Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
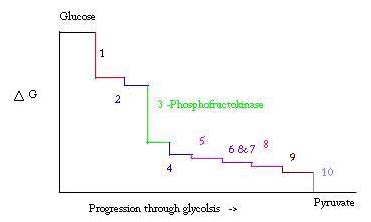
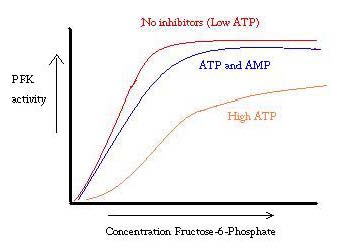
Phosphofructokinase binds both Mg2+-ATP and fructose-6-phosphate (F6P) to make fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and Mg2+-ADP. Although the image with both of these products has not been determined, <scene name='Phosphofructokinase_(PFK)/Pfk_ad_closeup/3'>F6P and Mg2+-ADP</scene> bound to the enzyme has been. There are three ligand binding sites per subunit. Two make up the active site, which binds F6P and ATP, while the third is an allosteric binding site.<ref>PMID:6115424</ref> Some proposed residues involved at the active site include <scene name='Phosphofructokinase_(PFK)/Pfk_ad_closeup/2'>ASP 127 and ARG 171</scene>.<ref>http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v327/n6121/abs/327437a0.html</ref> PFK exist in two conformational states, both <scene name='Zach_Westrick_Sandbox/R_state/1'>R</scene> and <scene name='Zach_Westrick_Sandbox/T_state/1'>T states</scene> which are in equilibrium. ATP binds both active and allosteric sites in both conformations. While ATP binds the active site equally well, it preferentially binds the allosteric site of the T state <ref>Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.</ref> This preferential binding causes a shift from equilibrium of the two states, to a greater amount of T state <ref>PubMed:2136935</ref>, which decreases the affinity for F6P. <scene name='Zach_Westrick_Sandbox/Allosteric_activator/2'>Allosteric activator ADP</scene> also binds to allosteric site to increase the ratio of R state phosphofructokinase. Along with ADP,AMP and F2,6P inhibit the regulatory role of ATP. | Phosphofructokinase binds both Mg2+-ATP and fructose-6-phosphate (F6P) to make fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and Mg2+-ADP. Although the image with both of these products has not been determined, <scene name='Phosphofructokinase_(PFK)/Pfk_ad_closeup/3'>F6P and Mg2+-ADP</scene> bound to the enzyme has been. There are three ligand binding sites per subunit. Two make up the active site, which binds F6P and ATP, while the third is an allosteric binding site.<ref>PMID:6115424</ref> Some proposed residues involved at the active site include <scene name='Phosphofructokinase_(PFK)/Pfk_ad_closeup/2'>ASP 127 and ARG 171</scene>.<ref>http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v327/n6121/abs/327437a0.html</ref> PFK exist in two conformational states, both <scene name='Zach_Westrick_Sandbox/R_state/1'>R</scene> and <scene name='Zach_Westrick_Sandbox/T_state/1'>T states</scene> which are in equilibrium. ATP binds both active and allosteric sites in both conformations. While ATP binds the active site equally well, it preferentially binds the allosteric site of the T state <ref>Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.</ref> This preferential binding causes a shift from equilibrium of the two states, to a greater amount of T state <ref>PubMed:2136935</ref>, which decreases the affinity for F6P. <scene name='Zach_Westrick_Sandbox/Allosteric_activator/2'>Allosteric activator ADP</scene> also binds to allosteric site to increase the ratio of R state phosphofructokinase. Along with ADP,AMP and F2,6P inhibit the regulatory role of ATP. | ||
The PFK's Km for ATP is .020mM and .032mM.<ref>PMID: 6233271</ref> | The PFK's Km for ATP is .020mM and .032mM.<ref>PMID: 6233271</ref> | ||
| - | |||
==Regulation== | ==Regulation== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 60: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase | ||
| - | + | *Phosphofructokinase | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[3o8l]], [[3o8n]] – PFK – rabbit<BR /> | |
| + | **[[3o8o]] – PFK – yeast<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[2pfk]] – EcPFK-1 – ''Escherichia coli''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3umo]] – EcPFK-2 <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[2hig]] – TbPFK – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1zxx]] – PFK – ''Lactobacillus delbrueckii''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6pfk]], [[3pfk]], [[3u39]] – GsPFK – ''Geobacillus stearothermophilus''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4i36]] – GsPFK (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1u2x]] – PhPFK – ''Pyrococcus horikoshii''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3hic]] – LiPFK – ''Listeria innocua''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3opy]] – PFK – ''Pichia pastoris''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4du5]] – PFKB - ''Polaromonas''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4a3s]] – PFK – ''Bacillus subtilis'' | ||
| - | + | *Phosphofructokinase complexes | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[3n1c]] – EcPFK-2 + fructose-6-phosphate<BR /> | |
| + | **[[3cqd]], [[3ump]] – EcPFK-2 + ATP<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3uqe]] - EcPFK2 (mutant) + ATP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3uqd]] – EcPFK2 + fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ATP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1pfk]] – EcPFK + fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3drw]] – PhPFK (mutant) + ADP <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3f5m]] – TbPFK + ATP<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3ie7]] – LiPFK + ATP<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1mto]] - GsPFK (mutant) + fructose-6-phosphate <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[4i4i]], [[4i7e]] - GsPFK (mutant) + phosphoenolpyruvate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6pfk]] – GsPFK + phosphoglycolic acid<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4pfk]] - GsPFK + fructose-6-phosphate + ADP | ||
| - | + | *Pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[1kzh]] – PFK – ''Borrelia burgdorferi''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3k2q]] – PFK – ''Marinobacter aquaeolei''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3hno]] – PFK – ''Nitrosospira multiformis'' | ||
| + | }} | ||
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | ||
Revision as of 07:43, 3 December 2014
| |||||||||||
Contents |
3D structures of PFK
Updated on 03-December-2014 Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
- Phosphofructokinase
- 3o8l, 3o8n – PFK – rabbit
- 3o8o – PFK – yeast
- 2pfk – EcPFK-1 – Escherichia coli
- 3umo – EcPFK-2
- 2hig – TbPFK – Trypanosoma brucei
- 1zxx – PFK – Lactobacillus delbrueckii
- 6pfk, 3pfk, 3u39 – GsPFK – Geobacillus stearothermophilus
- 4i36 – GsPFK (mutant)
- 1u2x – PhPFK – Pyrococcus horikoshii
- 3hic – LiPFK – Listeria innocua
- 3opy – PFK – Pichia pastoris
- 4du5 – PFKB - Polaromonas
- 4a3s – PFK – Bacillus subtilis
- 3o8l, 3o8n – PFK – rabbit
- Phosphofructokinase complexes
- 3n1c – EcPFK-2 + fructose-6-phosphate
- 3cqd, 3ump – EcPFK-2 + ATP
- 3uqe - EcPFK2 (mutant) + ATP
- 3uqd – EcPFK2 + fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ATP
- 1pfk – EcPFK + fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP
- 3drw – PhPFK (mutant) + ADP
- 3f5m – TbPFK + ATP
- 3ie7 – LiPFK + ATP
- 1mto - GsPFK (mutant) + fructose-6-phosphate
- 4i4i, 4i7e - GsPFK (mutant) + phosphoenolpyruvate
- 6pfk – GsPFK + phosphoglycolic acid
- 4pfk - GsPFK + fructose-6-phosphate + ADP
- 3n1c – EcPFK-2 + fructose-6-phosphate
- Pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase
}}
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Schirmer T, Evans PR. Structural basis of the allosteric behaviour of phosphofructokinase. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):140-5. PMID:2136935 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/343140a0
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.
- ↑ Evans PR, Farrants GW, Hudson PJ. Phosphofructokinase: structure and control. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):53-62. PMID:6115424
- ↑ http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v327/n6121/abs/327437a0.html
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.
- ↑ PubMed:2136935
- ↑ Campos G, Guixe V, Babul J. Kinetic mechanism of phosphofructokinase-2 from Escherichia coli. A mutant enzyme with a different mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6147-52. PMID:6233271
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.
- ↑ PubMed:2136935
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008. Print.
- ↑ Campos G, Guixe V, Babul J. Kinetic mechanism of phosphofructokinase-2 from Escherichia coli. A mutant enzyme with a different mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6147-52. PMID:6233271
- ↑ Kimmel JL, Reinhart GD. Reevaluation of the accepted allosteric mechanism of phosphofructokinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 11;97(8):3844-9. PMID:10759544 doi:10.1073/pnas.050588097
External Links
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Judy Voet, Ann Taylor, Jaime Prilusky, David Canner, Eran Hodis, Joel L. Sussman, Zach Westrick