This tutorial illustrates some basic properties of protein structure and useful commands in Jmol and Proteopedia. Clicking the green links changes the view in the structure box to illustrate the principle described by the text. If the structure box has a puzzle piece in it, please make sure you have the latest version of Java installed and follow the directions to allow Proteopedia to run.
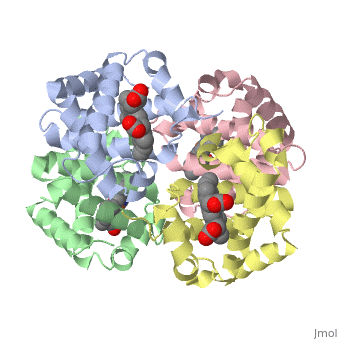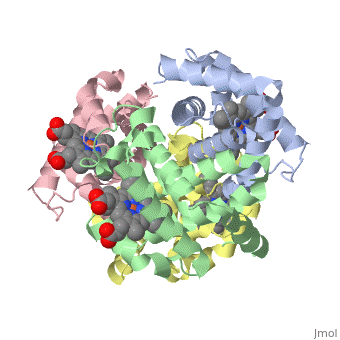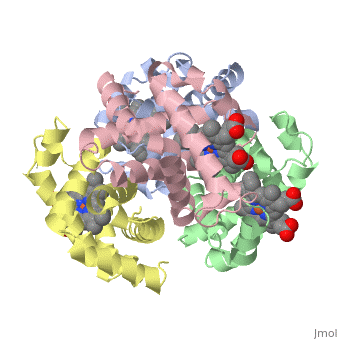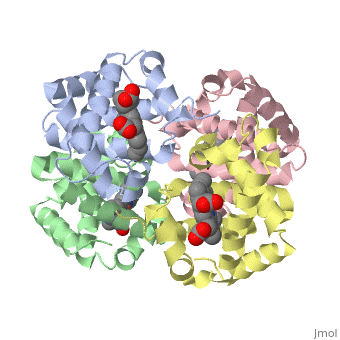
Proteins are condensation polymers of amino acids. The is the amino acid sequence. The is the local structure over short distances. This level of structure is stabilized by along the . These secondary structures to form the overall form of the entire peptide chain, called the . Some proteins, such as the displayed hemoglobin molecule, have more than one polypeptide chain that associate to form the functional unit of the protein; this is called .
Questions based upon these scenes:
What is the primary sequence shown in the first link?
Is the secondary structure shown an alpha helix or beta sheet?
The ith C=O of the backbone is hydrogen bonded to which N(-H) (use i +/- # to represent the number)?
What atom does this program NOT show?
What color is used to represent alpha helices?
How many alpha helices are present in the single peptide chain shown?
How many polypeptide chains make up the quaternary structure?
Ways of representing protein structure
Protein structures can be displayed in many different ways. In models, all of the non-hydrogen atoms are shown as spheres with their van der Waals radii. In the model, the atoms are shown as smaller balls, connected by sticks; this is further simplified in the model, which only shows the bonds between atoms. shows only the N-Calpha-C=O repeating unit; the representation shows the secondary structures.
Questions based upon these scenes:
Which of these representations would be best for showing...
--the secondary structures present in a molecule?
--Channels, holes, or pockets in a protein?
--Residues in the active site of an enzyme?
Explain your answers.
Secondary Structures
In this section, you will both learn about secondary structure properties and manipulating structures in Jmol. We will begin with some basic manipulation strategies so that you can analyze secondary structures. Try the following manipulations with the mouse:
--Click and move the mouse to the right, the left, up, and down; what happens to the molecule?
--Hold the shift button while you try the same manipulations. What does each do?
Clicking the right mouse button in the structure box brings up an extensive menu. This exercise will use commands in the style, color,zoom, measurements, and set picking categories.
We will begin with the structure of an alpha helix from hemoglobin. From this view, can you determine:
--The number of amino acids per turn?
--The position of the side chains?
Hold the mouse over each end of the alpha helix. A yellow box should appear, with [VAL]17:A:CA:#120. This indicates the amino acid residue, the position in the chain, which chain, what atom it is (CA means the alpha carbon), and the overall number of the atom. If there are two identical chains, one of the chains may be numbered slightly differently (like adding 200 to each residue number) to distinguish the residues.
--What is the amino acid range (numbers) of this alpha helix?
Rotate the helix so that you are looking down the helix. What does the middle of the helix look like?
Right click on the mouse, choose style, then scheme, then CPK spacefill.
What does the middle of the helix look like?
Which view is more representative of the true structure of the molecule?
Let's try changing to another view. Right click on the mouse, choose style, then scheme, then ball and stick. Based upon what you know about peptide composition or by holding the mouse over the atoms determine the color scheme:
red =
black =
blue =
Notice that hydrogens are not shown on this model. Xray crystallography is not able to resolve hydrogens, so they are omitted from the images. This also simplifies the data set, as there are many fewer atoms to position.
Jmol can be used to make measurements of various properties of the alpha helix, such as the dihedral angle. has the side chains removed (though the alpha carbons show where the side chain would be). Right click in the structure box. In the Measurements menu, select "double click begins and ends measurements". Double click on one of the nitrogens, then click once on the following atoms in order: the attached Calpha, carbonyl C, and N. Record this dihedral angle (a psi angle) in a table, recording the number of the nitrogen you began at. Repeat, starting at the N you ended on. Notice each click gives a different property: the first is the bond length, the second is the bond angle, and the third is the dihedral (torsional) angle. You may need to rotate around the helix to see the atoms you want to measure; repeat for four psi angles. After you have completed it for the psi angles, repeat for the phi angles by clicking on the carbonyl C, Calpha, N and carbonyl C. Do this for four different amino acids.
What is the average phi angle in this alpha helix? What is the range of values?
What is the average psi angle in this alpha helix? What is the range?
Since hemoglobin doesn't have any beta sheets, we will switch to another protein: , PDB code 1CYO.
What view is presented in this scene?
The coloring in this view is a N-->C rainbow, with the N terminus being blue and the C terminus red.
Describe the relative positioning of the alpha helices and beta sheets. Are all the alpha helices clustered with the beta sheets in another portion of the sequence, or are they interspersed?
Next, we will look at two of the . The side chains have been faded out to make the backbone more obvious.
Determine if these two strands are parallel or antiparallel.
Where are the side chains positioned, relative to the main direction of the strand?
Like before, measure four psi and four phi angles. Avoid the turn between the two strands. Record these values in a table.
What is the average psi angle? What is the range of values?
What is the average phi angle? What is the range of values?
Which has more variability in the dihedral angles, an alpha helix or a beta sheet?
The overall dihedral angles in a protein can be displayed in a , which graphs the interrelationship between phi and psi angles. Pink dots are angles found in alpha helices; yellow dots are found in beta sheets, and white dots are found in other regions (either disordered or turns). Mouse over the white dots on the right sides; what amino acids tend to have atypical phi and psi angles?
Tertiary Structure
The tertiary structure of a protein is the overall folding of a single polypeptide chain. While we are still understanding the folding process, it is obvious that part of the driving force is the sequestering of hydrophobic residues to the middle of the protein, while polar residues are found on the surface. In , the hydrophilic residues are purple, while the hydrophobic ones are grey. While some hydrophobic residues are on the surface, they do not dominate the structure. Disulfide bonds can also help stabilize the tertiary structure.
Quaternary structure
The of proteins is formed when polypeptide chains associate with one another to form a functional unit. This allows for additional regulatory strategies. Hemoglobin is the classic example of a quaternary protein structure, and you can explore more on the Hemoglobin page.
Qu