We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 911
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<StructureSection load='2VYA' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase 1' scene='57/573125/2vya/1'> | <StructureSection load='2VYA' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase 1' scene='57/573125/2vya/1'> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) degrades fatty acid amides to terminate their signaling activity. A serine hydrolase from the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amidase Amidase] signature superfamily of enzymes ([http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Amidase other amidases]), FAAH degrades endocannabinoid signaling lipids, molecules associated with pain relief. Because [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocannabinoid_system endocannabinoids] are lipid molecules, they cannot be compartmentalized in vesicles (the degradation method for other neurotransmitters) and must instead be degraded in the bilayer of the cell membrane. FAAH is an integral membrane protein that degrades FAAs as they enter the membrane bilayer. Current research about FAAH aims to find inhibitors for the enzyme, which would prolong the pain alleviation provided by endocannabinoid molecules. | + | Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) degrades fatty acid amides to terminate their signaling activity.(IMT5) A serine hydrolase from the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amidase Amidase] signature superfamily of enzymes ([http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Amidase other amidases]), FAAH degrades endocannabinoid signaling lipids, molecules associated with pain relief.(2VYA) Because [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocannabinoid_system endocannabinoids] are lipid molecules, they cannot be compartmentalized in vesicles (the degradation method for other neurotransmitters) and must instead be degraded in the bilayer of the cell membrane. FAAH is an integral membrane protein that degrades FAAs as they enter the membrane bilayer. (IMT5) Current research about FAAH aims to find inhibitors for the enzyme, which would prolong the pain alleviation provided by endocannabinoid molecules. (2VYA) |
[[Image:1MT5.png|400 px|left|thumb|FAAH Subunit]] | [[Image:1MT5.png|400 px|left|thumb|FAAH Subunit]] | ||
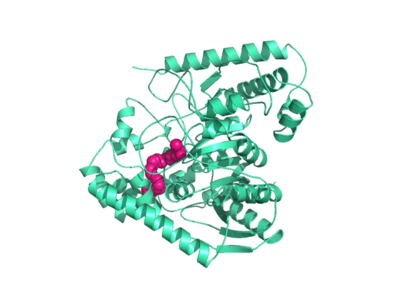
==Hydrolase Information== | ==Hydrolase Information== | ||
| - | Crystal structures of FAAH show that the enzyme is a homodimer in solution, with each subunit having a mass of 63 kD. The protein's <scene name='57/573125/2vya/8'>twisted Beta sheet core</scene> of 11 strands is surrounded by 24 alpha helices. The enzyme is embedded in the cell membrane to catch the lipid signaling molecules that can diffuse through membranes. The FAAH structure shows an entry channel leading from the lipid bilayer to the enzyme's active site, providing a path for endocannabinoids to enter the hydrolase. In addition, FAAH possesses a channel leading from the active site to the cell's cytoplasm, allowing the release of polar compounds released from lipid cleavage and the entry of water molecules necessary for the FAAH mechanism to proceed. | + | Crystal structures of FAAH show that the enzyme is a homodimer in solution, with each subunit having a mass of 63 kD. The protein's <scene name='57/573125/2vya/8'>twisted Beta sheet core</scene> of 11 strands is surrounded by 24 alpha helices. The enzyme is embedded in the cell membrane to catch the lipid signaling molecules that can diffuse through membranes. The FAAH structure shows an entry channel leading from the lipid bilayer to the enzyme's active site, providing a path for endocannabinoids to enter the hydrolase. In addition, FAAH possesses a channel leading from the active site to the cell's cytoplasm, allowing the release of polar compounds released from lipid cleavage and the entry of water molecules necessary for the FAAH mechanism to proceed. (IMT5) |
<scene name='57/573125/2vya/1'>humanized rat FAAH dimer</scene> with <scene name='57/573125/2vya/3'>PF-750 inhibitor</scene> | <scene name='57/573125/2vya/1'>humanized rat FAAH dimer</scene> with <scene name='57/573125/2vya/3'>PF-750 inhibitor</scene> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<scene name='57/573125/2vya/7'>helix-turn-helix motif</scene> alpha helices 18 and 19 form a membrane binding cap | <scene name='57/573125/2vya/7'>helix-turn-helix motif</scene> alpha helices 18 and 19 form a membrane binding cap | ||
===Catalytic Triad=== | ===Catalytic Triad=== | ||
| - | Mutagenesis and inhibitor studies have shown that FAAH has a <scene name='57/573125/2vya/6'>Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad</scene>, consisting of S241, S217, and K142. Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triads are not often seen in hydrolases, making FAAH an enzyme of interest for additional research. S241 acts as the catalytic nucleophile for the cleavage of amide bonds. | + | Mutagenesis and inhibitor studies have shown that FAAH has a <scene name='57/573125/2vya/6'>Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad</scene>, consisting of S241, S217, and K142. Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triads are not often seen in hydrolases, making FAAH an enzyme of interest for additional research. S241 acts as the catalytic nucleophile for the cleavage of amide bonds. (IMT5) |
| - | FAAH requires two water molecules in its active site to properly cleave amide bonds. One water molecule (W1) deacylates the substrate, and the other (W2) helps coordinate W1 through the catalytic K142. | + | FAAH requires two water molecules in its active site to properly cleave amide bonds. One water molecule (W1) deacylates the substrate, and the other (W2) helps coordinate W1 through the catalytic K142. (3LJ6) |
[[Image:Water_image.png|400 px|left|thumb|FAAH catalytic site with water molecules bound]] | [[Image:Water_image.png|400 px|left|thumb|FAAH catalytic site with water molecules bound]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Applications== | ==Applications== | ||
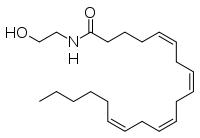
| - | The human nervous system has several types of chemical messengers, including amino acids, lipids, peptide hormones, and monoamines. FAAH primarily degrades [http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/anandamide/ananh.htm anandamide] (AEA), a naturally-occurring signaling lipid that functions in the brain. AEA brings pain relief to the body. Inhibiting FAAH would likely sustain AEA signaling, leading to prolonged pain relief and decreased inflammation. | + | The human nervous system has several types of chemical messengers, including amino acids, lipids, peptide hormones, and monoamines. (IMT5) FAAH primarily degrades [http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/anandamide/ananh.htm anandamide] (AEA), a naturally-occurring signaling lipid that functions in the brain. AEA brings pain relief to the body. Inhibiting FAAH would likely sustain AEA signaling, leading to prolonged pain relief and decreased inflammation. (2YVA) |
[[Image:AEA image.png|200 px|left|thumb|[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Anandamide_skeletal.svg Anandamide]]] | [[Image:AEA image.png|200 px|left|thumb|[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Anandamide_skeletal.svg Anandamide]]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 12:55, 25 March 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 06, 2014, through Aug 22, 2014 for use by the Biochemistry II class at the Butler University at Indianapolis, IN USA taught by R. Jeremy Johnson. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 911 through Sandbox Reserved 922. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
Applications
The human nervous system has several types of chemical messengers, including amino acids, lipids, peptide hormones, and monoamines. (IMT5) FAAH primarily degrades anandamide (AEA), a naturally-occurring signaling lipid that functions in the brain. AEA brings pain relief to the body. Inhibiting FAAH would likely sustain AEA signaling, leading to prolonged pain relief and decreased inflammation. (2YVA)