This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1cfc
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
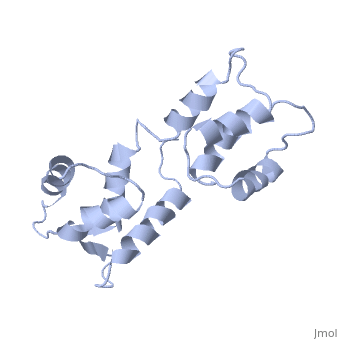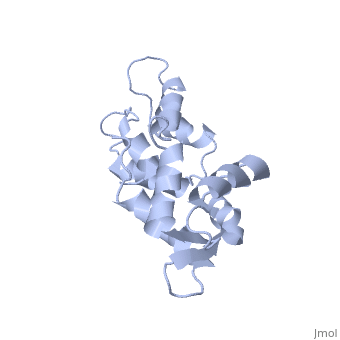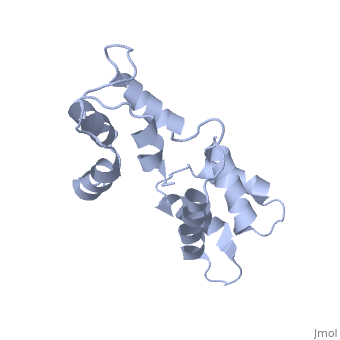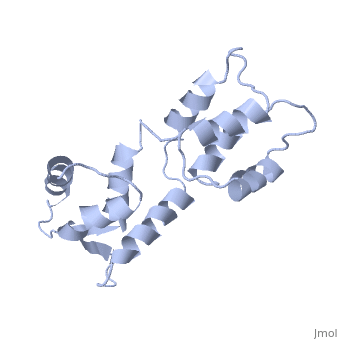
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1cfc]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xenopus_laevis Xenopus laevis]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1CFC OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1CFC FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1cfc]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xenopus_laevis Xenopus laevis]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1CFC OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1CFC FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1cfd|1cfd]]</td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1cfd|1cfd]]</td></tr> | ||
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1cfc FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1cfc OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1cfc RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1cfc PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1cfc FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1cfc OCA], [http://pdbe.org/1cfc PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1cfc RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1cfc PDBsum]</span></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CALM_XENLA CALM_XENLA]] Calmodulin mediates the control of a large number of enzymes, ion channels and other proteins by Ca(2+). Among the enzymes to be stimulated by the calmodulin-Ca(2+) complex are a number of protein kinases and phosphatases. | ||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 26: | ||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="pdbe-citations 1cfc" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Revision as of 20:39, 9 September 2015
CALCIUM-FREE CALMODULIN
| |||||||||||