine is muted as methionine (polymorphism) it can determine the disease phenotype in patients. Valine 129 is finding on CJD (Crutzfeld Jacob Disease) whereas methionine 129 is find in FFI.
A lot of others mutations can be finding in these diseases: for example, R208 => H208 is finding in CJD, N171=>S171 can be finding in schizoaffective disorder.
For this domain, two glycosylated sites exist on helix 2 and 3 at Asn181 and Asn197. A disulfide bond exist between Cys179 and helix 2 ans the other between Cys214 and helix3.
Disease
Function
See Also
Reference
- Lee S, Antony L, Hartmann R, Knaus KJ, Surewicz K, Surewicz WK, Yee VC. Conformational diversity in prion protein variants influences intermolecular beta-sheet formation. EMBO J. 2010 Jan 6;29(1):251-62. Epub 2009 Nov 19. PMID:19927125 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.333