This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Hyaluronidase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
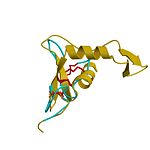
<StructureSection load="1c82" size="350" color="" frame="true" spin="on" Scene= caption='Hyaluronidase complex with hyaluronic acid disaccharide and dimethylarsinate, [[1c82]]' > | <StructureSection load="1c82" size="350" color="" frame="true" spin="on" Scene= caption='Hyaluronidase complex with hyaluronic acid disaccharide and dimethylarsinate, [[1c82]]' > | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
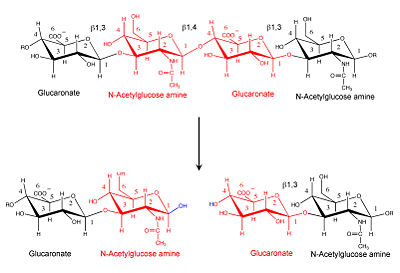
| + | '''Hyaluronidase''' (HU) hydrolyzes complex carbohydrates such as hyaluronan which is part of the extracellular matrix. The hydrolysis increases tissue permeability. | ||
| - | + | == Relevance == | |
| + | HU is used in medicine to speed drug delivery. Hyaluronic acid (HUA) is a popular dermal filler material. | ||
{| | {| | ||
|-valign="top" | |-valign="top" | ||
Revision as of 08:15, 27 March 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of hyaluronidase
Updated on 27-March-2016
Reference
Structure of human hyaluronidase-1, a hyaluronan hydrolyzing enzyme involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis., Chao KL, Muthukumar L, Herzberg O, Biochemistry. 2007 Jun 12;46(23):6911-20. Epub 2007 May 16. PMID:17503783
Created with the participation of Osnat Herzberg, Eran Hodis, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky.