Introduction
is the serine protease that catalyzes the penultimate step in blood coagulation. It is activated from its zymogen, prothrombin, at the site of tissue injury by FXa and its cofactor FVa in the presence of phospholipid membrane and calcium. Thrombin is then able to catalyze the cleavage of fibrinogen to insoluable fibrin which spontaneously polymerizes to form a stable clot.[1][2] Thrombin also acts as a procoagulant by:
- Activating platelets through their protease activated receptors (PARs)[3]
- Preventing VWF processing by cleaving ADAMTS13 [4][5]
- Enhancing its own production through FIX activation [6]
- Activating the fibrin crosslinking transglutaminase FXIII [7]
- Activation of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) [8]
Activity of thrombin is regulated physiologically by the serpin inhibitors:
Generation of thrombin is decreased when thrombin reaches endothelial lining and interacts with thrombomodulin which significantly increases activity of thrombin in activating protein C (APC).[21] This enzyme will go on to inactivate FVa[22][23] and FVIIIa[24] , cofactors for activation of prothrombin[25] and FXa[26], respectively.
By balancing substrate specificity, activity, and inhibition thrombin plays a central role in the blood coagulation cascade. [27]
Prothrombin Activation
Prothrombin is the zymogen form of thrombin. From N-terminal to C-terminal it consists of a Gla domain, two kringle domains, and a catalytic domain.
Prothrombin is activated by prothrombinase which consists of FXa, FVa, calcium, and a phospholipid surface. In vivo the first cleavage occurs at the R320-I321 bond, corresponding to residues 15-16 in thrombin which is the N-terminus of the B chain, producing meizothrombin.[28] Subsequent cleavage at R271-T272 yields thrombin.[29] The initial cleavage can also occur at R271 resulting in prothrombin-2 which will then be cleaved at R320 to produce thrombin.[30]
After cleavage by prothrombinase the new B chain N-terminus (Ile16) folds into the core protease domain and forms a salt bridge with Asp194.[31] This leads to stabilization of regions of the 180s-loop, Na+ binding loop, and γ-loop (zymogen activation domains). These changes provide the correct conformation for the S1 pocket and oxanion hole for catalysis.[32]
Thrombin Structure and Function
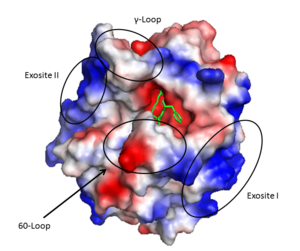
Thrombin (1PPB) overlayed with electrostatic surface. Structural features 60-loop, γ-loop, exosite I, and exosite II labeled
Thrombin is a α/β heterodimer composed of a 36 amino acid A chain and 259 amino acid B chain connected by a bridge between Cys1 and Cys122, in addition to 3 other intrachain disulfide bonds.[33] Its overall fold is similar to trypsin and chymotrypsin and it belongs to the peptidase S1 protease family[34]. It is an overall spherical protein with approximate dimensions of 45 X 45 X 50 Å^3.[35]
Important structural features include:
- A prominent active site cleft flanked by the 60- and γ-loops
- A sodium binding loop
- Two surface patches referred to as exosite I and exosite II.
The is mostly helical and is wound around the B chain and shaped like a boomerang. It is bound to the B chain mostly through side chain interactions including a salt bridge and H-bond cluster at residues D14, E8, and E14c.[36] Furthermore the C-terminus region forms a short amphipathic helix with hydrophobic side chains interacting with the B chain.[37]
The contains the active site of the protein and has numerous notable structural features. The active site is formed at the rims of two interacting 6 stranded which are surrounded by 4 helical regions and many turns.
The serine protease , based on chymotrypsin numbering, are Ser195, His57, and Asp102. As is common with serine proteases, an oxanion hole is formed by backbone amides of Ser195 and Gly193. This has the functional role of stabilizing the oxanion intermediate involved in the serine protease mechanism. In addition, since thrombin cleaves after Arg/Lys the S1 specificity site, formed by the 180s- and 220s- loops, has Asp189 at the base to form a salt bridge with the incoming substrate. Furthermore, the S4 binding pocket accommodates hydrophobic substrate residues.
The active site cleft rims are formed by the hydrophobic and rigid (residues L60, Y60a, P60b, P60c, W60d, D60e, K60f, N60g, F60h, T60i, and N60g) and the (residues T147, W147a, T147b, A147c, N147d, and V147f) while the base is mostly hydrophilic negatively charged amino acids. The cleft is deep compared to more promiscuous serine proteases, consequently substrates must either have a large loop that is cleaved or have favorable interactions with the insertion loops [38].
Many other loops project out of the B chain but most are rigid due to proline and tryptophan residues.
Exosite I is located on the B chain and had both basic and hydrophobic character. It is important in binding fibrinogen, platelet activated receptors, and thrombomodulin.
Exosite II is also part of the B chain, and derived from numerous basic amino acids, this is the site of heparin binding through the sulfate groups on the glycosaminoglycan. It is also the site of GpIα on the platelet surface.
The is formed by the 180s- and 220s- loops. Na+ is bound by the backbone oxygens of Arg221a and Lys224 in addition to four water molecules in a classic octahedral geometry[39]. Through the covelent disulfide linkage between Cys220 and Cys 191 the sodium binding site is linked to Ser195 and the oxanion hole.
Thrombin Allostery
Binding of thrombin by sodium or at exosite I stabilizes a form of thrombin that improves substrate recognition. This occurs due to energetic linkage between these sites to the S1 binding pocket and oxanion hole. Rapid kinetic analysis suggests that thrombin is in a dynamic equilibrium that consists of a fast, slow, and inactive state. There is question as to the physiologic relevance of the inactive state. Regardless, there will be a proportion of fast:slow thrombin and sodium binding to the fast form stabilizes that conformation. Indeed, mutation of the residues involved in sodium binding diminishes the activity of thrombin. It should be restated, that current data suggest that sodium binding does not induce a conformation change, rather, it stabilizes a conformation of thrombin that has greater activity.
References
- ↑ Fenton JW 2nd. Thrombin specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:468-95. PMID:7023326
- ↑ Coughlin SR. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature. 2000 Sep 14;407(6801):258-64. PMID:11001069 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35025229
- ↑ Coughlin SR. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature. 2000 Sep 14;407(6801):258-64. PMID:11001069 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35025229
- ↑ Crawley JT, Lam JK, Rance JB, Mollica LR, O'Donnell JS, Lane DA. Proteolytic inactivation of ADAMTS13 by thrombin and plasmin. Blood. 2005 Feb 1;105(3):1085-93. Epub 2004 Sep 23. PMID:15388580 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-03-1101
- ↑ Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Takagi T, Doolittle RF. Amino acid sequence studies on factor XIII and the peptide released during its activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):750-6. PMID:4811064
- ↑ Miljic P, Heylen E, Willemse J, Djordjevic V, Radojkovic D, Colovic M, Elezovic I, Hendriks D. Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI): a molecular link between coagulation and fibrinolysis. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2010 Jan;138 Suppl 1:74-8. PMID:20229688
- ↑ Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Huntington JA. Natural inhibitors of thrombin. Thromb Haemost. 2014 Apr 1;111(4):583-9. doi: 10.1160/TH13-10-0811. Epub 2014 Jan, 30. PMID:24477356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1160/TH13-10-0811
- ↑ Huntington JA. Thrombin inhibition by the serpins. J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;11 Suppl 1:254-64. doi: 10.1111/jth.12252. PMID:23809129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jth.12252
- ↑ Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Huntington JA. Natural inhibitors of thrombin. Thromb Haemost. 2014 Apr 1;111(4):583-9. doi: 10.1160/TH13-10-0811. Epub 2014 Jan, 30. PMID:24477356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1160/TH13-10-0811
- ↑ Huntington JA. Thrombin inhibition by the serpins. J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;11 Suppl 1:254-64. doi: 10.1111/jth.12252. PMID:23809129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jth.12252
- ↑ Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Huntington JA. Natural inhibitors of thrombin. Thromb Haemost. 2014 Apr 1;111(4):583-9. doi: 10.1160/TH13-10-0811. Epub 2014 Jan, 30. PMID:24477356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1160/TH13-10-0811
- ↑ Huntington JA. Thrombin inhibition by the serpins. J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;11 Suppl 1:254-64. doi: 10.1111/jth.12252. PMID:23809129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jth.12252
- ↑ Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Huntington JA. Natural inhibitors of thrombin. Thromb Haemost. 2014 Apr 1;111(4):583-9. doi: 10.1160/TH13-10-0811. Epub 2014 Jan, 30. PMID:24477356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1160/TH13-10-0811
- ↑ Huntington JA. Thrombin inhibition by the serpins. J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;11 Suppl 1:254-64. doi: 10.1111/jth.12252. PMID:23809129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jth.12252
- ↑ Esmon CT. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348-52. PMID:3029867
- ↑ Kalafatis M, Rand MD, Mann KG. The mechanism of inactivation of human factor V and human factor Va by activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31869-80. PMID:7989361
- ↑ Lu D, Kalafatis M, Mann KG, Long GL. Comparison of activated protein C/protein S-mediated inactivation of human factor VIII and factor V. Blood. 1996 Jun 1;87(11):4708-17. PMID:8639840
- ↑ Lu D, Kalafatis M, Mann KG, Long GL. Comparison of activated protein C/protein S-mediated inactivation of human factor VIII and factor V. Blood. 1996 Jun 1;87(11):4708-17. PMID:8639840
- ↑ Duga S, Asselta R, Tenchini ML. Coagulation factor V. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;36(8):1393-9. PMID:15147718 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2003.08.002
- ↑ Saenko EL, Shima M, Sarafanov AG. Role of activation of the coagulation factor VIII in interaction with vWf, phospholipid, and functioning within the factor Xase complex. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999 Oct;9(7):185-92. PMID:10881749
- ↑ Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Lechtenberg BC, Freund SM, Huntington JA. An ensemble view of thrombin allostery. Biol Chem. 2012 Sep;393(9):889-98. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0178. PMID:22944689 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0178
- ↑ Lechtenberg BC, Freund SM, Huntington JA. An ensemble view of thrombin allostery. Biol Chem. 2012 Sep;393(9):889-98. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0178. PMID:22944689 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0178
- ↑ Tijburg PN, van Heerde WL, Leenhouts HM, Hessing M, Bouma BN, de Groot PG. Formation of meizothrombin as intermediate in factor Xa-catalyzed prothrombin activation on endothelial cells. The influence of thrombin on the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):4017-22. PMID:1995649
- ↑ Lechtenberg BC, Freund SM, Huntington JA. An ensemble view of thrombin allostery. Biol Chem. 2012 Sep;393(9):889-98. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0178. PMID:22944689 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0178
- ↑ Lechtenberg BC, Freund SM, Huntington JA. An ensemble view of thrombin allostery. Biol Chem. 2012 Sep;393(9):889-98. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0178. PMID:22944689 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0178
- ↑ Bode W, Mayr I, Baumann U, Huber R, Stone SR, Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467-75. PMID:2583108
- ↑ Page MJ, Di Cera E. Evolution of peptidase diversity. J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 31;283(44):30010-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804650200. Epub 2008 , Sep 3. PMID:18768474 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804650200
- ↑ Bode W, Mayr I, Baumann U, Huber R, Stone SR, Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467-75. PMID:2583108
- ↑ Bode W, Mayr I, Baumann U, Huber R, Stone SR, Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467-75. PMID:2583108
- ↑ Bode W, Mayr I, Baumann U, Huber R, Stone SR, Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467-75. PMID:2583108
- ↑ Huntington JA. Molecular recognition mechanisms of thrombin. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Aug;3(8):1861-72. PMID:16102053 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01363.x
- ↑ Zhang E, Tulinsky A. The molecular environment of the Na+ binding site of thrombin. Biophys Chem. 1997 Jan 31;63(2-3):185-200. PMID:9108691

