This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 970
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
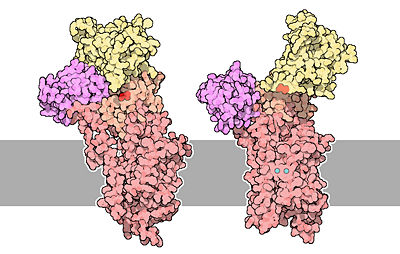
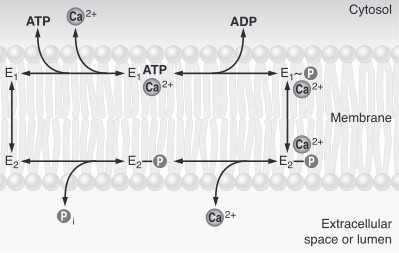
| - | To sum up, calcium pumps have two conformations, E1 and E2. These two conformations are characterized by different specificity for ion binding. When the pump is in the | + | To sum up, calcium pumps have two conformations, E1 and E2. These two conformations are characterized by different specificity for ion binding. When the pump is in the E1 state, it has high calcium affinity and interacts with calcium at one side of the membrane. In the E2 state, the enzyme has a lower calcium affinity and that leads to the release of the ion at the opposite side. E1 has the calcium binding site oriented toward the cytoplasm. E2 has the calcium binding site oriented toward the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum or toward the extracellular background<ref name="third">Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - ''Membrane, structure and function'' - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136</ref>. The phosphorylated intermediate, E1 can phosphorylate ADP, whereas E2 can only react with water<ref>David H.MacLennan, William J.Rice and N. Michael Green, 1997 - ''The Mechanism of Ca2+ Transport by Sarco(Endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPases'' - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.272, 28815-28818, http://www.jbc.org/content/272/46/28815.full.html</ref>. |
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Calcium is a very important molecule for cell signalling. Eucaryotic cells need to maintain a very low calcium concentration in their cytosol. The extracellular calcium concentration is much higher. That difference of concentrations across the membrane creates a gradient of concentration and allows the signalling to be very effective. Indeed, even a very small influx of calcium significantly increases the concentration of calcium inside the cell. Therefore, calcium pumps are very important to maintain the calcium concentration gradient and to remove calcium from the cell after signalling. | Calcium is a very important molecule for cell signalling. Eucaryotic cells need to maintain a very low calcium concentration in their cytosol. The extracellular calcium concentration is much higher. That difference of concentrations across the membrane creates a gradient of concentration and allows the signalling to be very effective. Indeed, even a very small influx of calcium significantly increases the concentration of calcium inside the cell. Therefore, calcium pumps are very important to maintain the calcium concentration gradient and to remove calcium from the cell after signalling. | ||
| - | Calcium is involved in many physiological processes such as programmed cell death, fertilization, gene transcription, secretion (including neurotransmitter secretion) etc. For example, the SERCA pump is mainly found in skeletal muscle cells and cardiac cells. It is involved in the relaxation of skeletal muscle cells. Those cells contain a special endoplasmic reticulum called the sarcoplasmic reticulum which is the place of calcium storage. After contraction, calcium ions are transported from the cytoplasm into the sarcoplasmic reticulum through the SERCA pump. This causes the relaxation of the muscle cells because the cytosolic concentration of calcium decreases. The SERCA pump works together with the PMCA pump to export calcium ions from the cytosol and to set the resting level of the cytosolic calcium concentration<ref name="first">Benjamin Lewin, 2007 - Cells - Jones & Bartlett Learning</ref>. | + | Calcium is involved in many physiological processes such as programmed cell death, fertilization, gene transcription, secretion (including neurotransmitter secretion) etc. For example, the SERCA pump is mainly found in skeletal muscle cells and cardiac cells. It is involved in the relaxation of skeletal muscle cells. Those cells contain a special endoplasmic reticulum called the sarcoplasmic reticulum which is the place of calcium storage. After contraction, calcium ions are transported from the cytoplasm into the sarcoplasmic reticulum through the SERCA pump. This causes the relaxation of the muscle cells because the cytosolic concentration of calcium decreases. The SERCA pump works together with the PMCA pump to export calcium ions from the cytosol and to set the resting level of the cytosolic calcium concentration<ref name="first">Benjamin Lewin, 2007 - Cells - Jones & Bartlett Learning</ref>. |
| + | In the absence of calcium, calcium pump are mainly in E1 state. | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 7 January 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Benjamin Lewin, 2007 - Cells - Jones & Bartlett Learning
- ↑ Marisa Brini , Ernesto Carafoli, 2009 - Calcium pumps in health and disease - Physiological Reviews
- ↑ Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - Membrane, structure and function - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136
- ↑ David H.MacLennan, William J.Rice and N. Michael Green, 1997 - The Mechanism of Ca2+ Transport by Sarco(Endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPases - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.272, 28815-28818, http://www.jbc.org/content/272/46/28815.full.html
- ↑ Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.
- ↑ Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full