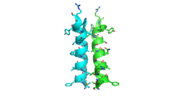We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Brittany Carroll/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Homology == | == Homology == | ||
[[Image:topocarboxy.png|left|thumb]] | [[Image:topocarboxy.png|left|thumb]] | ||
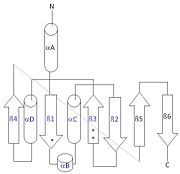
| - | [[Image:thg1topology.jpg|right|thumb| This 2D topology diagram shows the βαββαβ fold of Thg1. The helices and strands involved in the fold are in blue font. The fold is most similar to that of cylcases. The mechanism is more likely the same as family A polymerases, with the conserved carboxylates shown as asterisks(*).]] | + | [[Image:thg1topology.jpg|right|thumb| This 2D topology diagram shows the βαββαβ fold of Thg1. The helices and strands involved in the fold are in blue font. The fold is most similar to that of cylcases. The mechanism is more likely the same as family A polymerases, with the conserved carboxylates shown as asterisks(*). [[3otb]]]] |
Interestingly, Thg1 shares structural similarities to both [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclase cyclases] and the palm domain of canonical [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_polymerase polymerases], without sequence similarities. The βαββαβ motif is most homologous with adenylyl and guanylyl cyclases. However, based upon the model the mechanism seems to be more like that of a family A polymerase. The model suggests Thg1 has three catalytic carboxylates: aspartate 29, aspartate 76, and glutamate 77. Cyclases only have two catalytic carboxylates, two aspartates and either cysteine, alanine, or glycine. The position of the carboxylates in Thg1 is homologous to those of [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T7_DNA_polymerase T7 DNA Polymerase]. An overlay of the palm domain of T7 and Thg1 shows that the three carboxylates, two metal ions, and the incoming nucleotide are conserved and in similar postions. This indicates that Thg1 most likely uses the two-metal-ion mechaism of canonical 5' to 3' polymerases. | Interestingly, Thg1 shares structural similarities to both [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclase cyclases] and the palm domain of canonical [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_polymerase polymerases], without sequence similarities. The βαββαβ motif is most homologous with adenylyl and guanylyl cyclases. However, based upon the model the mechanism seems to be more like that of a family A polymerase. The model suggests Thg1 has three catalytic carboxylates: aspartate 29, aspartate 76, and glutamate 77. Cyclases only have two catalytic carboxylates, two aspartates and either cysteine, alanine, or glycine. The position of the carboxylates in Thg1 is homologous to those of [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T7_DNA_polymerase T7 DNA Polymerase]. An overlay of the palm domain of T7 and Thg1 shows that the three carboxylates, two metal ions, and the incoming nucleotide are conserved and in similar postions. This indicates that Thg1 most likely uses the two-metal-ion mechaism of canonical 5' to 3' polymerases. | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | [[Image:thgdimer.png|300|left|thumb|The dimer interface is highlighted between monomers, chain A (green) & chain B (cyan), showing a large contact area. Part of chain A was removed to show more clearly the extensive interface between the monomers. The two salt bridges, between K95 to D128 and E13 to R30, are highlighted as well as some hydrogen bonding. ]] | + | [[Image:thgdimer.png|300|left|thumb|The dimer interface is highlighted between monomers, chain A (green) & chain B (cyan), showing a large contact area. Part of chain A was removed to show more clearly the extensive interface between the monomers. The two salt bridges, between K95 to D128 and E13 to R30, are highlighted as well as some hydrogen bonding.[[3otb]] ]] |
| - | [[Image:alpha_dimer.png|300|right|thumb|The interface between alpha helices D of the two monomers shows the large amount of contacts helping to stablize the dimer.]] | + | [[Image:alpha_dimer.png|300|right|thumb|The interface between alpha helices D of the two monomers shows the large amount of contacts helping to stablize the dimer.[[3otb]]]] |
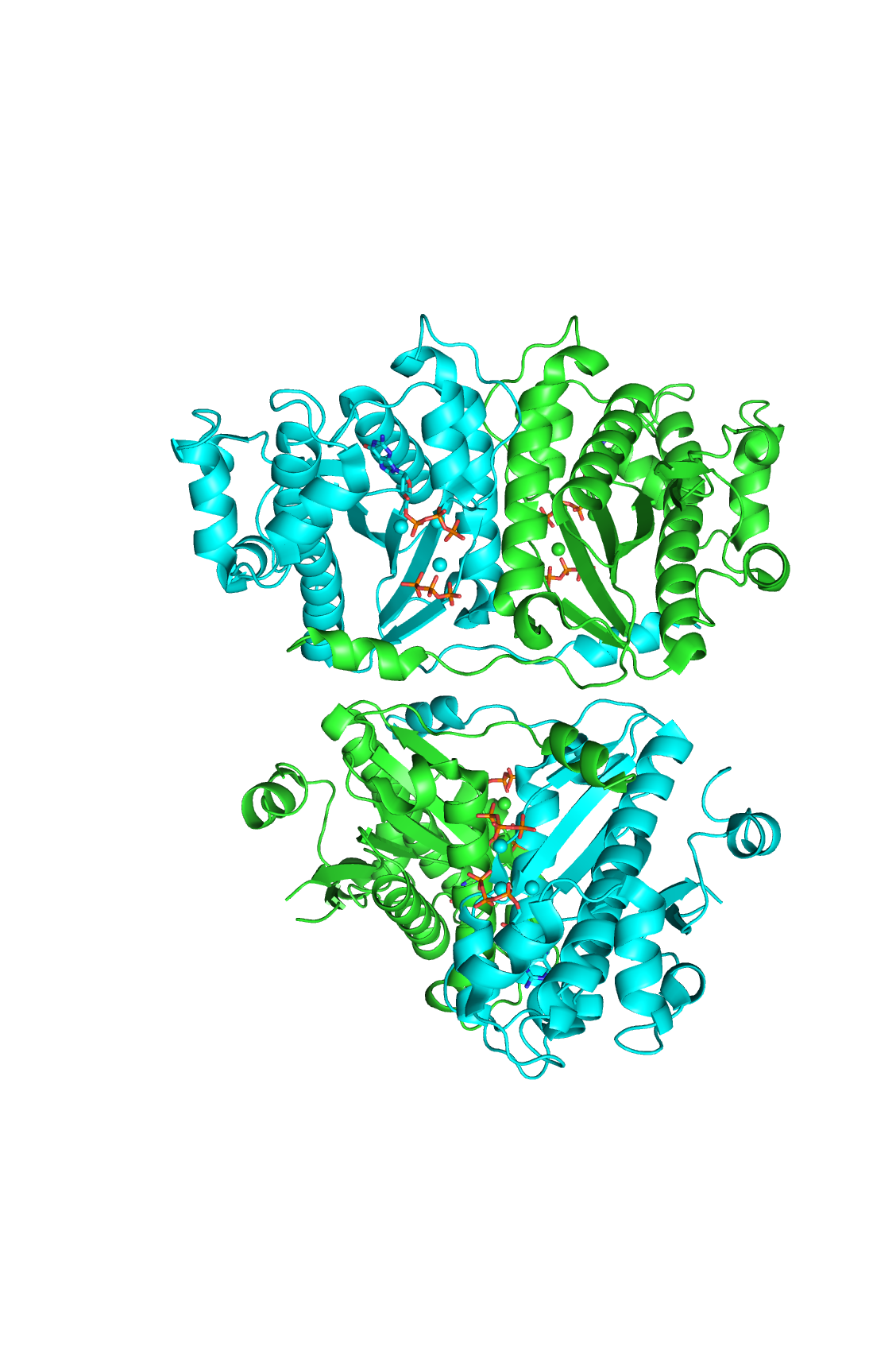
Each monomer has an antiparallel β-sheet with seven strands and four α-helices around the sheet. Thg1 forms a homotetramer, with extensive contacts between the dimer. Even though there are fewer contacts between the dimer of dimers, the tetramer is the most stable oligomeric form. | Each monomer has an antiparallel β-sheet with seven strands and four α-helices around the sheet. Thg1 forms a homotetramer, with extensive contacts between the dimer. Even though there are fewer contacts between the dimer of dimers, the tetramer is the most stable oligomeric form. | ||
The dimer is stabilized mainly by hydrogen bonds from αD and β4. There are also two salt bridges that help hold the dimer together: Lys to Asp and Glu to Arg (chain A to B). | The dimer is stabilized mainly by hydrogen bonds from αD and β4. There are also two salt bridges that help hold the dimer together: Lys to Asp and Glu to Arg (chain A to B). | ||
| - | [[Image:tetra.png|300|left|thumb]] | + | [[Image:tetra.png|300|left|thumb [[3otb]]]] |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
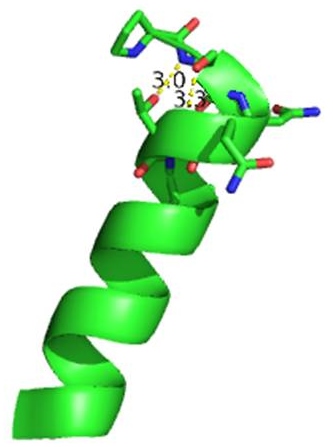
N-terminal helix cap | N-terminal helix cap | ||
| - | [[Image:Ntermcap.jpg|left|thumb]] | + | [[Image:Ntermcap.jpg|left|thumb [[3otb]]]] |
The N-terminal cap of the helix follows a Ib motiff. This motiff is also known as a capping box. | The N-terminal cap of the helix follows a Ib motiff. This motiff is also known as a capping box. | ||
N’ -> N4 h-xpxph | N’ -> N4 h-xpxph | ||
| - | N’- P S N Q T L –N4 (residues 135-140 | + | N’- P S N Q T L –N4 (residues 135-140 chain A [[3otb]]) |
Hydrogen bonds between N’ and the backbone of N3 and N3 with N’ backbone are shown in the figure. The figure is difficult to see the T with P bb but it is not linear, this may just be due to modeling as it is close enough to form a h-bond. There is also a hydrophobic interaction between P and L. | Hydrogen bonds between N’ and the backbone of N3 and N3 with N’ backbone are shown in the figure. The figure is difficult to see the T with P bb but it is not linear, this may just be due to modeling as it is close enough to form a h-bond. There is also a hydrophobic interaction between P and L. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
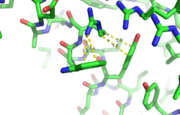
A cation-π interaction occurs between a cation and the face of a simple aromatic, there is partial negative charge in the center of the ring. The cation-π interaction is actually stronger than a salt bridge because of the desolvation penalty. With the cation-π interaction the cation has a similar dosolvation penalty to pay as the salt bridge ions but the π system is already poorly solvated. Also there is not neutralization of charge that occurs between the two groups. These properties of the cation-π interaction imply that thecation-π interactions on protein surfaces (mainly where they are seen) could contribute to protein structure and stability. | A cation-π interaction occurs between a cation and the face of a simple aromatic, there is partial negative charge in the center of the ring. The cation-π interaction is actually stronger than a salt bridge because of the desolvation penalty. With the cation-π interaction the cation has a similar dosolvation penalty to pay as the salt bridge ions but the π system is already poorly solvated. Also there is not neutralization of charge that occurs between the two groups. These properties of the cation-π interaction imply that thecation-π interactions on protein surfaces (mainly where they are seen) could contribute to protein structure and stability. | ||
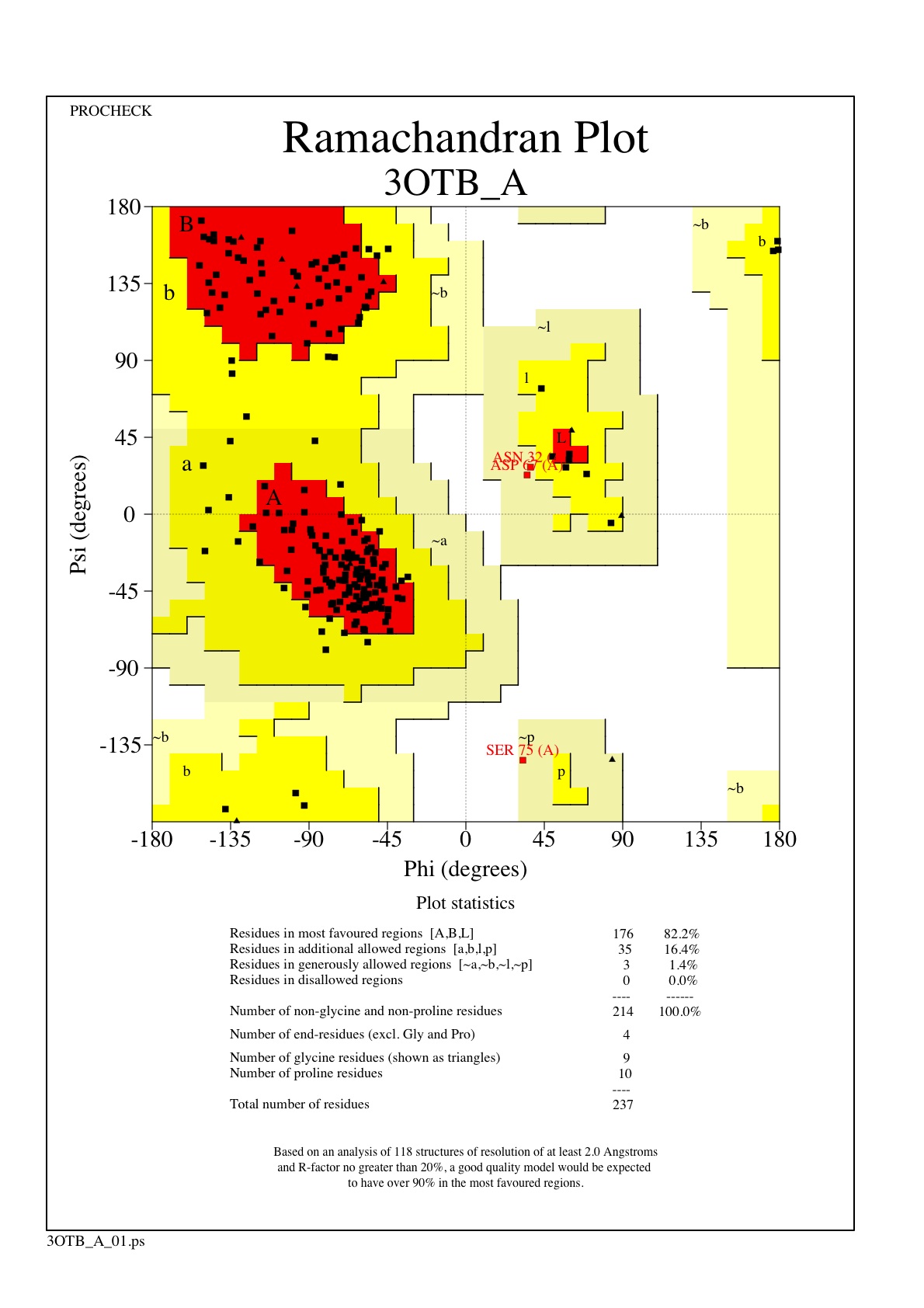
| - | [[Image:ramachandran.jpg|300|left|thumb]] | + | [[Image:ramachandran.jpg|300|left|thumb [[3otb]]]] |
The Ramachandran plot shows that most of the amino acids follow Ramachadran's restraints. The three that are questionable, N32, D67, S75 are all located in turns. | The Ramachandran plot shows that most of the amino acids follow Ramachadran's restraints. The three that are questionable, N32, D67, S75 are all located in turns. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==Addition SD Structures of Thg1== | ==Addition SD Structures of Thg1== | ||
| + | [[3otc]], [[3otd]], [[3ote]] - Thg1 - ''Homo sapiens'' | ||
| + | [[4kgk]], [[4kgm]] - Thg1-like - ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' | ||
| + | [[ 3WBZ]], [[3WC0]], [[3WC1]], [[3WC2]] - Thg1 - ''Candida albicans'' | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 03:15, 27 April 2014
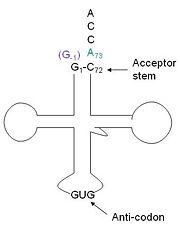
tRNA(His) guanylyltransferase
| |||||||||||
Addition SD Structures of Thg1
3otc, 3otd, 3ote - Thg1 - Homo sapiens 4kgk, 4kgm - Thg1-like - Bacillus thuringiensis 3WBZ, 3WC0, 3WC1, 3WC2 - Thg1 - Candida albicans
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644