Insulin-Degrading Enzyme
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
IDE-C is also involved in the oligomerization of IDE. | IDE-C is also involved in the oligomerization of IDE. | ||
| - | + | == Catalytic chamber == | |
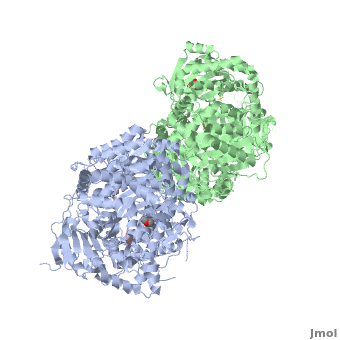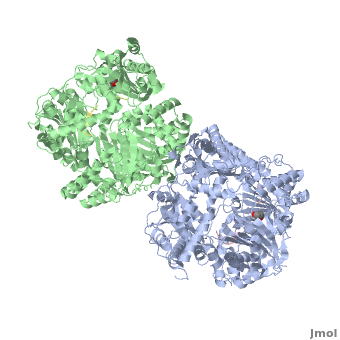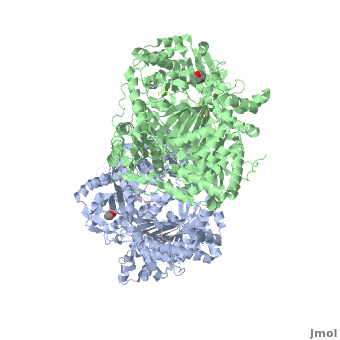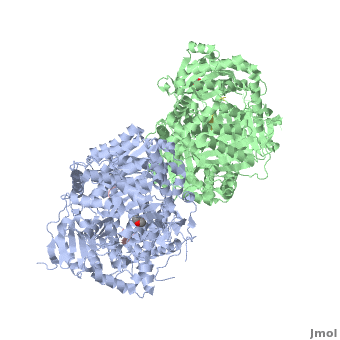
IDE-N and IDE-C create substantial contact to form an enclosed catalytic chamber to encapsulate its substrates. This enclosed chamber is shaped like a triangular prism, with triangular base dimensions of 35x34x30 Ȧ and a height of 36 Ȧ. So the total volume of this prism is about 1.3x104 Ȧ<sup>3</sup>. | IDE-N and IDE-C create substantial contact to form an enclosed catalytic chamber to encapsulate its substrates. This enclosed chamber is shaped like a triangular prism, with triangular base dimensions of 35x34x30 Ȧ and a height of 36 Ȧ. So the total volume of this prism is about 1.3x104 Ȧ<sup>3</sup>. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
In the domain 2, there is an exosite that accommodates the N-terminus of substrates and is involved in the substrates binding. | In the domain 2, there is an exosite that accommodates the N-terminus of substrates and is involved in the substrates binding. | ||
| - | + | == Substrate binding == | |
IDE can adopt two conformations, called “open” (IDE-o) and “closed” (IDE-c). | IDE can adopt two conformations, called “open” (IDE-o) and “closed” (IDE-c). | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
IDE-N and IDE-C have extensive interactions that bury a large surface of 11,496 Ȧ<sup>2</sup> with good shape complementarity and numerous hydrogen bonds. In the absence of interactions with factors or proteins, the substrate-free IDE-c state is stable and the catalytic chamber of IDE is mostly closed. So we can consider that IDE-c is the resting and inactive state of IDE. | IDE-N and IDE-C have extensive interactions that bury a large surface of 11,496 Ȧ<sup>2</sup> with good shape complementarity and numerous hydrogen bonds. In the absence of interactions with factors or proteins, the substrate-free IDE-c state is stable and the catalytic chamber of IDE is mostly closed. So we can consider that IDE-c is the resting and inactive state of IDE. | ||
| - | + | == Han ethnicity-specific type 2 diabetic treatment from traditional Chinese medicine? <ref>doi 10.1080/07391102.2012.732340</ref>== | |
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) is a zinc-metalloendopeptidase found mostly in cytosol. Since overexpression of IDE increases the rate of extracellular insulin degradation, IDE is a potential target for controlling insulin degradation. | Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) is a zinc-metalloendopeptidase found mostly in cytosol. Since overexpression of IDE increases the rate of extracellular insulin degradation, IDE is a potential target for controlling insulin degradation. | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| - | + | ||
==3D structures of insulin-degrading enzyme== | ==3D structures of insulin-degrading enzyme== | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 27 November 2014
| |||||||||||
3D structures of insulin-degrading enzyme
Updated on 27-November-2014
References
- Im H, Manolopoulou M, Malito E, Shen Y, Zhao J, Neant-Fery M, Sun CY, Meredith SC, Sisodia SS, Leissring MA, Tang WJ. Structure of substrate-free human insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) and biophysical analysis of ATP-induced conformational switch of IDE. J Biol Chem. 2007 Aug 31;282(35):25453-63. Epub 2007 Jul 5. PMID:17613531 doi:10.1074/jbc.M701590200
- Shen Y, Joachimiak A, Rosner MR, Tang WJ. Structures of human insulin-degrading enzyme reveal a new substrate recognition mechanism. Nature. 2006 Oct 19;443(7113):870-4. Epub 2006 Oct 11. PMID:17051221 doi:10.1038/nature05143
- Li P, Kuo WL, Yousef M, Rosner MR, Tang WJ. The C-terminal domain of human insulin degrading enzyme is required for dimerization and substrate recognition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 May 19;343(4):1032-7. Epub 2006 Mar 22. PMID:16574064 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.083
- ↑ Chen KC, Chang SS, Tsai FJ, Chen CY. Han ethnicity-specific type 2 diabetic treatment from traditional Chinese medicine? J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012 Nov 12. PMID:23146021 doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.732340
- ↑ Leissring MA, Malito E, Hedouin S, Reinstatler L, Sahara T, Abdul-Hay SO, Choudhry S, Maharvi GM, Fauq AH, Huzarska M, May PS, Choi S, Logan TP, Turk BE, Cantley LC, Manolopoulou M, Tang WJ, Stein RL, Cuny GD, Selkoe DJ. Designed inhibitors of insulin-degrading enzyme regulate the catabolism and activity of insulin. PLoS One. 2010 May 7;5(5):e10504. PMID:20498699 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010504
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Élodie Weider, Karsten Theis, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky