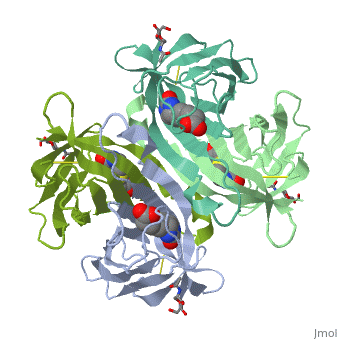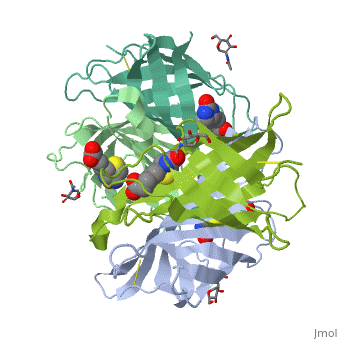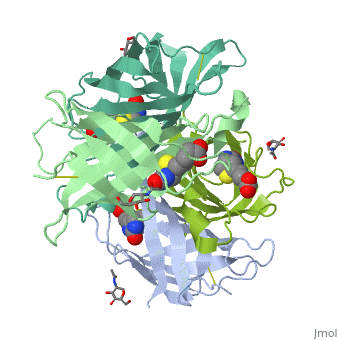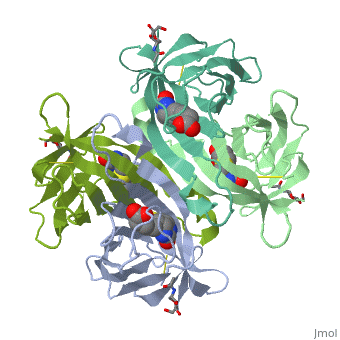User:Noam Gonen/Avidin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== INTRODUCTION == | == INTRODUCTION == | ||
| - | Avidin is a tetrameric or dimeric[1] biotin-binding protein produced in the oviducts of birds, reptiles and amphibians and deposited in the whites of their eggs. | + | Avidin is a tetrameric or dimeric[1] biotin-binding protein produced in the oviducts of birds, reptiles and amphibians and deposited in the whites of their eggs. |
<StructureSection load='2avi' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2avi' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | == | + | == Structure == |
| - | + | The tetrameric protein contains four identical subunits (homotetramer), each of which can bind to biotin (Vitamin B7, vitamin H) with a high degree of affinity and specificity. The dissociation constant of avidin is measured to be KD ≈ 10−15 M, making it one of the strongest known non-covalent bonds.[2] | |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 15:28, 17 January 2015
INTRODUCTION
Avidin is a tetrameric or dimeric[1] biotin-binding protein produced in the oviducts of birds, reptiles and amphibians and deposited in the whites of their eggs.
| |||||||||||