We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 820
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
== Calcium Binding == | == Calcium Binding == | ||
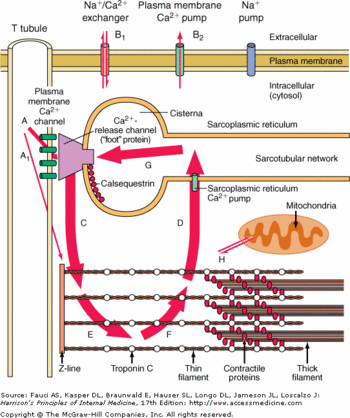
| - | Each monomere of CASQ2 can bind between <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/12'>18 to 50 Ca2+</scene>. The Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions bind to two or more acidic amino acids like <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/13'>Glutamate</scene> or <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/ | + | Each monomere of CASQ2 can bind between <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/12'>18 to 50 Ca2+</scene>. The Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions bind to two or more acidic amino acids like <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/13'>Glutamate</scene> or <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/19'>Aspartate</scene>. These amino acids are mainly oriented outside and in the C-terminal region. It had been shown that Ca<sup>2+</sup>ions mainly bind an Asp-rich region on the disordered C-terminal domain. When CASQ2 form homooligomers, Ca<sup>2+</sup> can be bound in the electronegative pockets created by the <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/17'>front-to-front</scene> and <scene name='56/568018/Oligomere_and_ligand/16'>back-to-back</scene> dimer interactions.<ref name="The asp-rich region at the carboxyl-terminus of calsequestrin binds to Ca2+ and interacts with triadin (Shin et al., 2000)">The Asp-rich region at the carboxyl-terminus of calsequestrin binds to Ca<sup>2+</sup> and interacts with triadin (Shin et al., 2000) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014579300022468</ref> |
CASQ2 can also bind other ions like Mg<sup>2+</sup> or H<sup>+</sup>. The affinity for Mg<sup>2+</sup> is lower than the affinity for Ca<sup>2+</sup> however the concentration of Ca<sup>2+</sup> decreases. When the pH is low, the calcium-binding capacity of CASQ2 decreases as H<sup>+</sup> ions occupy the acidic sites and inhibit the polymerization.<ref name="Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle (Beard et Al., 2004)">PMID:15050380</ref> | CASQ2 can also bind other ions like Mg<sup>2+</sup> or H<sup>+</sup>. The affinity for Mg<sup>2+</sup> is lower than the affinity for Ca<sup>2+</sup> however the concentration of Ca<sup>2+</sup> decreases. When the pH is low, the calcium-binding capacity of CASQ2 decreases as H<sup>+</sup> ions occupy the acidic sites and inhibit the polymerization.<ref name="Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle (Beard et Al., 2004)">PMID:15050380</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:29, 8 January 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cerrone M, Napolitano C, Priori SG. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: A paradigm to understand mechanisms of arrhythmias associated to impaired Ca(2+) regulation. Heart Rhythm. 2009 Nov;6(11):1652-9. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.06.033. Epub 2009 , Jun 30. PMID:19879546 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.06.033
- ↑ NCBI Gene Ressource: CASQ2 calsequestrin 2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/845
- ↑ Martin JL. Thioredoxin--a fold for all reasons. Structure. 1995 Mar 15;3(3):245-50. PMID:7788290
- ↑ NCBI Structure Ressource: CASQ2 calsequestrin 2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?ascbin=8&maxaln=10&seltype=2&uid=239372&querygi=429544235&aln=1,227,0,109
- ↑ Polymerization of Calsequestrin: IMPLICATIONS FOR Ca2+ and REGULATION (Park et al., 2003) http://www.jbc.org/content/278/18/16176.full.pdf+html
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Crystal Structure of calsequestrin from rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum (Wang et al., 1998) http://www.nature.com/nsmb/journal/v5/n6/abs/nsb0698-476.html
- ↑ NCBI Structure Ressource: CASQ2 calsequestrin 2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi
- ↑ The Asp-rich region at the carboxyl-terminus of calsequestrin binds to Ca2+ and interacts with triadin (Shin et al., 2000) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014579300022468
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Beard NA, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF. Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2004 May;85(1):33-69. PMID:15050380 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2003.07.001
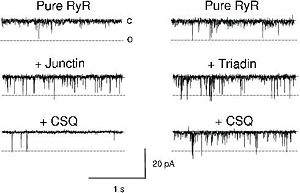
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Beard NA, Casarotto MG, Wei L, Varsanyi M, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF. Regulation of ryanodine receptors by calsequestrin: effect of high luminal Ca2+ and phosphorylation. Biophys J. 2005 May;88(5):3444-54. Epub 2005 Feb 24. PMID:15731387 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.104.051441
Proteopedia page contributors and editors
Marc-Antoine JACQUES and Thomas VUILLEMIN