Molecular Playground/E. coli ClpP
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Here in the Chien lab, we study how degradation plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein levels plays an important role during cell homeostasis and cell transitions/differentiation, yet much of what governs these processes has yet to be fully understood. | Here in the Chien lab, we study how degradation plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein levels plays an important role during cell homeostasis and cell transitions/differentiation, yet much of what governs these processes has yet to be fully understood. | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
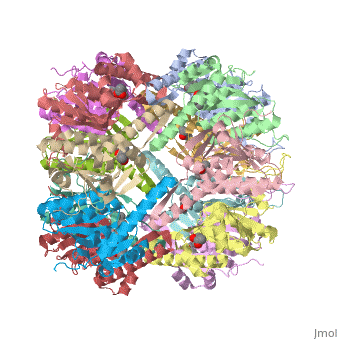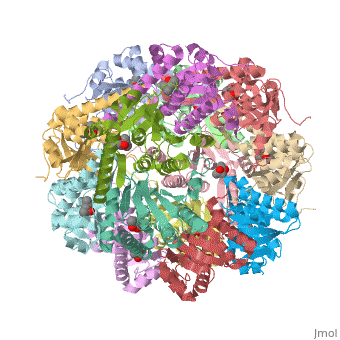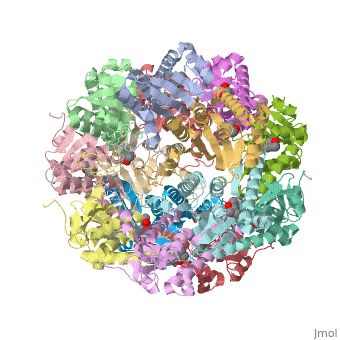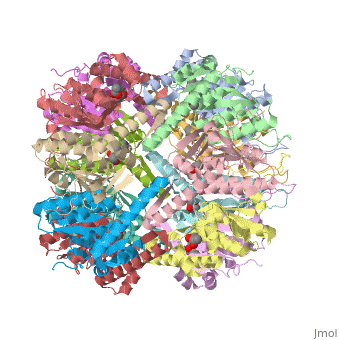
| - | + | {i}E. coli{i} Casein lytic proteinase P (ClpP) is a double ring tetradecameric homo oligomer compartmentalized peptidase [1]. ClpP requires the use of ATP dependent regulatory elements that independently bind to ClpP in order for substrates to have access the active core [2-4]. Here, proteins that are translocated by regulatory elements into the peptidase core are cleaved into smaller amino acid chains approximately on average 6-8aa in length [5]. | |
<StructureSection load='1yg6' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1yg6' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
Revision as of 16:22, 3 December 2014
Here in the Chien lab, we study how degradation plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein levels plays an important role during cell homeostasis and cell transitions/differentiation, yet much of what governs these processes has yet to be fully understood.
Introduction
{i}E. coli{i} Casein lytic proteinase P (ClpP) is a double ring tetradecameric homo oligomer compartmentalized peptidase [1]. ClpP requires the use of ATP dependent regulatory elements that independently bind to ClpP in order for substrates to have access the active core [2-4]. Here, proteins that are translocated by regulatory elements into the peptidase core are cleaved into smaller amino acid chains approximately on average 6-8aa in length [5].
| |||||||||||
References
Acknowledgements
Kamal Joshi, Joanne Lau, Jing Liu, Rob Vass