We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 959
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
We can observe this bridge on the following figure. There are two charged amino acid residues, <scene name='60/604478/Argglu/1'>Arg5, and Glu13</scene>, forming a conserved salt bridge, and <scene name='60/604478/Gly17/1'>Gly17</scene>, which constitutes a signature structural motif which is essential for correct folding. <br /> | We can observe this bridge on the following figure. There are two charged amino acid residues, <scene name='60/604478/Argglu/1'>Arg5, and Glu13</scene>, forming a conserved salt bridge, and <scene name='60/604478/Gly17/1'>Gly17</scene>, which constitutes a signature structural motif which is essential for correct folding. <br /> | ||
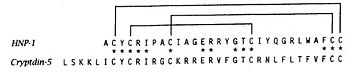
| - | Each defensin monomer consists of three strands of antiparallel β-sheet incorporating 60% of the residues. Two β-turns and three disulfide bonds add further restrictions to the conformational freedom of the monomer.<ref>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2049026/</ref> | + | Each defensin monomer consists of three strands of antiparallel β-sheet incorporating 60% of the residues. Two β-turns and three disulfide bonds add further restrictions to the conformational freedom of the monomer.<ref>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2049026/</ref> |
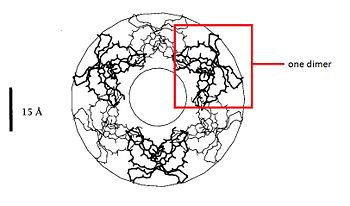
=== Dimere structure === | === Dimere structure === | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
== Example == | == Example == | ||
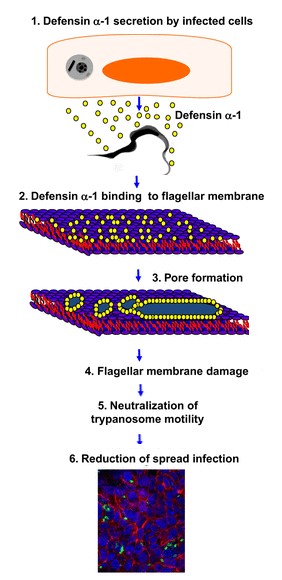
| - | DEF are known to play a role in the in the initiation of innate immune responses to some microbial pathogens. They are antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity functioning by non-specific binding to anionic phospholipids in bacterial membranes. For example defensins-α-1 have a role against the bacteria ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. | + | DEF are known to play a role in the in the initiation of innate immune responses to some microbial pathogens. They are antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity functioning by non-specific binding to anionic phospholipids in bacterial membranes. For example defensins-α-1 have a role against the bacteria ''Trypanosoma cruzi''.<ref>http://iai.asm.org/content/81/11/4139.full/ref</ref><br /> |
| + | ''Trypanosoma cruzy'' or ''Cruzy'' debilitats Chagas disease, which affects millions of people and products significant morbidity and mortality. The defensine-α-1 are secreted by the HCT116 cells (which are Paneth cells), when they are infect by ''Cruzy''. They reduces the infection making damage of the flagella structure. This damage inhibit parasite motility and reduce cellular infection. This reaction is introduce in the following drawing. | ||
{| align=center | {| align=center | ||
| Line 78: | Line 79: | ||
| - | <scene name='60/604478/Arg/1'>résidus arginine</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='60/604478/Hydrophobe-charge/1'>hydrophobes-chargés</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='60/604478/Hydrophobe/1'>hydrophobes</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='60/604478/Positifs/1'>positifs</scene> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 4 January 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Defensins-α-1
Introduction
Defensins (DEF) are a family of proteins which are involved in host defense in the epithelia of mucosal surfaces such as those of the intestin, respiratory tract, urinary tract, and vagina. They are antimicrobial and cytotoxic. All the protein of the family are distinguished by a cystein motif and are encoded on the chromozome 8.[1]
There are many defensin but in this article we'll focus on the defensin-α-1. It is a polypeptide which is found in the microbicidal granules of neutrophils. It's syntetisize in the neutrophils, which plays a role in the defense process. defensin-α-1 plays a particular role in phagocite-mediated host defense.[2]
| |||||||||||