Tropomyosin
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='1c1g' size='450' side='right' scene='User:Gregory_Hoeprich/Sandbox_1/Tropomyosin_dimer/2' caption='Pig tropomyosin (PDB code [[1c1g]])'> | <StructureSection load='1c1g' size='450' side='right' scene='User:Gregory_Hoeprich/Sandbox_1/Tropomyosin_dimer/2' caption='Pig tropomyosin (PDB code [[1c1g]])'> | ||
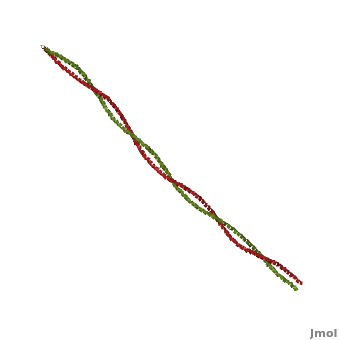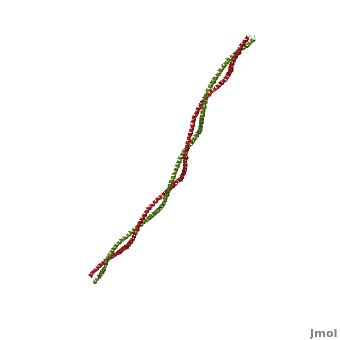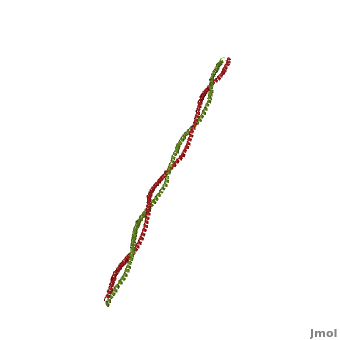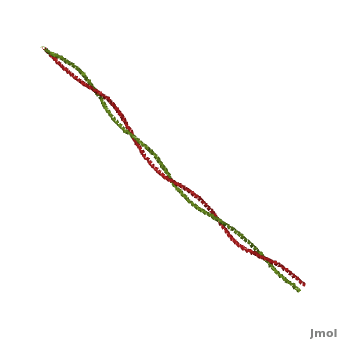
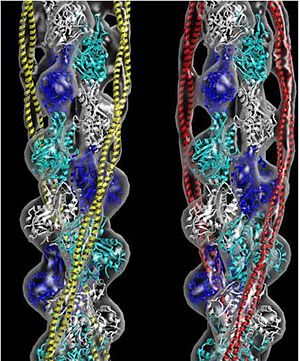
| - | + | '''Tropomyosin:''' Coiled-Coil Dimer, which is composed of two alpha helices [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1C1G (1C1G)] ]][[Image:B Lehman1.jpg | thumb | 300 x 430px | left | alt text | '''Tropomyosin''' (seen in yello and red) wrapped around actin filaments, which are EM reconstructions with G-actin ribbion structures filling in the EM structure. (Picture generated from William Lehman's [http://www.bumc.bu.edu/phys-biophys/research/filhel/ Website]) ]] | |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
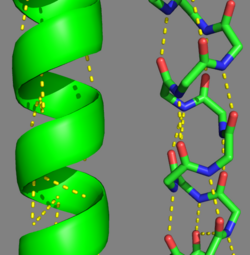
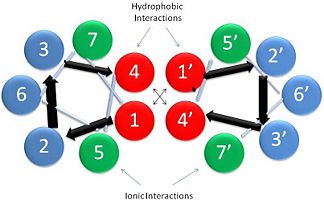
'''[[Tropomyosin]] (TM)''' is an [[actin]] binding protein, which consists of a coiled-coil dimer (see left) and forms a polymer along the length of actin by a head-to-tail overlap along the major grove of actin (see down & left)<ref name="Gunning">Tropomyosins. I. Gunning, Peter, 1950- II. Series.[DNLM: 1. Tropomyosin. W1 AD559 v.644 2008 / WE 500 T856 2008]</ref>. The head-to-tail overlap allows flexibility between the tropomyosin dimers so it will lay unstrained along the filament<ref name="Gunning"/>. Each tropomyosin molecule spans seven actin monomers within a filament and lays N- to C- terminally from actin's pointed to barbed end<ref name="Frye">PMID:20465283</ref>. The 284 amino acid helix has a length of 420 Angstroms and has a molecular weight around 65-70 kilodaltons (vertebrate tropomyosin)<ref name="Gunning"/><ref name="Whitby">PMID:10651038</ref>. A few of tropomyosin's characteristics as an actin binding protein includes regulation, stabilization and recruitment. | '''[[Tropomyosin]] (TM)''' is an [[actin]] binding protein, which consists of a coiled-coil dimer (see left) and forms a polymer along the length of actin by a head-to-tail overlap along the major grove of actin (see down & left)<ref name="Gunning">Tropomyosins. I. Gunning, Peter, 1950- II. Series.[DNLM: 1. Tropomyosin. W1 AD559 v.644 2008 / WE 500 T856 2008]</ref>. The head-to-tail overlap allows flexibility between the tropomyosin dimers so it will lay unstrained along the filament<ref name="Gunning"/>. Each tropomyosin molecule spans seven actin monomers within a filament and lays N- to C- terminally from actin's pointed to barbed end<ref name="Frye">PMID:20465283</ref>. The 284 amino acid helix has a length of 420 Angstroms and has a molecular weight around 65-70 kilodaltons (vertebrate tropomyosin)<ref name="Gunning"/><ref name="Whitby">PMID:10651038</ref>. A few of tropomyosin's characteristics as an actin binding protein includes regulation, stabilization and recruitment. | ||
Revision as of 08:16, 21 August 2014
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Tropomyosin
Updated on 21-August-2014
3mtu, 3mud – cTPM alpha-1 – chicken
1ic2 - cTPM alpha-1 (mutant)
3u1a, 3u1c – cTPM α-1 N terminal
3u59 – cTPM β N terminal
2w49, 2w4u – cTnnC+cTnnT+cTnnI+cTPM alpha-1+cActin
2z5h – yTPM alpha-1 N-terminal+C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper+TnnT – yeast
2z5i - yTPM alpha-1 N-terminal+C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper
2efr, 2efs, 2d3e - raTPM alpha-1 C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper – rabbit
4a7f, 4a7h, 4a7l - raTPM α-1 + myosin + actin – Cryo EM
3j4k - raTPM + actin – Cryo EM
1kql - TPM alpha-1 C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper - rat
1mv4 - rTPM alpha-1 C-terminal
2g9j - rTPM alpha-1 TM9A+GNC4
2b9c – rTPM mid region
3azd – rTPM N terminal
1c1g – TPM – pig
2tma – TPM - model
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 Tropomyosins. I. Gunning, Peter, 1950- II. Series.[DNLM: 1. Tropomyosin. W1 AD559 v.644 2008 / WE 500 T856 2008]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Frye J, Klenchin VA, Rayment I. Structure of the tropomyosin overlap complex from chicken smooth muscle: insight into the diversity of N-terminal recognition . Biochemistry. 2010 Jun 15;49(23):4908-20. PMID:20465283 doi:10.1021/bi100349a
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Whitby FG, Phillips GN Jr. Crystal structure of tropomyosin at 7 Angstroms resolution. Proteins. 2000 Jan 1;38(1):49-59. PMID:10651038
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Clayton JE, Sammons MR, Stark BC, Hodges AR, Lord M. Differential regulation of unconventional fission yeast myosins via the actin track. Curr Biol. 2010 Aug 24;20(16):1423-31. Epub 2010 Aug 12. PMID:20705471 doi:10.1016/j.cub.2010.07.026
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Stark BC, Sladewski TE, Pollard LW, Lord M. Tropomyosin and myosin-II cellular levels promote actomyosin ring assembly in fission yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 15;21(6):989-1000. Epub 2010 Jan 28. PMID:20110347 doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-10-0852
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Drees B, Brown C, Barrell BG, Bretscher A. Tropomyosin is essential in yeast, yet the TPM1 and TPM2 products perform distinct functions. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(3):383-92. PMID:7844152
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Lehman W, Galinska-Rakoczy A, Hatch V, Tobacman LS, Craig R. Structural basis for the activation of muscle contraction by troponin and tropomyosin. J Mol Biol. 2009 May 15;388(4):673-81. Epub 2009 Mar 31. PMID:19341744 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.060
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Tyska MJ, Warshaw DM. The myosin power stroke. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2002 Jan;51(1):1-15. PMID:11810692 doi:10.1002/cm.10014
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Gregory Hoeprich, Jaime Prilusky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman