A prion is an infectious particle, composed of abnormally folded protein, that causes progressive neurodegenerative disorders. Prion diseases, or transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), are a family of rare progressive neurodegenerative disorders that affect both human and animals.
The prion protein has two forms: normal and damaged form. The normal protein is called PRPc and the damaged form is called PRPsc. The normal prion is found in human and animal’s body, and it prevents neuronal dysfunction. All mammals appear to have prion protein genes. The protein in its misfolded form is the infectious agent. In contrast to all known infectious agents, the prion doesn't contain any nucleic acid.
The Discovery of Prions
1740s- Earliest written record of Scarpie in UK.
1950s- High levels of Kuru appear among the people on New Guinea.
1960s- Scientists experimentally transmit Kuru and CJD to chimpanzees, demonstrating the transmissible nature of these diseases.
1980s- 60 people died from CJD after being infected during surgeries. 85 people died after receiving prion-infected growth hormone injections.
1982- Highly purified PRPsc has shown to be the infectious agent. Dr. Stanley Prusiner coined the term “prion”.
1985- Scientists identified the PRP gene.
Isoforms
The normal form of the protein is called PRPc, while the infectious form is called PRPsc.
There are conformational differences between PRPc and PRPsc:
The PRPc is soluble in detergents, sensitive to digestion by Protease anzymes, and contains prodominantly alpha helices. In contrast, the PRPsc is insoluble, has a resistance to proteolysis, and contains prodominantly beta pleated.
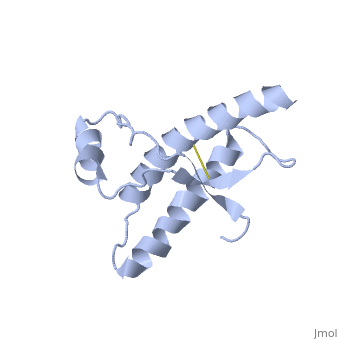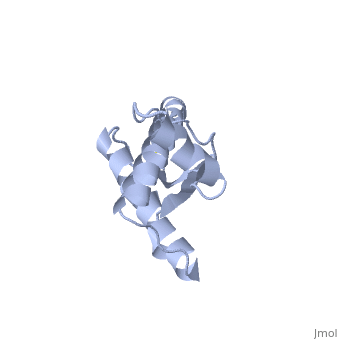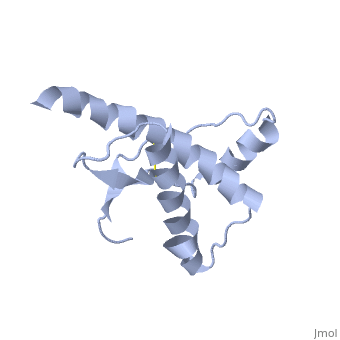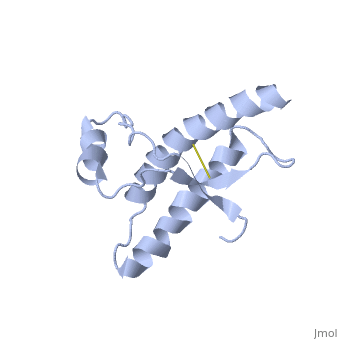
Structure
Structure of PRPc
Normal human Prion Protein, PRPc, contains 209 amino acids, and has a molecular weight of 35–36 kDa. The average life span of PRPc is approximately 5 hours.
It contains several domains: signal peptide (residues 1-23), N-terminal (residues 23-120), folded C-terminal (residues 121-231), and a single peptide for mambrane attachment via GPI anchor (residues 232-254) [1].
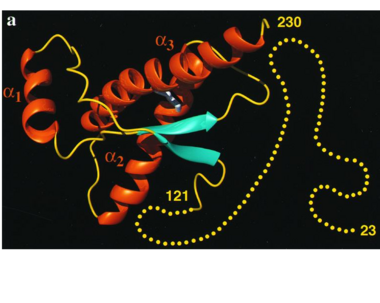
The NMR structure of the c-terminal domain, which was obtained from the recombinant PRPc, is being presented . it contains three (comprising the residues 144-154, 173-194, and 200-228), and a short anti-parallel comprising the residues 128-131, and 161-164. There is a , between , which connects helices 2 and 3. The N-terminal unstructured domain of PRPc contains an eight amino acid repetitive motif comprised of the residues PHGGGWGQ, which has a high affinity for copper ions [2].
Structure of PRPsc
The damaged form (PRPsc) is built from the same amino acids but takes a different shape, and contains mainly beta sheets. Little is known about the molecular details of this isoform, however it is wildly accepted that during the conversion of PRPc to PRPsc the β-strand content increases substantially, and this altered structure is insoluble, extremely stable, and has a resistance to denaturation by chemical and physical agents. All these features cause accumulations in infected tissues and therefore tissue damage and cell death.
During the formation of amyloids from recombinant PRPc in vitro, a2 and a3 helices have been shown to undergo a vest structural rearrangement into a , which is characteristic for amyloid.
The a2 and a3 helices of the PRPc are beeing converted into two discontinuous segments, that are covalently linked by a disulfide bond between . Then, specific hydrogen bonding interactions between exposed beta strends facilities the formation of a large molecular weight aggregates.
Recent evidence suggests a similar conformational change in this region of the protein upon conversion to the PrPsc isoform. The assembly of these fragments into the hexamer is driven by the maximization of hydrogen bonding and burial of hydrophobic sidechains.[3]
Mutations
Mutations in the Prion Protein Gene (PRPN) are known to encourage the spontaneous generation of the damaged form- PRPsc.
The NMR structure of the recombinant human PRP from residue 90 to 237 carrying the Q212P, is being presented . The mutations is caused as a result of glutamine-prolin . This amino acid residue is located in the middle of a3 in close proximity to the disulfide bond. This mutation is believed to cause GSS syndrom (a familial prion disease). There are two main differences between and the WT structure. First of all, there are four alpha helices (insted of three), as a result of a small rotation in a3 derive from interruption by Glu221 and Ser222. The break into 2 different helices results in dramatic changes in . As Tyr225 is unable to contact with Met166, hydrophobic cluster is opened and accesible to solvent and to hypothetical facilitator of prion convertion. The other remarkable difference is the shape of b2-a2 loop region, as a result of the changes in the hydrophobic interactions. [4]
Function
The cellular normal prion is found in verious tissues and cell types, but it most highly found in central nervous system [5]. the PRPc is expressed on the membranes of cells, and it prevents neuronal dysfunction, by using its anti-oxidant activity, and its ability to bind with copper. The PRPc has also been reported to play an important role in cell-cell adhesion, and may therefore be involved in cell-cell communication in the brain.
The misfolded prion causes the prion diseases- a group of progressive, neurodegenerative disorders [6].
PRPsc Mechanism
When the damaged prion (PRPsc) enters into a healthy tissue, it induces the normal prion to convert into the infectious form, in a process that isn't completely understood. This triggers a chain reaction that produces high amounts of infectious prions. The mostly accepted model which try to explain the prion replication mechanism assumes that PRPsc acts as template to promote and catalyze the conversion of PRPc into PRPsc. The insolubility of PRPsc makes this process irreversible. The two PRPsc then come apart and catalyze the conversion of another normal prions.
Diseases
The damaged prions cause neurodegenerative diseases by aggregating to form plaques known as amyloid. Brain consists of hundred billions of neurons, supporting neural tissue. When enough PRPsc have been made, they form aggregates that gradually damage neural tissue. When neuron in the brain are all dead, the appearance of the brain will become sponge-like, which eventually cause to death. All known prion diseases are untreatable and fatal. Many different mammals can be affected by prion diseases. The most common prion diseases in animals are Mad Cow Disease (cows) and Scarpie (goats and sheep). In human, prion causes Creutzfeldt- Jakob disease, Kuru, Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome (GSS), and more.
Creutzfeldt- Jakob disease (CJD)
CJD is a rapidly progressive, degenerative brain disorder, that leads to dementia and death. Symptoms of CJD sometimes resemble those of other dementia-like brain disorders. CJD occurs worldwide. Annual incidence rate of CJD is approximately equal to one per million. The CJD disease is more common in individuals above 60 years. Average life span after onset of symptoms is 4 months. There is no record of anyone recovering from the disease and there is no known treatment. CJD disease can arise in several different ways:
Genetic- This condition can be inherited. in this case it can also be called familial CJD.
Sporadic- Sporadic CJD develops suddenly without any known risk factors, because of a spontaneous mutation in the Prion Protein Gene (PRNP). These mutations may lead to changes in the secondary and teritary structure of the PRPc, and could result in the appearance of PRPsc confomers (viruses 2014). Most cases of CJD are sporadic and tend to strike people around age 60.
Acquired- The Variant CJD is an infectious type of the disease that is related to “mad cow disease”. Eating infectious meat may cause the disease in humans. The meat may cause normal human prion protein to develop abnormally. The disease is also thought to have been spread to people receiving transplants from infected donors and from contaminated medical equipment. This type of the disease usually affects younger people.
Scarpie
Scarpie is a fatal, degenerative disease that affects the nervous systems of sheep and goats. Scarpie has been known since the 18th century (1732). The disease causes intense itching which makes the sheep to scrape off their wool.
Kuru
Kuru is an incurable degenerative neurological disorder, endemic to tribal regions of Papua New Guinea. It's caused by eating human brain tissue contaminated with infectious prions. Because of increased awareness about the disease and how it is transmitted, Kuru is now rare.
Mad Cow Disease
The other name of this disease is BSE (Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy). The BSE has been first noted in UK in early 1985. The cause of BSE may be from the contamination of sheep with scarpie that were processed in the same slaughterhouse. Infected sheep brains and other sheep byproducts infected with Scarpie was used to feed cattle with the meat and bone meal. BSE results when a sufficient number of nerve cells have become damaged, affecting the behavior of the cow and eventually the cow is dead.
Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome (GSS)
GSS is an extremely rare, usually familial, fatal neurodegenerative disease that affects patients from 20 to 60 years in age. This neurogenetic brain disorder is always inherited and is found in only a few families all over the world. The trait is an autosomal-dominant trait, caused by a gene mutation. [7]
References
- ↑ Zahn R et al. NMR solution structure of the human prion protein. 2000
- ↑ Acevedo-Morantes CY et al. The structure of human prions: from biology to structural models-considerations and pitfalls. 2014
- ↑ Apostol MI et al. Crystal structure of a human prion protein fragment reveals a motif for oligomer formation. 2013
- ↑ Ilc G et al. NMR structure of the human prion protein with the pathological Q212P mutation reveals unique structural features. 2010
- ↑ Acevedo-Morantes CY et al. The structure of human prions: from biology to structural models-considerations and pitfalls. 2014
- ↑ Acevedo-Morantes CY et al. The structure of human prions: from biology to structural models-considerations and pitfalls. 2014
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gerstmann%E2%80%93Str%C3%A4ussler%E2%80%93Scheinker_syndrome