This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 970
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
== Regulations == | == Regulations == | ||
| - | There are different | + | There are different kinds of calcium ATPase regulations. For example, the <scene name='60/604489/Phospholamban/2'>phospholamban</scene> (PLN or PLB) and the <scene name='60/604489/Sarcolipin/1'>sarcolipin</scene> are membrane proteins that regulate the calcium pump in cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle cells. These two proteins are close homologous and play the same role. The phospholamban is a phosphoprotein that can be phosphorylated at three distinct sites by various protein kinases (PKA, PKC, CamK...). The phosphorylation state is mediated through beta-adrenergic stimulation. In unphosphorylate state, the phospholamban inhibits the activity of calcium pump in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells by decreasing the apparent affinity of the ATPase for calcium. The phosphorylation of the protein results in the dissociation of the protein from the ATPase<ref>Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - ''Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction'' - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.</ref>. |
Another example of regulation. The plasma membrane calcium pump carboxy-terminal tail contains the calmodulin binding domain (regulatory domain) which acts as an auto-inhibitory domain. The binding of the calmodulin frees the pump from autoinhibition<ref>Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - ''The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium'' - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full</ref>. | Another example of regulation. The plasma membrane calcium pump carboxy-terminal tail contains the calmodulin binding domain (regulatory domain) which acts as an auto-inhibitory domain. The binding of the calmodulin frees the pump from autoinhibition<ref>Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - ''The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium'' - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 20:08, 9 January 2015
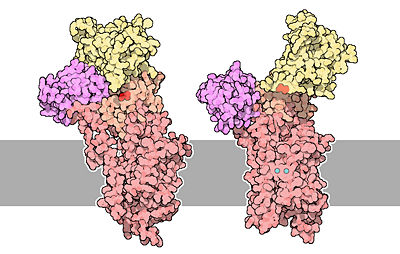
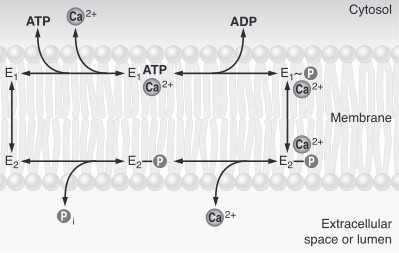
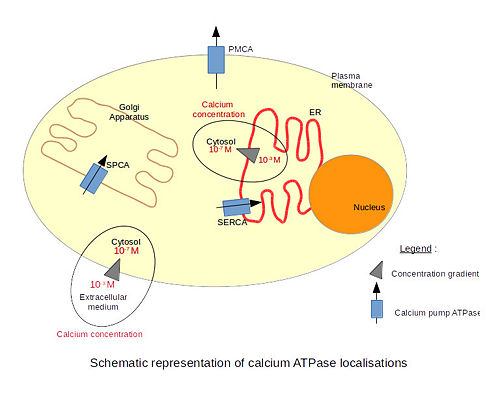
Calcium ATPase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Benjamin Lewin, 2007 - Cells - Jones & Bartlett Learning
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Marisa Brini , Ernesto Carafoli, 2009 - Calcium pumps in health and disease - Physiological Reviews
- ↑ David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3
- ↑ Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - Membrane, structure and function - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136
- ↑ David H.MacLennan, William J.Rice and N. Michael Green, 1997 - The Mechanism of Ca2+ Transport by Sarco(Endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPases - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.272, 28815-28818, http://www.jbc.org/content/272/46/28815.full.html
- ↑ Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.
- ↑ Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full
- ↑ Nyamkhishig Sambuughin, Elena Zvaritch, Natasha Kraeva, Olga Sizova, Erica Sivak, Kelley Dickson, Margaret Weglinski, John Capacchione, Sheila Muldoon, Sheila Riazi, Susan Hamilton, Barbara Brandom and David H. MacLennan, 2014 - Exome analysis identifies Brody myopathy in a family diagnosed with malignant hyperthermia susceptibility - Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine