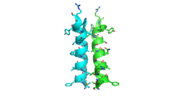We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Brittany Carroll/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| - | == | + | == Homology == |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
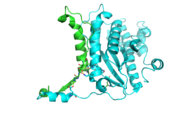
| + | [[Image:topology.jpg|left|thumb| This 2D topology diagram shows the βαββαβ fold of Thg1. The helices and strands involved in the fold are in blue font. The fold is most similar to that of cylcases. The mechanism is more likely the same as family A polymerases, with the conserved carboxylates shown as asterisks(*).]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Interestingly, Thg1 shares structural similarities to both cyclases and the palm domain of canonical polymerases, without sequence similarities. The βαββαβ motif is most homologous with adenylyl and guanylyl cyclases. However, based upon the model the mechanism seems to be more like that of a family A polymerase. The model suggests Thg1 has three catalytic carboxylates: aspartate 29, aspartate 76, and glutamate 77. Cyclases only have two catalytic carboxylates, two aspartates and either cysteine, alanine, or glycine. The position of the carboxylates in Thg1 is homologous to those of T7 DNA Polymerase. An overlay of the palm domain of T7 and Thg1 shows that the three carboxylates, two metal ions, and the incoming nucleotide are conserved and in similar postions. This indicates that Thg1 most likely uses the two-metal-ion mechaism of canonical 5' to 3' polymerases. | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
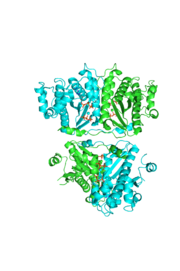
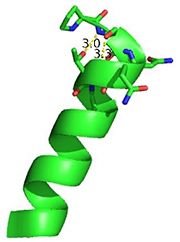
[[Image:thgdimer.png|300|left|thumb|The dimer interface is highlighted between monomers, Chain a (green) & Chain b (cyan), showing a large contact area. The two salt bridges between _____ are highlighted as well as some hydrogen bonding. ]] | [[Image:thgdimer.png|300|left|thumb|The dimer interface is highlighted between monomers, Chain a (green) & Chain b (cyan), showing a large contact area. The two salt bridges between _____ are highlighted as well as some hydrogen bonding. ]] | ||
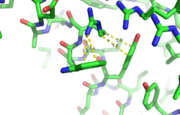
| - | [[Image:alpha_dimer.png|300|right|thumb|The interface between | + | [[Image:alpha_dimer.png|300|right|thumb|The interface between alpha helices D of the two monomers.]] |
Revision as of 20:38, 26 April 2014
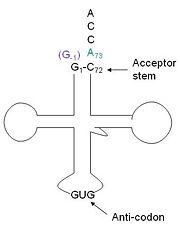
tRNA(His) guanylyltransferase
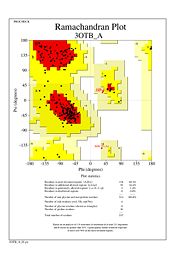
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644