Introduction
All living organisms depend on P-type ATPase to pump cations across membranes. P-type ATPases are distinct from other ATPases because there is an autophosphorylation step in their catalytic cycle. They play a fundamental role in organisms metabolism and physiology. Ca2+ ATPase is one type of P-type ATPases which transports calcium ions across membranes against a concentration gradient. These pumps clear the cytoplasm of the calcium, which is a second messenger. It's very important to keep a low concentration of calcium in the cell for a good cell signaling. The hydrolysis of ATP is necessary for the pump's functioning. For each ATP hydrolyzed, it transfers two calcium ions through the membrane, and two or three hydrogen ions in the opposite direction.
Structural Highlights
The calcium ATPase is a protein composed of 994 aminoacids.
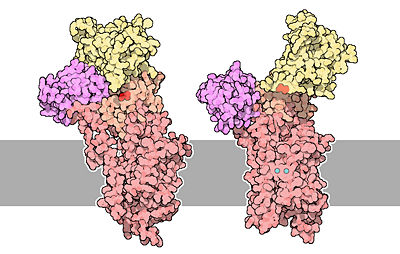
The of the protein is composed of helical regions (47%), beta sheet regions (16%) and loops. There are , and three of them line a channel that spans the lipid bilayer and that allows calcium to pass through membranes. It also contains too cytoplasmic loops between the transmembrane helices. When the protein is not phosphorylated, two of the transmembrane helices are disrupted and form a cavity that can bind two molecules of calcium.
The protein is divided in . The of the protein contains the channel that span the lipid bilayer, and the calcium binding cavity.
The two cytoplasmic loops form three separate domains. The contains the site where ATP binds to the protein. The contains an Aspartate residue () that can be phosphorylated. Finally, the is involved in the transmission of major conformational changes. The phosphorylation and the nucleotide binding domains form the of the protein[1].
Mechanism of action
The architecture of calcium ATPase (determined by X-Ray crystallography) allows to understand mechanisms by which the energy of ATP is coupled to the calcium transport across a membrane.
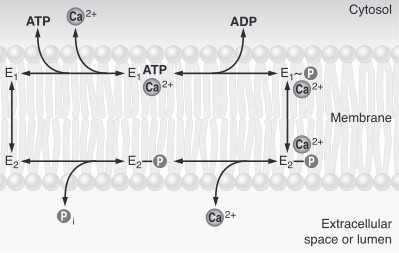
The first step of the calcium pump catalytic cycle is the cooperative binding of in the calcium binding cavity. Then, ATP binds to the ATP binding site (nucleotide binding domain) and transfers its γ-phosphate to the (phosphorylation domain). That creates a acid-stable aspartyl phosphate intermediate. The phosphorylation of Asp351 allows a large conformational changes in cytoplasmic domains: the nucleotide binding domain and the phosphorylation domain are brought into close proximity. This rearrangement causes a 90° rotation of the actuator domain, which leads to a rearrangement of the transmembrane helices. This rearrangement alters the affinity of the protein for the calcium and disrupts the calcium binding cavity. Calcium is released in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi Apparatus or outside the cell. After releasing calcium, two or three protons bind to the transport sites (charges compensation) and the aspartyl phosphate is hydrolyzed to complete the cycle. [2]
The structure on the left is the empty state (free from calcium). Two calcium ions are show in blue and Asp351 is show in red.[3]
To sum up, calcium pumps have two conformations, E1 and E2. These two conformations are characterized by different specificity for ion binding. When the pump is in the E1 state, it has high calcium affinity and interacts with calcium at one side of the membrane. In the E2 state, the enzyme has a lower calcium affinity and that leads to the release of the ion at the opposite side. E1 has the calcium binding site oriented toward the cytoplasm. E2 has the calcium binding site oriented toward the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum or toward the extracellular background[4]. The phosphorylated intermediate, E1 can phosphorylate ADP, whereas E2 can only react with water[5]. In the absence of calcium, calcium pumps are mainly in E1 state.
[2]
Biological Function and Localisation
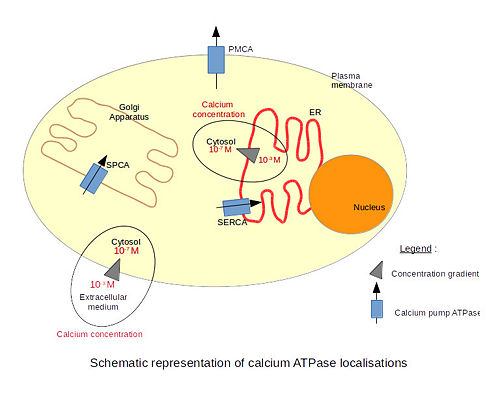
There are 3 types of calcium ATPase depending on their localization. The SERCA (Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase) is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum membranes, including the nuclear envelope. Only the structure of the SERCA has been resolved by x-ray crystallography. The PMCA (Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase) is localized in plasma membranes. The SPCA (Secretory Pathway Calcium ATPase) is localized in the Golgi apparatus membranes. The particularity of this pump is that it is also able to transport Mn2+ ions.
Calcium is a very important molecule for cell signalling. Eucaryotic cells need to maintain a very low calcium concentration in their cytosol. The extracellular calcium concentration is much higher. That difference of concentrations across the membrane creates a gradient of concentration and allows the signalling to be very effective. Indeed, even a very small influx of calcium significantly increases the concentration of calcium inside the cell. Therefore, calcium pumps are very important to maintain the calcium concentration gradient and to remove calcium from the cell after signalling.
Calcium is involved in many physiological processes such as programmed cell death, fertilization, gene transcription, secretion (including neurotransmitter secretion) etc. For example, the SERCA pump is mainly found in skeletal muscle cells and cardiac cells. It is involved in the relaxation of skeletal muscle cells. Those cells contain a special endoplasmic reticulum called the sarcoplasmic reticulum which is the place of calcium storage. After contraction, calcium ions are transported from the cytoplasm into the sarcoplasmic reticulum through the SERCA pump. This causes the relaxation of the muscle cells because the cytosolic concentration of calcium decreases. The SERCA pump works together with the PMCA pump to export calcium ions from the cytosol and to set the resting level of the cytosolic calcium concentration[1].
Regulations
There are different kind of calcium ATPase regulations. For example, the phospholamban (PLN or PLB) and the sarcolipin are membrane proteins that regulate the calcium pump in cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle cells. These two proteins are close homologous and play the same role. The phospholamban is a phosphoprotein that can be phosphorylated at three distinct sites by various protein kinases (PKA, PKC, CamK...). The phosphorylation state is mediated through beta-adrenergic stimulation. In unphosphorylate state, the phospholamban inhibits the activity of calcium pump in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells by decreasing the apparent affinity of the ATPase for calcium. The phosphorylation of the protein results in the dissociation of the protein from the ATPase. The phosphoprotein binds just downstream of the asp351 residue.
Most of the activation mechanisms implicate the C-terminal region of the pump containing the high affinity calmodulin binding domain, which is involved in the autoinhibition of the pump[6].
Another example of regulation. The plasma membrane calcium pump carboxy-terminal tail contains the calmodulin binding domain (regulatory domain) which acts as an auto-inhibitory domain. The binding of the calmodulin frees the pump from autoinhibition[7].
Dysfunctions and Diseases