We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 914
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
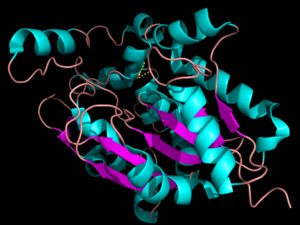
[[Image:pymol.png|300px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1:'''Three dimensional structure of Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1. The blue color represents the α-helices and the purple represents the β-sheets. The pink signifies random coil.]] | [[Image:pymol.png|300px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1:'''Three dimensional structure of Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1. The blue color represents the α-helices and the purple represents the β-sheets. The pink signifies random coil.]] | ||
| - | Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 (PPT1) is a lysosomal enzyme that plays a role in the degradation of lipid-modified proteins<ref name="human">Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 Precursor - Homo Sapiens. N.p., 1 Oct. 1996.</ref>. PPT1 derives its catalytic power from its [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalytic_triad catalytic triad], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha/beta_hydrolase_fold α/β hydrolase fold], and hydrophobic groove in order to remove fatty acid acyl groups, typically palmitate from cysteine residues in proteins<ref name="human"/>. PPT1 is able to be modified by cofactor enzymes, which can induce biological changes<ref name="human"/>. Misregulation of PPT1 modifications can cause various diseases, including infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis<ref name="PPT"/>, kufs disease<ref name="PPT"/>, and late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis<ref name="PPT"/>. Within these diseases, the production of PPT1 is decreased or eliminated completely, which leads to fatty acid buildup primarily in neuronal cells, leading to slowed developmental progress<ref name="PPT"/>. | + | Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 (PPT1) is a lysosomal enzyme that plays a role in the degradation of lipid-modified proteins<ref name="human">Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 Precursor - Homo Sapiens. N.p., 1 Oct. 1996.</ref>. PPT1 derives its catalytic power from its [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalytic_triad catalytic triad], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha/beta_hydrolase_fold α/β hydrolase fold], and hydrophobic groove in order to remove fatty acid acyl groups, typically [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palmitic_acid palmitate] from cysteine residues in proteins<ref name="human"/>. PPT1 is able to be modified by cofactor enzymes, which can induce biological changes<ref name="human"/>. Misregulation of PPT1 modifications can cause various diseases, including infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis<ref name="PPT"/>, kufs disease<ref name="PPT"/>, and late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis<ref name="PPT"/>. Within these diseases, the production of PPT1 is decreased or eliminated completely, which leads to fatty acid buildup primarily in neuronal cells, leading to slowed developmental progress<ref name="PPT"/>. |
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=== Catalytic Triad === | === Catalytic Triad === | ||
| - | The <scene name='57/573128/2/1'>catalytic triad</scene> is composed of Ser115, His289, and Asp233, which is the same as the catalytic triad in chymotrypsin <ref name="human"/>. A water molecule is occupying the <scene name='57/573128/7/1'>oxyanion hole</scene> and it is hydrogen bonded to Ser115 <ref name="Prom"/>. The purpose of the oxyanion hole is to stabilize the oxyanion that is formed after the nucleophilic attack of the transition state. Ser115 acts as a nucleophile, while His289 and Asp233 are coordinated to Ser115 to lower its pKa value so it can undergo catalytic activity<ref name="Prom"/>. The pKa of the nucleophile in the catalytic triad is lowered to allow the nucleophilic attack<ref name="Prom">Branneby, Cecilia. Exploiting Enzyme Promiscuity for Rational Design. KTH Biotechnology. N.p., May 2005</ref>. | + | The <scene name='57/573128/2/1'>catalytic triad</scene> is composed of Ser115, His289, and Asp233, which is the same as the catalytic triad in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chymotrypsin chymotrypsin] <ref name="human"/>. A water molecule is occupying the <scene name='57/573128/7/1'>oxyanion hole</scene> and it is hydrogen bonded to Ser115 <ref name="Prom"/>. The purpose of the oxyanion hole is to stabilize the oxyanion that is formed after the nucleophilic attack of the transition state. Ser115 acts as a nucleophile, while His289 and Asp233 are coordinated to Ser115 to lower its pKa value so it can undergo catalytic activity<ref name="Prom"/>. The pKa of the nucleophile in the catalytic triad is lowered to allow the nucleophilic attack<ref name="Prom">Branneby, Cecilia. Exploiting Enzyme Promiscuity for Rational Design. KTH Biotechnology. N.p., May 2005</ref>. |
===Hydrophobic Groove === | ===Hydrophobic Groove === | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
===Molecular === | ===Molecular === | ||
| - | The main molecular function of PPT1 is to breakdown lipid-modified proteins and act as a hydrolase of thioester bonds<ref name="RSCB"/>. In the main catalytic reaction for PPT1, a cysteine residue is removed from the palmitoylated protein by PPT, resulting in a free cysteine residue and palmitoyl-CoA<ref name="RSCB"/>. A water molecule was suggested to come in and stabilize the transition state, along with protonating the cysteine residue on the palmitoylated protein, allowing the palmitoyl-CoA to break free. | + | The main molecular function of PPT1 is to breakdown lipid-modified proteins and act as a hydrolase of thioester bonds<ref name="RSCB"/>. In the main [http://lipidlibrary.aocs.org/Lipids/protlip/index.htm catalytic reaction] for PPT1, a cysteine residue is removed from the palmitoylated protein by PPT, resulting in a free cysteine residue and palmitoyl-CoA<ref name="RSCB"/>. A water molecule was suggested to come in and stabilize the transition state, along with protonating the cysteine residue on the palmitoylated protein, allowing the palmitoyl-CoA to break free. |
==Medical Relevance== | ==Medical Relevance== | ||
Revision as of 11:56, 22 April 2014
ββ
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 06, 2014, through Aug 22, 2014 for use by the Biochemistry II class at the Butler University at Indianapolis, IN USA taught by R. Jeremy Johnson. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 911 through Sandbox Reserved 922. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 Precursor - Homo Sapiens. N.p., 1 Oct. 1996.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 PPT1. Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine, Aug. 2013.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Bellizzi JJ 3rd, Widom J, Kemp C, Lu JY, Das AK, Hofmann SL, Clardy J. The crystal structure of palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 and the molecular basis of infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 25;97(9):4573-8. PMID:10781062 doi:10.1073/pnas.080508097
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Branneby, Cecilia. Exploiting Enzyme Promiscuity for Rational Design. KTH Biotechnology. N.p., May 2005
External Resources
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palmitoyl_protein_thioesterase
https://www.counsyl.com/diseases/ppt1-related-neuronal-ceroid-lipofuscinosis/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha/beta_hydrolase_fold
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalytic_triad
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2121/8/22
http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=PPT1