B-cell lymphoma protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='1g5m' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='NMR structure of bcl-2 [[1g5m]]'> | ||
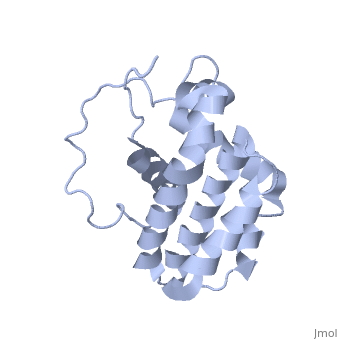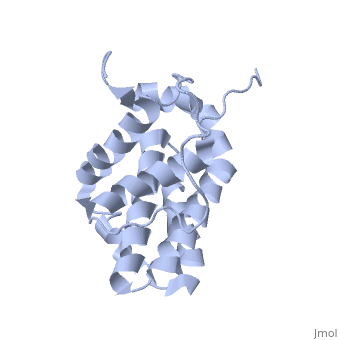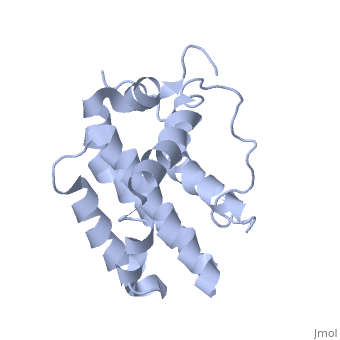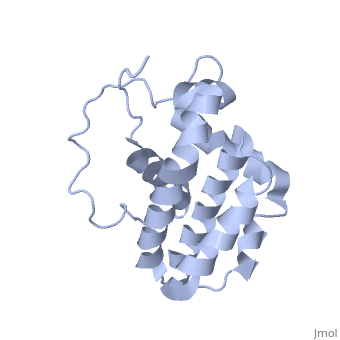
[[Image:Bcl-2_3D.jpg|left|200px]] [[Bcl-2]] family are pro-survival proteins. The name is derived from B-cell lymphoma 2. | [[Image:Bcl-2_3D.jpg|left|200px]] [[Bcl-2]] family are pro-survival proteins. The name is derived from B-cell lymphoma 2. | ||
'''Bcl-xL''' known as survival protein is the regulator of apoptosis. '''Mcl-1''' is an induced myeloid cell leukemia differentiation protein. '''Bcl-2-L-7''' is called '''Bak''' for Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer. | '''Bcl-xL''' known as survival protein is the regulator of apoptosis. '''Mcl-1''' is an induced myeloid cell leukemia differentiation protein. '''Bcl-2-L-7''' is called '''Bak''' for Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer. | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | + | ||
Bcl-2 is a family of genes and proteins that govern the mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP). Bcl-2 derives its name from B-cell lymphoma 2 which came from being the second member of a range of proteins initially described as a reciprocal gene translocation in chromosomes 14 and 18 in follicular lymphomas. The genes and proteins can be either pro-apoptotic (Bax, BAD, Bak and Bok) or anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Bcl-w). These genes interact with the Bcl-2 protein structure, which result in either a pro- or anti-apoptosis function. The sites on Bcl-2 where the genes interact, have been characterized by Dr. JC Reed et al[2]. These domains are <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh1/3'>BH1 (residues 136-155)</scene>, <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh2/1'>BH2 (187-202)</scene>, <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh3/2'>BH3 (93-107)</scene> and <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh4/1'>BH4 (10-30)</scene>. Dr. Reed found that any deletion of these domains, abolishes Bcl-2's ability to suppress cell death. | Bcl-2 is a family of genes and proteins that govern the mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP). Bcl-2 derives its name from B-cell lymphoma 2 which came from being the second member of a range of proteins initially described as a reciprocal gene translocation in chromosomes 14 and 18 in follicular lymphomas. The genes and proteins can be either pro-apoptotic (Bax, BAD, Bak and Bok) or anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Bcl-w). These genes interact with the Bcl-2 protein structure, which result in either a pro- or anti-apoptosis function. The sites on Bcl-2 where the genes interact, have been characterized by Dr. JC Reed et al[2]. These domains are <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh1/3'>BH1 (residues 136-155)</scene>, <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh2/1'>BH2 (187-202)</scene>, <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh3/2'>BH3 (93-107)</scene> and <scene name='Bcl-2/Bh4/1'>BH4 (10-30)</scene>. Dr. Reed found that any deletion of these domains, abolishes Bcl-2's ability to suppress cell death. | ||
Revision as of 13:42, 21 May 2015
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Colin Ridenour, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky
Categories: Topic Page | Bcl 2 | Bax | Bok | Bad | Bak | Bcl-xl | Bcl xl | Bcl-w | Bcl w | Apoptosis | Mmp | Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization | B cell lymphoma 2 | Signal transduction