Anything in this section will appear adjacent to the 3D structure and will be scrollable.
This is a default text for your page Daud Akhtar/Sandbox 1
Introduction
Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) is a metabolic X-linked enzyme, which catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) to 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone[1] . This redox reaction is the first and rate-determining step in the pentose phosphate pathway in which coenzyme NADP+ is reduced through the transfer of a hydride from G6P . Consequently, NADPH is generated and helps restore reduced glutathione (GSH), which is an important anti-oxidant. NADPH and GSH thereby helping protect cells from oxidative stress by converting peroxides into water. (2). G6PD is most abundant in intracellular fluid and is conserved over a large array of different organisms. Specifically, higher plants exhibit several isoforms of G6PD in different cellular locations such as the cytosol, the plastidic stroma, and peroxisomes. [2] In humans, active G6PD generally exists as a dimer/tetramer equilibrium, which is depending on pH and ionic strength. At high pH and ionic strength, the equilibrium is shifted towards the dimer, whereas low pH conditions cause a shift to the tetramer. Each monomer of G6PD consists of 514 amino acids with a molecular weight of 59 kDa, More than 400 different variants of G6PD have been identified where these variants differ in the location of point mutations in the G6PD gene. The G6PD gene is located on the chromosome Xq28 region. These mutation results in deficiencies, which range from mild to severe phenotypic abnormalities such as hemolytic anemia. The exposure of erythrocytes to oxidative stress due to a lack of NADPH in cells results in their destruction causing hemolytic anemia.
Glucose 6 Phophate Dehydrogenease is an enzyme that plays a key role in the pentose phosphate pathway [2]
Species Distribution
G6PD is a ubiquitous protein and consequently is conserved and distributed in a variety of species ranging from bacteria to humans. A multiple alignment of 35 currently known G6PD amino acid sequences showed 30% conserved identity between the human sequence and those of other species [14] Based on this alignment it was observed that 2 conserved sequence motifs were apparent: the completely conserved eight-residue peptide RIDHYLGK (residues 198-205) corresponding to the substrate binding site [15-17]; and the dinucleotide-binding fingerprint GxxGDLx (residues 38-44). The presence of this dinucleotide-binding fingerprint region implies that G6PD function involves nucleotide molecules.
Overall Structure
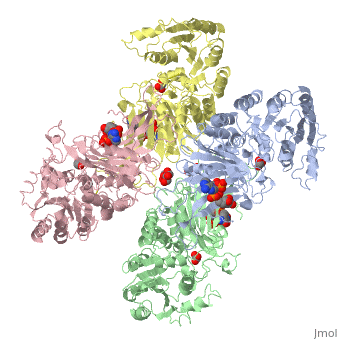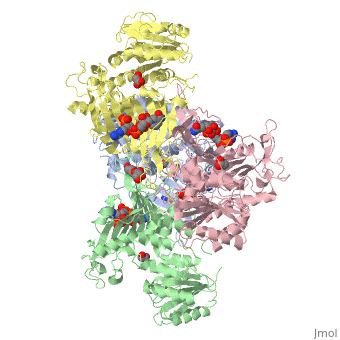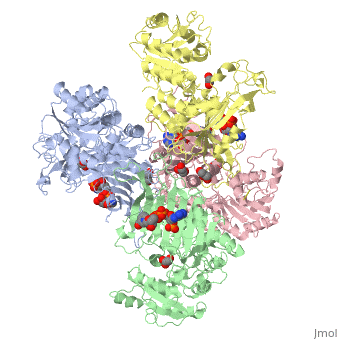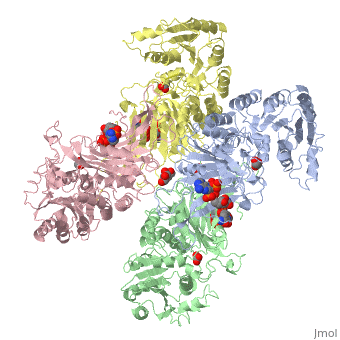
G6PD belongs to the Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-like family of proteins, which are characterized by rossmann-like domains. It also belongs to the superfamily GAPDH-like domain, which consists of 2-domain proteins with an alpha+beta domain. The overall structure of Human G6PD is present as a homodimer/homotetramer equilibrium that is dependant on pH and ionic strength. The individual monomers appear to be inactive where each monomer consists of 514 amino acids with a molecular weight of 59kDa. . At high pH and ionic strength, the equilibrium is shifted towards the dimer, whereas low pH conditions cause a shift to the tetramer. Specifically, G6PD has a structural NADP+ moiety next to a separate catalytic site for NADP+. Cohen (1968) showed that NADP+ binding stabilized the hydrophobic interactions between subunits, thus preventing disassociation of the dimer state into monomers in the absence of NADP+. Crystallization experiments by Au (2000) using the Canton Arg459->Leu (R459L) which is the most common Chinese variant, showed that the Canton R459L G6PD enzyme as a dimer of dimers. Each specific monomer consists of two domains.
Image:G6pd ABCD tetramer image with figure title.jpg
NADP+ Binding Domain
The first domain is a with a β-β fold. The binding site for the coenzyme NADP+ is between the first β-sheet and the α-helix with a finger print sequence of GASGDLA (residues 38-44). At the C-terminus of the β-sheet, a highly conserved Arginine (residue 72) functions to bind the 2’phosphate of NADP to increase specificity.
Substrate(Glucose-6-Phosphate) Binding Domain
The second domain is the consists of both α-helices and β-sheets and nine distinct anti-parallel β-sheets. The active site in this domain corresponds to the site for substrate (G6P) and is characterized by the highly conserved amino acid residues RIDHYLGK (amino acids 198-205). In regards to the overall dimer stability, Au (2000) illustrated that the second domain plays a role in dimerization. Specifically, within each subunit a NADP+ is buried in a structural moiety between the β-sheet and the C-terminus of the first domain. In this structural moiety, NADP+ does not act as a coenzyme but rather as a stabilizer. Specifically, the adenine and nicotinamide form hydrophobic interactions with Tyr503 and Arg487, and Trp509 and Tyr 401. The amide portion of the NADP+ interacts with Asp421 and ARg393 and the bisphosphate interacts with Arg370 through Hydrogen bonding. The two monomers are linked together with the amino acids Lys275 and Lys290 of one monomer forming salt bridges with Glu347 and Glu287.
Substrate Binding and Catalytic Mechanism
The catalytic mechanism involved with G6PD is a general acid/base reaction. It begins with G6P binding to its active site in the second domain by interacting with Lys205. His 263 then acts as a general base that abstracts the proton from the C1-hydroxyl of G6P. Cosgrove (1998) suggest that Asp200 stabilizes the positive charge on the N atom of His264 in the transition state forming a catalytic dyad. Asp200 also plays a role in binding the phosphate moiety of G6P.
Image:Catalytic dyad g6p.jpg
Biological Role
The major catabolic fate of G6P is glycolytic breakdown through glycolysis. Another fate however is the oxidation of G6P into pentose phosphates through the pentose phosphate pathway. The first reaction of the pentose phosphate pathway is the oxidation of G6P by G6PD to form 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone. NADP+ is the electron acceptor, and the overall equilibrium lies far in the direction of NADPH formation. In this pathway, G6PD is the rate-limiting enzyme. Biologically, the pentose phosphate pathway plays an important role in generating NADPH. High levels of NADP+ in the cytosol act as an allosteric stimulator of G6PD by promoting G6P usage as a substrate in the pentose phosphate pathway. The ultimate product of the pentose phosphate pathway is ribose-5- phosphate. Rapidly dividing cells, such as those of bone marrow, skin, and tumors use ribose-5-phosphate to make RNA, DNA, and coenzymes such as ATP, NADH, and FADH2. In other tissues, the essential product of the pentose phosphate pathway is not the pentose products but the electron donors NADPH. NADPH is needed for reductive biosynthesis or to counter the damaging effects of oxygen radicals. Additionally tissues that are heavily involved in fatty acid synthesis such as liver and adipose tissue, require NADPH to fuel the synthesis of cholesterols and steroid hormones. In the case of erythrocytes and cells, which are directly exposed to oxygen such as the cornea, maintain a high ratio of NADPH/NADP+ and glutathione to prevent or undo oxidative damage caused by the generation of free radicals. A genetic defect in G6PD is known as G6PD Deficiency and can have serious medical consequences.
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
Classification
The World Health Organization classifies G6PD genetic variants into five classes, the first three of which are deficiency states.[3]
- Severe deficiency (<10% activity) with chronic (nonspherocytic) hemolytic anemia
- Severe deficiency (<10% activity), with intermittent hemolysis
- Mild deficiency (10-60% activity), hemolysis with stressors only
- Non-deficient variant, no clinical sequelae
- Increased enzyme activity, no clinical sequelae
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms that are linked with G6PD deficiency include hemolytic aneaemia, favism, neonatal jaundice, and in severe cases can be fatal. Hemolytic anemia is the most common symptom of individuals with defects in G6PD. Individuals with hemolytic aneamia exhibit phenotypes where read blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can replace them. [4]
Epidemiology
G6PD Deficiency is most prevalent in tropical Africa, the Middle East, tropical and subtropical Asia and some areas of the Mediterranean. G6PD deficiency affects all races. Specifically however, highest prevalence is among individuals with African, Asian and Mediterranean heritage. Due to the X-lined nature of G6PD it primarily effects males.[5] [6]