We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
LisaRob/Sandbox2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: Here in the Chien lab, we study how [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proteolysis proteolysis] plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein ...) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
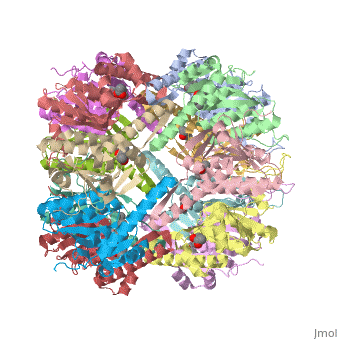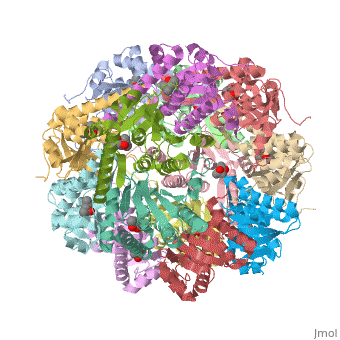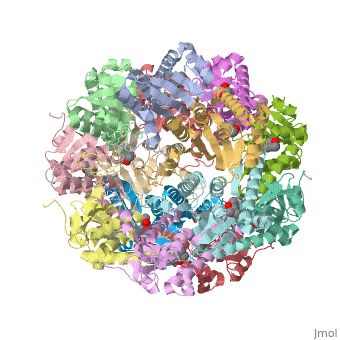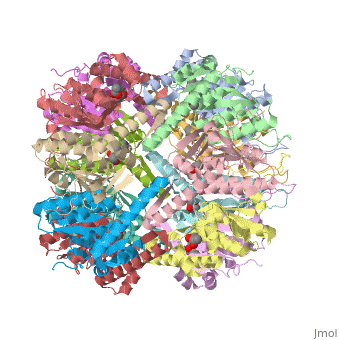
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
== Role of ClpP/Biological Relevance == | == Role of ClpP/Biological Relevance == | ||
| - | ''E. coli'' ClpAP/ClpXP complexes play a critical role in maintaining protein homeostasis under several levels of quality control. Improperly folded or aggregated proteins are potential ClpP substrates based on properties of the associated regulatory element recognition. Targeted removal of aberrant proteins resulting from and rescue of stalled ribosomes by the SsrA tagging system are directly recognized and degraded by ClpAP/ClpXP complexes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9573050]. In ''E. coli'' ClpP and ClpP homologues found in other bacteria require regulatory elements to recognize and import proteins for destruction. To gain access to the active sites is tightly controlled and therefore a potential antimicrobial target where loss of regulation (for example, through use of acyldepsipeptides or ADEPs) literally digests the bacteria from the inside out [10]. ''E. coli'' ClpAP and ClpXP has been used as a structural model for the 26 proteasome to gain insight into its workings [ | + | ''E. coli'' ClpAP/ClpXP complexes play a critical role in maintaining protein homeostasis under several levels of quality control. Improperly folded or aggregated proteins are potential ClpP substrates based on properties of the associated regulatory element recognition. Targeted removal of aberrant proteins resulting from and rescue of stalled ribosomes by the SsrA tagging system are directly recognized and degraded by ClpAP/ClpXP complexes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9573050]. In ''E. coli'' ClpP and ClpP homologues found in other bacteria require regulatory elements to recognize and import proteins for destruction. To gain access to the active sites is tightly controlled and therefore a potential antimicrobial target where loss of regulation (for example, through use of acyldepsipeptides or ADEPs) literally digests the bacteria from the inside out [http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-6787-4_24]. ''E. coli'' ClpAP and ClpXP has been used as a structural model for the 26 proteasome to gain insight into its workings [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7623377][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14990998]. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9573050 9. ''The ClpXP and ClpAP proteases degrade proteins with carboxy-terminal peptide tails added by the SsrA-tagging system.'' Gottesman S ''et. al'' (1998 Genes Dev.)] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9573050 9. ''The ClpXP and ClpAP proteases degrade proteins with carboxy-terminal peptide tails added by the SsrA-tagging system.'' Gottesman S ''et. al'' (1998 Genes Dev.)] | ||
| - | [10. Bacterial Cell Stress Protein ClpP: A Novel Antibiotic Target | + | [http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-6787-4_24 10. ''Bacterial Cell Stress Protein ClpP: A Novel Antibiotic Target.'' Brötz-Oesterhelt ''et. al'' (2013 Heat Shock Proteins Volume 7, pp 375-385)] |
| - | [11. Homology in structural organization between E. coli ClpAP protease and the eukaryotic 26 S proteasome | + | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7623377 11. ''Homology in structural organization between E. coli ClpAP protease and the eukaryotic 26 S proteasome.'' Kessel M ''et. al'' (1995 J Mol Bio)] |
| - | [12. Proteasomes and their kin: proteases in the machine age | + | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14990998 12. ''Proteasomes and their kin: proteases in the machine age.'' Pickart CM ''et. al'' (2004 Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.)] |
== Acknowledgements== | == Acknowledgements== | ||
Kamal Joshi, Joanne Lau, Jing Liu, Rob Vass | Kamal Joshi, Joanne Lau, Jing Liu, Rob Vass | ||
Current revision
Here in the Chien lab, we study how proteolysis plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein levels plays an important role during cell homeostasis and cell transitions/differentiation, yet much of what governs these processes has yet to be fully understood.
| |||||||||||
References
6. Clp P represents a unique family of serine proteases. Maurizi MR et. al (1990 J Biolchem)
Acknowledgements
Kamal Joshi, Joanne Lau, Jing Liu, Rob Vass