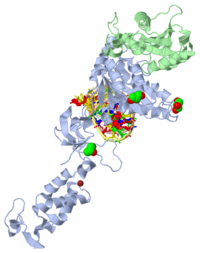
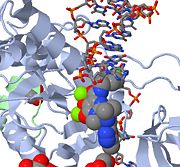
Retroviral Integrase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=1k6y size='450' side='right' scene='' caption=''> | + | <StructureSection load=1k6y size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='N-terminal and core domain of HIV-1 integrase (PDB code [[1k6y]])'> |
[[Image:3l2q.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of Integrase [[3l2q]]]] | [[Image:3l2q.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of Integrase [[3l2q]]]] | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | *Human spumaretrovirus integrase | |
| - | [[3os0]], [[3os1]], [[3os2]], [[3oy9]], [[3l2q]], [[3l2r]] – IN + DNA – human spumaretrovirus<br /> | + | **[[3os0]], [[3os1]], [[3os2]], [[3oy9]], [[3l2q]], [[3l2r]] – IN + DNA – human spumaretrovirus<br /> |
| - | [[3oyb]], [[3oyc]], [[3oyd]], [[3oye]], [[3oyf]], [[3oyg]], [[3oyh]], [[3oyi]], [[3oyj]], [[3oyk]], [[3oyl]], [[3oym]], [[3oyn]], [[3oya]], [[3l2u]], [[3l2v]], [[3l2w]] – IN + DNA + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[3oyb]], [[3oyc]], [[3oyd]], [[3oye]], [[3oyf]], [[3oyg]], [[3oyh]], [[3oyi]], [[3oyj]], [[3oyk]], [[3oyl]], [[3oym]], [[3oyn]], [[3oya]], [[3l2u]], [[3l2v]], [[3l2w]] – IN + DNA + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | [[2x6n]], [[2x6s]], [[2x74]], [[2x78]], [[3dlr]] - IN catalytic core domain | + | **[[2x6n]], [[2x6s]], [[2x74]], [[2x78]], [[3dlr]] - IN catalytic core domain |
| - | + | *Bovine immunodeficiency virus integrase | |
| - | [[3kkr]], [[3kks]] – IN catalytic core domain – BIV | + | **[[3kkr]], [[3kks]] – IN catalytic core domain – BIV |
| - | + | *Human immunodeficiency virus 1 integrase | |
| - | [[3lpt]], [[3lpu]], [[3l3u]], [[1exq]], [[1b92]], [[1b9d]], [[1b9f]], [[1bi4]], [[1bhl]], [[1bl3]], [[1bis]], [[1biu]], [[1biz]], [[2itg]], [[3zcm]] - IN catalytic core domain (mutant) – HIV-1<br /> | + | **[[3lpt]], [[3lpu]], [[3l3u]], [[1exq]], [[1b92]], [[1b9d]], [[1b9f]], [[1bi4]], [[1bhl]], [[1bl3]], [[1bis]], [[1biu]], [[1biz]], [[2itg]], [[3zcm]] - IN catalytic core domain (mutant) – HIV-1<br /> |
| - | [[3l3v ]]- IN catalytic core domain (mutant) + sucrose<br /> | + | **[[3l3v ]]- IN catalytic core domain (mutant) + sucrose<br /> |
| - | [[1hyv]], [[1hyz]], [[1qs4]] - IN N-terminal + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[1hyv]], [[1hyz]], [[1qs4]] - IN N-terminal + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | [[1k6y]] - IN N-terminal + catalytic core domain<br /> | + | **[[1k6y]] - IN N-terminal + catalytic core domain<br /> |
| - | [[1itg]] - IN catalytic core domain<br /> | + | **[[1itg]] - IN catalytic core domain<br /> |
| - | [[1wje]], [[1wjf]] - IN N-terminal zinc-binding domain (mutant) – NMR<br /> | + | **[[1wje]], [[1wjf]] - IN N-terminal zinc-binding domain (mutant) – NMR<br /> |
| - | [[1wja]], [[1wjb]], [[1wjc]], [[1wjd]] - IN N-terminal zinc-binding domain<br /> | + | **[[1wja]], [[1wjb]], [[1wjc]], [[1wjd]] - IN N-terminal zinc-binding domain<br /> |
| - | [[1ex4]] - IN C-terminal DBD + catalytic core domain (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[1ex4]] - IN C-terminal DBD + catalytic core domain (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[1ihv]], [[1ihw]] – IN DBD - NMR<br /> | + | **[[1ihv]], [[1ihw]] – IN DBD - NMR<br /> |
| - | [[1qmc]] – IN DBD - NMR<br /> | + | **[[1qmc]] – IN DBD - NMR<br /> |
| - | [[2b4j]], [[3av9]], [[3ava]], [[3avb]], [[3avc]], [[3avf]], [[3avg]], [[3avh]], [[3avi]], [[3avj]], [[3avk]], [[3avl]], [[3avm]], [[3avn]] - IN (mutant) + lens epithelium-derived growth factor <br /> | + | **[[2b4j]], [[3av9]], [[3ava]], [[3avb]], [[3avc]], [[3avf]], [[3avg]], [[3avh]], [[3avi]], [[3avj]], [[3avk]], [[3avl]], [[3avm]], [[3avn]] - IN (mutant) + lens epithelium-derived growth factor <br /> |
| - | [[3nf6]], [[3nf7]], [[3nf8]], [[3nf9]], [[3nfa]], [[4e1m]], [[4e1n]], [[4cj4]], [[4jlh]] - IN core domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[3nf6]], [[3nf7]], [[3nf8]], [[3nf9]], [[3nfa]], [[4e1m]], [[4e1n]], [[4cj4]], [[4jlh]] - IN core domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | + | *Human immunodeficiency virus 2 integrase | |
| - | [[3f9k]] - IN N-terminal + catalytic core domain + LEDGF IBD – HIV-2<br /> | + | **[[3f9k]] - IN N-terminal + catalytic core domain + LEDGF IBD – HIV-2<br /> |
| - | [[1e0e]] - IN N-terminal – NMR | + | **[[1e0e]] - IN N-terminal – NMR |
| - | + | *Moloney murine leukemia virus integrase | |
| - | [[3nnq]] – IN N-terminal – MOMLV | + | **[[3nnq]] – IN N-terminal – MOMLV |
| - | + | *Maedi Visna virus integrase | |
| - | [[3hpg]], [[3hph]] – IN N-terminal + catalytic core domain + LEDGF IBD – MVV | + | **[[3hpg]], [[3hph]] – IN N-terminal + catalytic core domain + LEDGF IBD – MVV |
| - | + | *Simian immunodeficiency virus integrase | |
| - | [[1c6v]] – IN catalytic domain + DNA binding domain - SIV | + | **[[1c6v]] – IN catalytic domain + DNA binding domain - SIV |
| - | + | *Rous sarcoma virus integrase | |
| - | [[1c0m]], [[1c1a]] – IN fragment (mutant) – RSV<br /> | + | **[[1c0m]], [[1c1a]] – IN fragment (mutant) – RSV<br /> |
| - | [[1vsk]], [[1vsl]], [[3o4q]] - IN catalytic core domain (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[1vsk]], [[1vsl]], [[3o4q]] - IN catalytic core domain (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[1vsm]], [[1vsh]], [[1vsi]], [[1vsj]], [[1vsd]], [[1vse]], [[1vsf]], [[3o4n]] - IN catalytic core domain<br /> | + | **[[1vsm]], [[1vsh]], [[1vsi]], [[1vsj]], [[1vsd]], [[1vse]], [[1vsf]], [[3o4n]] - IN catalytic core domain<br /> |
| - | [[1a5v]], [[1a5w]], [[1a5x]] - IN catalytic core domain + inhibitor | + | **[[1a5v]], [[1a5w]], [[1a5x]] - IN catalytic core domain + inhibitor |
| - | + | *Avian sarcoma virus integrase | |
| - | [[1cxq]], [[1cxu]], [[1cz9]], [[1czb]], [[1asu]], [[1asv]], [[1asw]] - IN catalytic core domain (mutant) – ASV | + | **[[1cxq]], [[1cxu]], [[1cz9]], [[1czb]], [[1asu]], [[1asv]], [[1asw]] - IN catalytic core domain (mutant) – ASV |
Bacterial IN | Bacterial IN | ||
| - | + | *Various integrases | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[3nkh]] – IN fragment – ''Staphylococcus aureus'' MRSA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1b69]], [[1tn9]] - EfIN N-terminal DBD + DNA – ''Enterococcus faecalis'' – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1bb8]], [[2bb8]] - EfIN N-terminal DBD – NMR | ||
| + | }} | ||
Revision as of 11:05, 7 December 2014
| |||||||||||
Integrase Inhibitors
| Name | Brand | Company | Patent | Notes |
| Raltegravir | Isentress | Merck & Co. | - | also known as MK-0518. The isopropyl and methyl-oxadiazole of MK-0518 are involved in hydrophobic and stacking interactions with side chains of Pro 214 and Tyr 212 to stabilize this drug within the PFV intasome active site. This manner of drug-binding interaction causes displacement of the reactive 3' viral DNA end from the active site of PFV intasome. After binding of MK-0518 to active site, the reactive 3' hydroxyl group moves away from the active site of the PFV intasome by more than 6 Angstroms. Raltegravir was approved by the FDA on October 12, 2007, for use with other anti-HIV agents in the treatment of HIV infection in adults. It is the first integrase inhibitor approved by the FDA. |
| Elvitegravir | - | Gilead Science | - | GS-9137 interacts with Pro 214 of PFV intasome through its quinolone base and isopropyl group. In experimental stages; shares the core structure of quinolone antibiotics. Phase II studies of elvitegravir in people who are treatment experienced have been completed. Phase III studies in treatment experienced patients are ongoing. A phase II study of elvitegravir in people who have never taken antiretroviral therapy is underway. This study will also be evaluated a boosting agent in place of Norvir, currently called GS9350. Elvitegravir holds promise for HIV-positive patients who have taken other anti-HIV drugs in the past. |
| MK-2048 | - | Merck & Co. | - | A second generation integrase inhibitor, intended to be used against HIV infection. It is superior to the first available integrase inhibitor, raltegravir, in that it inhibits the HIV enzyme integrase 4 times longer. It is being investigated for use as part of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). |
See also Retroviral Integrase Inhibitor Pharmacokinetics.
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
3D Structures of Retroviral Integrase
Updated on 07-December-2014
Bacterial IN
References
1.Hare, Stephen; Gupta, Saumya Shree; Valkov, Eugene; Engelman, Alan & Cherepanov, Peter (2010) Retroviral intasome assembly and inhibition of DNA strand transfer. Nature 2010/01/31/online doi:10.1038/nature08784 <http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature08784.html>
2. http://www.isentress.com/raltegravir/isentress/consumer/index.jsp
3. deJesus, Edwin HIV Antiretroviral Agents in Development. The Body: The Complete HIV/AIDS Resource. March 30, 2006.
4. AIDS Info
5. Krishan K. Pandey and Duane P. Grandgenett (2008) HIV-1 Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors: Novel Insights into their Mechanism of Action. Retrovirology: Research and Treatment" 2008:2 11-16
6.James F. Braun, DO, Ruth J. Cronje, PhD, Marnie G. Henderson (2008) HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors. www.prn.org Volume 13, Pages 1–9
Further Reading
- GEN News Highlights "Scientists Solve 3-D Crystal Structure of Retroviral Integrase Bound to Viral DNA", Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News February 1, 2010.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Rhysly Martinez, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jordan Heard, Eugene Babcock, Garrett Asanuma