This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Antibody
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
<scene name='Antibody/Rituxan_starting_scene/1'>Crystal structure of Rituximab Fab in complex with an epitope peptide</scene> ([[2osl]]). | <scene name='Antibody/Rituxan_starting_scene/1'>Crystal structure of Rituximab Fab in complex with an epitope peptide</scene> ([[2osl]]). | ||
| - | + | == Antibody Diversity == | |
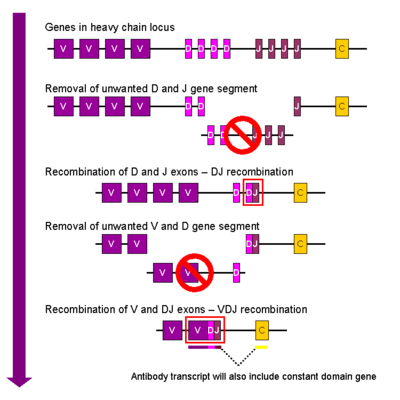
Considering the nearly infinite number of possible antigens that can invade the body, the immune system had to develop a method for accurately targeting each one of these compounds, ranging from small molecules, to stray proteins, to viruses capable of infecting cells. The antibody was the immune systems response to this problem. It has been estimated that humans generate about 10^10 different antigens, each capable of binding a unique epitope of an antigen. Since antibodies are proteins, and proteins are controlled by the genes from which they are transcribed, a clever system of gene shuffling and manipulations developed to enable the immune system to create a huge repertoire of antibodies from a limited number of genes. <ref>PMID:8612345</ref> The variable region of each immunoglobulin chain is encoded in several pieces known as gene segments. For heavy chains, these segments are called the variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) segments. (Only V and J exist for light chains) 50 V segments, 25 D segments, and 6 J segments exist and are randomly arranged and rearranged in the genome in a process called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VDJ_recombination V(D)J recombination]. Each B-cell is programmed to produce antibodies of a single V(D)J recombination order. | Considering the nearly infinite number of possible antigens that can invade the body, the immune system had to develop a method for accurately targeting each one of these compounds, ranging from small molecules, to stray proteins, to viruses capable of infecting cells. The antibody was the immune systems response to this problem. It has been estimated that humans generate about 10^10 different antigens, each capable of binding a unique epitope of an antigen. Since antibodies are proteins, and proteins are controlled by the genes from which they are transcribed, a clever system of gene shuffling and manipulations developed to enable the immune system to create a huge repertoire of antibodies from a limited number of genes. <ref>PMID:8612345</ref> The variable region of each immunoglobulin chain is encoded in several pieces known as gene segments. For heavy chains, these segments are called the variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) segments. (Only V and J exist for light chains) 50 V segments, 25 D segments, and 6 J segments exist and are randomly arranged and rearranged in the genome in a process called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VDJ_recombination V(D)J recombination]. Each B-cell is programmed to produce antibodies of a single V(D)J recombination order. | ||
Revision as of 10:56, 17 November 2014
| |||||||||||
Contents |
3D Structures of Immunoglobulin
Updated on 17-November-2014
Humanized mouse antibody (hmFab) is a modified mFab which resembles more hFab.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Roit, I. M. Roit's Essential Immunology. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd., 1997.
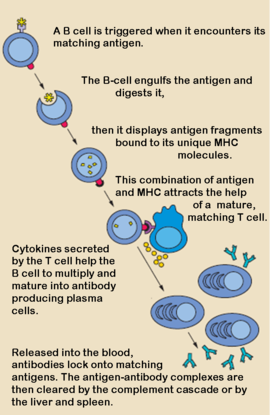
- ↑ Parker DC. T cell-dependent B cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:331-60. PMID:8476565 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001555
- ↑ Rus H, Cudrici C, Niculescu F. The role of the complement system in innate immunity. Immunol Res. 2005;33(2):103-12. PMID:16234578 doi:10.1385/IR:33:2:103
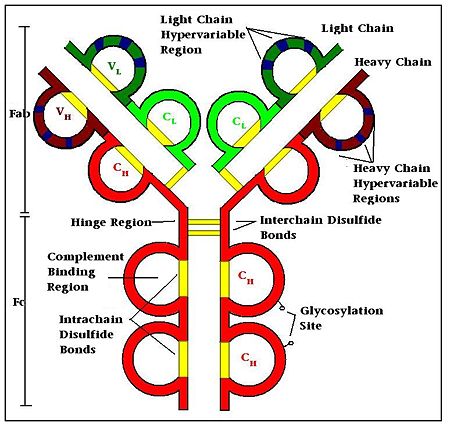
- ↑ Roux KH. Immunoglobulin structure and function as revealed by electron microscopy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999 Oct;120(2):85-99. PMID:10545762
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Woof JM, Burton DR. Human antibody-Fc receptor interactions illuminated by crystal structures. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Feb;4(2):89-99. PMID:15040582 doi:10.1038/nri1266
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Harris LJ, Larson SB, Hasel KW, McPherson A. Refined structure of an intact IgG2a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1997 Feb 18;36(7):1581-97. PMID:9048542 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi962514+
- ↑ Hochman J, Inbar D, Givol D. An active antibody fragment (Fv) composed of the variable portions of heavy and light chains. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1130-5. PMID:4569769
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Woof JM, Burton DR. Human antibody-Fc receptor interactions illuminated by crystal structures. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Feb;4(2):89-99. PMID:15040582 doi:10.1038/nri1266
- ↑ Wright A, Morrison SL. Effect of glycosylation on antibody function: implications for genetic engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 1997 Jan;15(1):26-32. PMID:9032990 doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(96)10062-7
- ↑ Heyman B. Complement and Fc-receptors in regulation of the antibody response. Immunol Lett. 1996 Dec;54(2-3):195-9. PMID:9052877
- ↑ Ravetch JV, Bolland S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:275-90. PMID:11244038 doi:19/1/275
- ↑ Fanning LJ, Connor AM, Wu GE. Development of the immunoglobulin repertoire. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Apr;79(1):1-14. PMID:8612345
- ↑ Diaz M, Casali P. Somatic immunoglobulin hypermutation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002 Apr;14(2):235-40. PMID:11869898
- ↑ Borghesi L, Milcarek C. From B cell to plasma cell: regulation of V(D)J recombination and antibody secretion. Immunol Res. 2006;36(1-3):27-32. PMID:17337763 doi:10.1385/IR:36:1:27
- ↑ Durandy A. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase: a dual role in class-switch recombination and somatic hypermutation. Eur J Immunol. 2003 Aug;33(8):2069-73. PMID:12884279 doi:10.1002/eji.200324133
- ↑ CHOWN B, LEWIS M, KAITA K. A new Kell blood-group phenotype. Nature. 1957 Oct 5;180(4588):711. PMID:13477267
- ↑ Burnette WN. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195-203. PMID:6266278
- ↑ Brehm-Stecher BF, Johnson EA. Single-cell microbiology: tools, technologies, and applications. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004 Sep;68(3):538-59. PMID:15353569 doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.3.538-559.2004
Additional Pages
See Also
- Variable Lymphocyte Receptors
- Antibody at High school teachers' resources, where you will find tutorials on antibody structure.
- Antibodies at Wikipedia.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
David Canner, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Wayne Decatur, Mark Hoelzer, Eric Martz