1esz
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|ACTIVITY= | |ACTIVITY= | ||
|GENE= | |GENE= | ||
| + | |DOMAIN= | ||
| + | |RELATEDENTRY=[[1efd|1EFD]] | ||
| + | |RESOURCES=<span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1esz FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1esz OCA], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1esz PDBsum], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1esz RCSB]</span> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 27: | Line 30: | ||
[[Category: Vogel, H J.]] | [[Category: Vogel, H J.]] | ||
[[Category: Winkelmann, G.]] | [[Category: Winkelmann, G.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: CPO]] | ||
[[Category: abc transport protein]] | [[Category: abc transport protein]] | ||
[[Category: fhud]] | [[Category: fhud]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
[[Category: siderophore binding protein]] | [[Category: siderophore binding protein]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Sun Mar 30 20:09:01 2008'' |
Revision as of 17:09, 30 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 2.0Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||
| Related: | 1EFD
| ||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
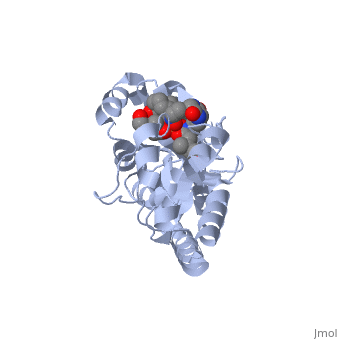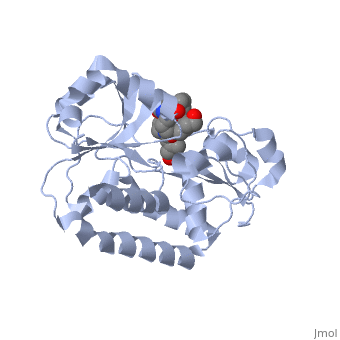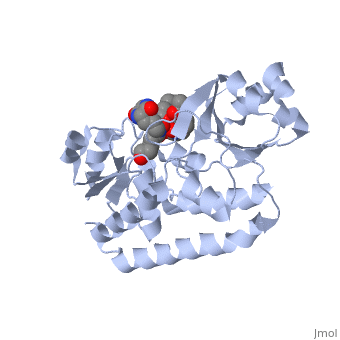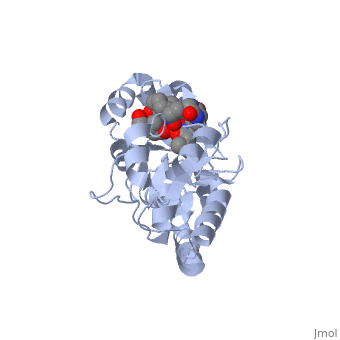
STRUCTURE OF THE PERIPLASMIC FERRIC SIDEROPHORE BINDING PROTEIN FHUD COMPLEXED WITH COPROGEN
Overview
Siderophore-binding proteins play an essential role in the uptake of iron in many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. FhuD is an ATP-binding cassette-type (ABC-type) binding protein involved in the uptake of hydroxamate-type siderophores in Escherichia coli. Structures of FhuD complexed with the antibiotic albomycin, the fungal siderophore coprogen and the drug Desferal have been determined at high resolution by x-ray crystallography. FhuD has an unusual bilobal structure for a periplasmic ligand binding protein, with two mixed beta/alpha domains connected by a long alpha-helix. The binding site for hydroxamate-type ligands is composed of a shallow pocket that lies between these two domains. Recognition of siderophores primarily occurs through interactions between the iron-hydroxamate centers of each siderophore and the side chains of several key residues in the binding pocket. Rearrangements of side chains within the binding pocket accommodate the unique structural features of each siderophore. The backbones of the siderophores are not involved in any direct interactions with the protein, demonstrating how siderophores with considerable chemical and structural diversity can be bound by FhuD. For albomycin, which consists of an antibiotic group attached to a hydroxamate siderophore, electron density for the antibiotic portion was not observed. Therefore, this study provides a basis for the rational design of novel bacteriostatic agents, in the form of siderophore-antibiotic conjugates that can act as "Trojan horses," using the hydroxamate-type siderophore uptake system to actively deliver antibiotics directly into targeted pathogens.
About this Structure
1ESZ is a Single protein structure of sequence from Escherichia coli. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
X-ray crystallographic structures of the Escherichia coli periplasmic protein FhuD bound to hydroxamate-type siderophores and the antibiotic albomycin., Clarke TE, Braun V, Winkelmann G, Tari LW, Vogel HJ, J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):13966-72. Epub 2002 Jan 22. PMID:11805094
Page seeded by OCA on Sun Mar 30 20:09:01 2008