We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 972
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Bradykinin== | ==Bradykinin== | ||
| - | + | <scene name='60/604491/Bradykinin/1'>Bradykinin</scene> is a short lived vasoactive nonapeptide mediator of the family of kinins. It's secreted in response to an inflammatory envent and serves as a mediator of pain, inflammation and vasodilatation. It is secreted by the enzymatic action of kallikreins on kininogen precursors (?). Kallidin is a produt of the enzymatic action of kallikrein to kininogens. Then Kallidin is transformed into bradykinin | |
| - | <scene name='60/604491/Bradykinin/1'>Bradykinin</scene> is a short lived vasoactive nonapeptide mediator of the family of kinins. It's secreted in response to an inflammatory envent and serves as a mediator of pain, inflammation and vasodilatation. | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Today, we know that kinins can be degraded by IDE. | Today, we know that kinins can be degraded by IDE. | ||
| - | |||
==Recognition and interactions between bradykinin and IDE== | ==Recognition and interactions between bradykinin and IDE== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 36: | ||
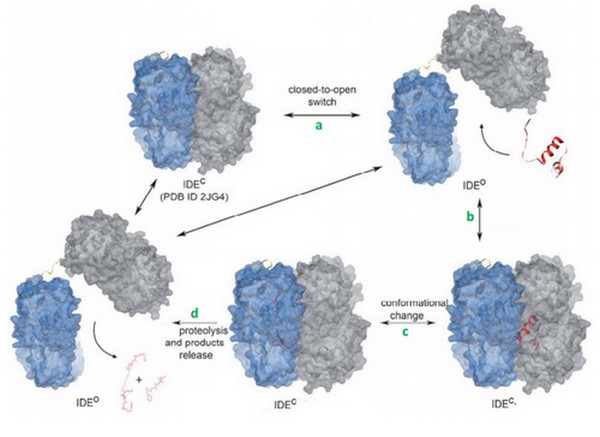
First, the lenght of the substrate peptide is essential. The peptide must be long enough to touch both the exosite and the catalytic site. Second, the peptide must be short enough in order to enter the catalytic chamber. In the case of the bradykinin, the length is too small to touch the catalytic site when it binds the exosite. | First, the lenght of the substrate peptide is essential. The peptide must be long enough to touch both the exosite and the catalytic site. Second, the peptide must be short enough in order to enter the catalytic chamber. In the case of the bradykinin, the length is too small to touch the catalytic site when it binds the exosite. | ||
Tang et al have shown that bradykinin is too small to bind both at the exosite and the catalytic side. They prooved that IDE binds 2 bradykinin at the same time : the first one interacts with the exosite and the second one touches the catalytic site. The bradykinin in the catalytic site is the one which is going to be cleaved by the enzyme. | Tang et al have shown that bradykinin is too small to bind both at the exosite and the catalytic side. They prooved that IDE binds 2 bradykinin at the same time : the first one interacts with the exosite and the second one touches the catalytic site. The bradykinin in the catalytic site is the one which is going to be cleaved by the enzyme. | ||
| - | This can be a discriminate factor, because IDE binds 2 | + | This can be a discriminate factor, because IDE binds <scene name='60/604491/Bradykinin/1'>2 bradykinins</scene> at the same time. |
IDE catalytic site has a high affinity for hydrophobic and basic. Bradykinin is essentially composed by proline and arginine, which are basic amino acids. So, bradykinin structure may explain this strange interaction. | IDE catalytic site has a high affinity for hydrophobic and basic. Bradykinin is essentially composed by proline and arginine, which are basic amino acids. So, bradykinin structure may explain this strange interaction. | ||
Revision as of 20:41, 9 January 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/11/2014, through 15/05/2015 for use in the course "Biomolecule" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the Strasbourg University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 951 through Sandbox Reserved 975. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644