We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Brittany Carroll/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
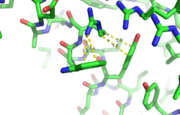
Hydrogen bonds between N’ and the backbone of N3 and N3 with N’ backbone are shown in the figure. The figure is difficult to see the T with P bb but it is not linear, this may just be due to modeling as it is close enough to form a h-bond. There is also a hydrophobic interaction between P and L. | Hydrogen bonds between N’ and the backbone of N3 and N3 with N’ backbone are shown in the figure. The figure is difficult to see the T with P bb but it is not linear, this may just be due to modeling as it is close enough to form a h-bond. There is also a hydrophobic interaction between P and L. | ||
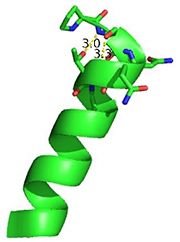
| - | [[Image:Cationpi.png|300|Right|thumb|This image depicts two cation-π interactions between Arg and Tyr or Trp. The energetic significances are -1.22 and -6.55 kj/mol respectively. (site website) | + | [[Image:Cationpi.png|300|Right|thumb|This image depicts two cation-π interactions between Arg and Tyr or Trp. The energetic significances are -1.22 and -6.55 kj/mol respectively. (site website) [[3otb]]]] |
A cation-π interaction occurs between a cation and the face of a simple aromatic, there is partial negative charge in the center of the ring. The cation-π interaction is actually stronger than a salt bridge because of the desolvation penalty. With the cation-π interaction the cation has a similar dosolvation penalty to pay as the salt bridge ions but the π system is already poorly solvated. Also there is not neutralization of charge that occurs between the two groups. These properties of the cation-π interaction imply that thecation-π interactions on protein surfaces (mainly where they are seen) could contribute to protein structure and stability. | A cation-π interaction occurs between a cation and the face of a simple aromatic, there is partial negative charge in the center of the ring. The cation-π interaction is actually stronger than a salt bridge because of the desolvation penalty. With the cation-π interaction the cation has a similar dosolvation penalty to pay as the salt bridge ions but the π system is already poorly solvated. Also there is not neutralization of charge that occurs between the two groups. These properties of the cation-π interaction imply that thecation-π interactions on protein surfaces (mainly where they are seen) could contribute to protein structure and stability. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | ==Addition SD Structures of Thg1== | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 03:02, 27 April 2014
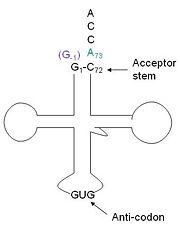
tRNA(His) guanylyltransferase
| |||||||||||
Addition SD Structures of Thg1
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644