1p8x
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
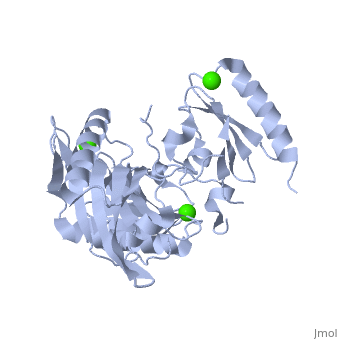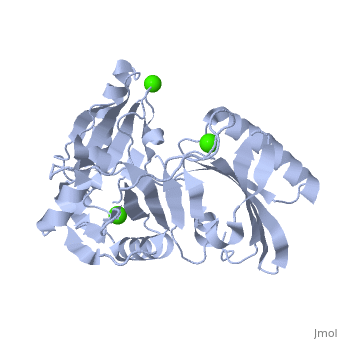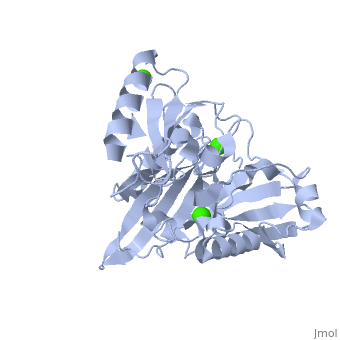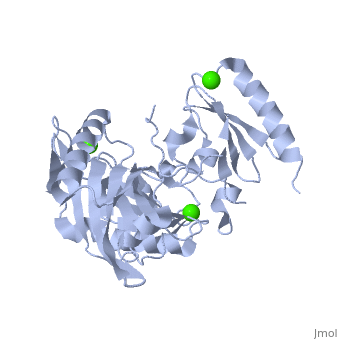
|PDB= 1p8x |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>1p8x</scene>, resolution 2.0Å | |PDB= 1p8x |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>1p8x</scene>, resolution 2.0Å | ||
|SITE= | |SITE= | ||
| - | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM ION'>CA</scene> | + | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM+ION'>CA</scene> |
|ACTIVITY= | |ACTIVITY= | ||
|GENE= | |GENE= | ||
| + | |DOMAIN= | ||
| + | |RELATEDENTRY= | ||
| + | |RESOURCES=<span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1p8x FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1p8x OCA], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1p8x PDBsum], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1p8x RCSB]</span> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Gelsolin requires activation to carry out its severing and capping activities on F-actin. Here, we present the structure of the isolated C-terminal half of gelsolin (G4-G6) at 2.0 A resolution in the presence of Ca(2+) ions. This structure completes a triptych of the states of activation of G4-G6 that illuminates its role in the function of gelsolin. Activated G4-G6 displays an open conformation, with the actin-binding site on G4 fully exposed and all three type-2 Ca(2+) sites occupied. Neither actin nor the type-l Ca(2+), which normally is sandwiched between actin and G4, is required to achieve this conformation. | Gelsolin requires activation to carry out its severing and capping activities on F-actin. Here, we present the structure of the isolated C-terminal half of gelsolin (G4-G6) at 2.0 A resolution in the presence of Ca(2+) ions. This structure completes a triptych of the states of activation of G4-G6 that illuminates its role in the function of gelsolin. Activated G4-G6 displays an open conformation, with the actin-binding site on G4 fully exposed and all three type-2 Ca(2+) sites occupied. Neither actin nor the type-l Ca(2+), which normally is sandwiched between actin and G4, is required to achieve this conformation. | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Disease== | ||
| - | Known disease associated with this structure: Amyloidosis, Finnish type OMIM:[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=137350 137350]] | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category: Narayan, K.]] | [[Category: Narayan, K.]] | ||
[[Category: Robinson, R C.]] | [[Category: Robinson, R C.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: CA]] | ||
[[Category: calcium-binding]] | [[Category: calcium-binding]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Sun Mar 30 22:56:33 2008'' |
Revision as of 19:56, 30 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 2.0Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
The Calcium-Activated C-terminal half of gelsolin
Overview
Gelsolin requires activation to carry out its severing and capping activities on F-actin. Here, we present the structure of the isolated C-terminal half of gelsolin (G4-G6) at 2.0 A resolution in the presence of Ca(2+) ions. This structure completes a triptych of the states of activation of G4-G6 that illuminates its role in the function of gelsolin. Activated G4-G6 displays an open conformation, with the actin-binding site on G4 fully exposed and all three type-2 Ca(2+) sites occupied. Neither actin nor the type-l Ca(2+), which normally is sandwiched between actin and G4, is required to achieve this conformation.
About this Structure
1P8X is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Activation in isolation: exposure of the actin-binding site in the C-terminal half of gelsolin does not require actin., Narayan K, Chumnarnsilpa S, Choe H, Irobi E, Urosev D, Lindberg U, Schutt CE, Burtnick LD, Robinson RC, FEBS Lett. 2003 Sep 25;552(2-3):82-5. PMID:14527664
Page seeded by OCA on Sun Mar 30 22:56:33 2008