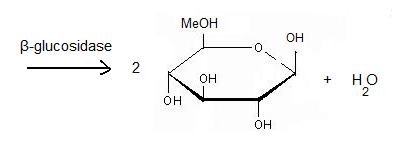
Beta-glucosidase
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''β-glucosidase''' is an enzyme which catalyses the hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing residues in β-glucosides (EC number : 3.2.1.21). In the case of 2VRJ, it comes from ''Thermotoga maritima'' which is a rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the order of Thermotogates. This bacterium was originally isolated from geothermal heated marine sediments. | '''β-glucosidase''' is an enzyme which catalyses the hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing residues in β-glucosides (EC number : 3.2.1.21). In the case of 2VRJ, it comes from ''Thermotoga maritima'' which is a rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the order of Thermotogates. This bacterium was originally isolated from geothermal heated marine sediments. | ||
2VRJ is here is in complex with an inhibitor called N-octyl-5-deoxy66-oxa-N-carbamoylcalystegine <ref>PMID: 18833549</ref>. Raucaffricine β-glucosidase (RGB) catalyzes the conversion of raucaffricine to glucose and vomilenine. Some more details in [[Molecular Playground/Beta-galactosidase]]. | 2VRJ is here is in complex with an inhibitor called N-octyl-5-deoxy66-oxa-N-carbamoylcalystegine <ref>PMID: 18833549</ref>. Raucaffricine β-glucosidase (RGB) catalyzes the conversion of raucaffricine to glucose and vomilenine. Some more details in [[Molecular Playground/Beta-galactosidase]]. | ||
| - | |||
===General action as biocatalyst=== | ===General action as biocatalyst=== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
==2VRJ== | ==2VRJ== | ||
===Structure and function=== | ===Structure and function=== | ||
| - | |||
In terms of structure 2VRJ is a homodimer. It means that it is composed of two chains <scene name='Sandbox_155/Chain_a/1'>A</scene> and <scene name='Sandbox_155/Chain_b/1'>B</scene> which are chiral. Each chain is composed of 438 residues and constitutes a subunit of the protein. Each subunit contains a''' catalytic site'''. | In terms of structure 2VRJ is a homodimer. It means that it is composed of two chains <scene name='Sandbox_155/Chain_a/1'>A</scene> and <scene name='Sandbox_155/Chain_b/1'>B</scene> which are chiral. Each chain is composed of 438 residues and constitutes a subunit of the protein. Each subunit contains a''' catalytic site'''. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 23: | ||
There are three different topologies for the active site of β-glucosidases : the pocket or crater, the cleft or groove and the tunnel <ref>PMID: 8535779</ref>. The topology of 2VRJ active site is a <scene name='Sandbox_155/Pocket/3'>pocket</scene> in which the ligand can bind. | There are three different topologies for the active site of β-glucosidases : the pocket or crater, the cleft or groove and the tunnel <ref>PMID: 8535779</ref>. The topology of 2VRJ active site is a <scene name='Sandbox_155/Pocket/3'>pocket</scene> in which the ligand can bind. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
===Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing residues in β-glucosides=== | ===Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing residues in β-glucosides=== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 35: | ||
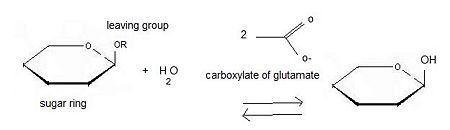
Inverting glycoside hydrolases lead to an inversion of the anomeric configuration to create an alpha configuration. The steps of the reaction are like the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution S2N. It is an one step process: the nucleophile (water) the anomeric carbon with simultaneous expulsion of the leaving group (OR). Bond making takes place at the same time as bond breaking. Such a mechanism is called''' concerted reaction'''. | Inverting glycoside hydrolases lead to an inversion of the anomeric configuration to create an alpha configuration. The steps of the reaction are like the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution S2N. It is an one step process: the nucleophile (water) the anomeric carbon with simultaneous expulsion of the leaving group (OR). Bond making takes place at the same time as bond breaking. Such a mechanism is called''' concerted reaction'''. | ||
The distance between the two carboxylates is about 10.5 angströms. | The distance between the two carboxylates is about 10.5 angströms. | ||
| - | |||
====Retaining glycoside hydrolases==== | ====Retaining glycoside hydrolases==== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 44: | ||
The distance between the two carboxylates for this mechanism is about 5.5 angströms. | The distance between the two carboxylates for this mechanism is about 5.5 angströms. | ||
For 2VRJ the distance between its two glutamates is about <scene name='Sandbox_155/Glu/1'>5</scene> angströms. So we can say that 2VRJ seems to be a retaining enzyme. | For 2VRJ the distance between its two glutamates is about <scene name='Sandbox_155/Glu/1'>5</scene> angströms. So we can say that 2VRJ seems to be a retaining enzyme. | ||
| - | |||
NB: The values of the pH and the nature of the solvent play a main role in the rate of the reaction. | NB: The values of the pH and the nature of the solvent play a main role in the rate of the reaction. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 57: | ||
For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | __NOTOC__ | ||
==3D structures of Beta-glucosidase== | ==3D structures of Beta-glucosidase== | ||
Revision as of 06:17, 17 August 2014
| |||||||||||
Contents |
3D structures of Beta-glucosidase
Updated on 17-August-2014
3ahx – GBA – Clostridium cellulovorans
3ahy – TrGB – Trichoderma reesei
3abz – KmGB – Kluyveromyces marxianus
2x40 – TnGB3B – Thermotoga neapolitana
3gno - JrGB residues 38-521 – Japanese rice
2rgl, 2rgm - JrGB residues 29-504
3f4v, 3f5j, 3f5k, 3f5l,3scn, 3sco, 3sct, 3scu, 3scv, 3scw, 3scp, 3scr - JrGB7 (mutant)
3ahz – tGB – termite
3fiy, 3cmj - UbGB catalytic domain (mutant) – Uncultured bacteria
2o9p, 1bga – PpGBB – Paenibacillus polymyxa
2jfe, 3gxd, 3gxi, 3gxm - hGB cystolic – human
3ke0, 3keh - hGB (mutant)
2e3z – PcGB – Phanerochaete crysosporium
2dga - wGB residues 1-520 – wheat
2vff, 1vff – GB – Pyrococcus horikoshii
1oif, 1od0 – TmGB catalytic domain - Thermotoga maritima
4gxp – TmGB/TrGB
1ug6 – GB - Thermus thermophilus
1hxj, 1e1e – ZmGB – Zea mays
1e4l - ZmGB (mutant)
1gon – SsGB – Streptomyces sp.
1qox – GB - Bacillus circulans
1tr1 - BpGBB (mutant) - Bacillus polymyxa
1cbg – GB cyanogenic – White clover
3aiu - rGB residues 50-568 – rye
3f93, 3f94 – PsGB residues 28-840 – Pseudoalteromonas
3f95 – PsGB residues 657-840
3ptk – rGB - rice
3apg – GB – Pyrococcus furiosus
3ta9 – GB – Halothermothrix orenii
3zyz, 3zz1 – GB – Hypocrea jecorina
4hz6 – ubGB – uncultured bacterium
4bce – GB (mutant) – Thermus thermophilus
4iib – AaGB – Aspergillus aculeatus
3w53 – GB – Micrococcus antarcticus
Beta-glucosidase complex with sugar
3ptm, 3ptq – rGB + glucoside
3wba, 3wbe – rGB (mutant) + glucose
3ai0 – tGB + glucoside
3ac0 - KmGB + glucoside
2x41, 2x42 - TnGB + glucoside
3air – wGB residues 50-569 + glucoside + dinitrophenol
3ais - wGB residues 50-569 (mutant) + glucoside + aglycone
3aiq - wGB residues 50-569 + aglycone
3aiv - rGB residues 50-568 + aglycone
3aiw - rGB residues 50-568 + glucoside + dinitrophenol
3gnp, 3gnr - JrGB residues 38-521 + glucoside
3aht, 3ahv, 3scq, 3scs – JrGB7 (mutant) + saccharide
1oin - TmGBA + glucoside
3fiz, 3fj0 - UbGB residues 18-482 (mutant) + glucoside
2zox, 2e9l, 2e9m - hGB cystolic + glucoside
2o9s, 2o9r, 2z1s – PpGB + saccharide
2o9t - PpGB + glucoside
1uyq - PpGB (mutant) + glucoside
1bgg - PpGB + gluconate
2jie - BpGB + glucoside
1e4i - BpGB (mutant) + glucoside
2e40 – PcGB + gluconolactone
3vif - NkGB + gluconolactone – Neotermes koshunensis
3vig, 3vii - NkGB + saccharide
3vih – NkGB + glycerol
3vij – NkGB (mutant) + glucose
3vik, 3vil, 3vim, 3vin, 3vio, 3vip – NkGB (mutant) + saccharide
4hz7, 4hz8 - ubGB (mutant) + glucose
1v08 – ZmGB + gluco-tetrazole
1e1f - ZmGB + glucoside
1h49, 1e4n, 1e56 - ZmGB (mutant) + aglycone
1gnx - SsGB + saccharide - Sulfolobus solfataricus
3gfx – hGB + drug
4iic, 4iid, 4iie, 4iif – AaGB + drug
4iig, 4iih – AaGB + saccharide
3vkk – hGB + mannose
4i3g – GB + glucose – Streptomyces venezuelae
Beta-glucosidase complex with inhibitor
2wbg, 2wc3, 2wc4, 2vrj, 2jal, 2j75, 2j77, 2j78, 2j79, 2j7b, 2j7d, 2j7e, 2j7f, 2j7g, 2j7h, 2j7c, 2ces, 2cet, 2cbu, 2cbv, 1uz1, 1w3j, 1oim – TmGBA + inhibitor
2cer – SsGB + inhibitor
1e55 - ZmGB (mutant) + inhibitor
3rik, 3ril - hGB + inhibitor
6-phospho-β-glucosidase
1s6y – PGB – Geobacillus stearothermophilus
1up4 – TmPGB
1up6, 1up7 – TmPGB + NAD + G6P
3qom, 4gze – PGB – Lactobacillus plantarum
2xhy – PGB – Escherichia coli
1h4p – PGB I/II – yeast
3eqn – WfPGB – White-rot fungus
3eqo – WfPGB + glucolactone
4b3k, 4b3l – GB – Streptococcus pyogenes
4gpn – GB + gentiobiose 6-phosphate – Streptococcus mutans
4ipl – SpGB – Streptococcus pneumoniae
4ipn – SpGB + thiocellobiose
Glucan 1,3-β-glucosidase
3n9k – CaGGB + glucoside – Candida albicans
3o6a – CaGGB (mutant)
3ur7, 3ur8 – poGGB – potato
4gzi – poGGB (mutant)
4gzj - poGGB (mutant) + saccharide
Raucaffricine-β-glucosidase
3u57, 3u5u – dpRGB (mutant) – devilpepper
3u5y – dpRGB (mutant)m + secologanin
4a3y, 4atd – seRGB - serpentwood
4atl – seRGB + glucose
4ek7 – seRGB (mutant)
3zj6 – seRGB + inhibitor
Strictosidine-β-glucosidase
3zj7, 3zj8 – seSGB + inhibitor
References
- ↑ Aguilar M, Gloster TM, Garcia-Moreno MI, Ortiz Mellet C, Davies GJ, Llebaria A, Casas J, Egido-Gabas M, Garcia Fernandez JM. Molecular basis for beta-glucosidase inhibition by ring-modified calystegine analogues. Chembiochem. 2008 Nov 3;9(16):2612-8. PMID:18833549 doi:10.1002/cbic.200800451
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B-glucosidase
- ↑ Davies G, Henrissat B. Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure. 1995 Sep 15;3(9):853-9. PMID:8535779
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/IEntry?ac=IPR018120#PUB00002205
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/CSA/CSA_Site_Wrapper.pl?pdb=2vrj
- ↑ Davies G, Henrissat B. Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure. 1995 Sep 15;3(9):853-9. PMID:8535779
- ↑ http://www.cazy.org/fam/ghf_INV_RET.html#3
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Muriel Breteau, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner