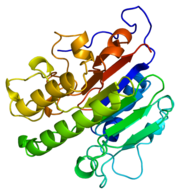
Figure 1.Ribbon Structure of APE1. Antiparallel beta sheets line the interior of the enzyme, while alpha helices line the exterior.
DNA is damaged frequently in living cells via endogenous and exogenous factors that have the ability to cause abasic sites in the DNA strand. Abasic DNA must be repaired both accuratly and efficiently in order to prevent the death of the cell or the accumulation of mutations within the genome. Abasic DNA is repaired in the base excision repair pathway. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease-1 (APE1) is the major repair enzyme in the base excision repair pathway in humans [1]. APE1 has the ability to cleave the phophodiester bond at the 5' end of abasic sites in damaged DNA strands [1].
An important point of gene regulation within a cell is the regulation of the half life of mRNA transcripts. The regulation of mRNA transcripts will control the amount of protein translated in a cell. Many mRNA transcripts have been linked to diseases such as cancer. These deleterious mRNA transcripts are known as proto-oncogene products and can greatly effect the health of cells[2]. APE1 has also been shown to have the ability to regulate the half life of c-myc mRNA by endonucleolytically cleaving the coding region determinant (CRD) of c-myc mRNA[2].
The oxidation states of molecules, such as many transcription factors, within the cell can activate or deactivate molecules and therefore regulate the expression of genes [3]The oxidation states of many amino acid residues within a protein can change the properties of the protein which can greatly affect the enzymatic activity of the protein. The oxidation states of cysteine residues, among other amino acid residues, within a polypeptide are regulated by APE1[3].Proteins that APE1 has been established to regulate the oxidation states of the cysteine residues of include NF-kB, Ehr-1, HIF-1, HLF, Pax-5, Pax-8 and p53, the mechanism of how APE1 contributes to the oxidation states of the cysteine residues on these proteins, however, is poorly understood[3] It is due to these many functions of APE1 that APE1 has become known as the multifunctional workhorse protein of the cell.
Structure and Function
APE1's major biological role is its activity in the BER pathway. APE1 is classified as a DNA lyase that has a structure weight of 50000-75000Da, depending on the crystal structure in question [4]. Many crystal structures of APE1 have been determined with amino acid numbers ranging from ~270 amino acid residues to ~320 amino acid residues[4][1]. The structure of APE1 has 15 anti-parallel beta sheets that line the interior of the protein, with 8 alpha helices lining the exterior of the protein. The beta sheets line the interior of the protein and form a convex binding surface for the DNA strand to fit in to. The binding surface of the protein is lined with positively charged amino acid residues that allow APE1 to bind to the negatively charged DNA strand. Metal ions assits the binding to the substrate by occupying the binding site.
Substrate Binding and Enzymatic Mechanism
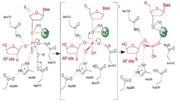
Figure 3. APE1 enzymatic mechanism of phosphodiester bond cleavage of abasic DNA
[4].
APE1 has numerous substrates in which in binds to ands acts on enzymatically, with abasic DNA being the most well known substrate for APE1. APE1 binds on the 5' side of the abasic DNA site with the amino acid residues Arg73, Ala74 and Lys78 interacting with three consecutive phosphate molecules on the DNA strand, while Tyr128 and Gly127 simultaneously span the minor grove causing the groove to widen a distance of ~2 Angstroms[4].The DNA is anchored and the abasic DNA is stabalized by APE1. APE1 then inserts Met270 into the minor groove causing the APE1/DNA structure to become extremely kinked[4].This kinking of the DNA strand is followed by an Arg177 insertion to the major groove donating a hydrogen bond to the 3' phosphate located at the abasic site[4].This is followed by a nucleophilic attack of an aspartate-activated hydroxyl group forming a transition state that is stabalized by a Mg2+ ion (Figure 3) which is followed by cleavage of the phosphodiester bond on the DNA strand[4].This is followed by the sequential events of residue Trp280 contacting a DNA phosphate and residues Asn222, Asn226 and Asn229 contacting the phosphates 3' of the abasic site, which is followed by Asn174 and Asn212 forming hydrogen bonds with an oxygen molecules 5' to the abasic site[4].
The nuclease domain
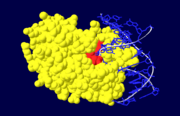
Figure 4. Nuclease domain (yellow) of APE1 bound to DNA (blue), with the active site amino acid residues labelled in red.
[4].
The nuclease domain of APE1 involves amino acid residues 128-318[1]. The nuclease activity of APE1 is due to its positively charged active site and its ability to bind to both the abasic and opposing DNA strand which leads to the displacement of the bound DNA glycosylase enzyme in the base excision repair pathway, allowing the DNA strand to be repaired[4].
The redox domain
The redox domain of APE1 invovles amino acid residues 1-127[1]. APE1 has the ability to activate and deactivate transcription factors by changing their redox states. This function of APE1 is handled by its redox domain.
Population Variants
Seven APE1 population variants have been identified and are a result of amino acid substitutions [1]. Amino acid substitutions that have been shown to be present in the general population include L104R, E126D, D148E, R237A, G241R, D283G and G306A[1]. The amino acid substitutions that seem to affect APE1's ability to cleave the phosphodiester bond of abasic sites within the DNA strand are the L104R, E126D and R237A[1]. The amino acid substitution to E from D at position 148 does not seem to exhibit and effect on the endonuclease activity of APE1[1]. The result of these population varients being present in the human population may give insight to the increased susceptibility to diseases, due to the importance of APE1 in the base excision repair pathway. Any problems or lowered efficiency within the repair of DNA can be detrimental to organisms.
See Also



