Mycobacterium tuberculosis ArfA Rv0899
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | The protein Rv0899 ArfA is restricted to pathogenic | + | The protein Rv0899 ArfA is restricted to pathogenic '''''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''''' [http://he.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis] associated with tuberculosis and, thus, is an attractive candidate for the development of anti-tuberculosis chemotherapeutic agents.The Rv0899 ArfA belongs to the OmpA (outer membrane protein A) family of outer membrane proteins and has been proposed to act as an outer membrane [[porin]]. The deletion of this gene impairs the uptake of some water-soluble substances, such as serine, glucose, and glycerol. |
==Peptidoglycan binding site== | ==Peptidoglycan binding site== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Structure Section== | ==Structure Section== | ||
| - | The 326-residue Rv0899 ArfA | + | The 326-residue Rv0899 ArfA contains three domains: an N-terminal domain (M domain) (residues 1-72) which includes a sequence of 20 hydrophobic amino acids required for membrane translocation. |
[[Image:N-ter domain.jpg|150px]] | [[Image:N-ter domain.jpg|150px]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR014004]. | [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR014004]. | ||
<scene name='61/612805/Surface/1'>The core is hydrophobic, while the exterior is polar and predominantly acidic</scene>. | <scene name='61/612805/Surface/1'>The core is hydrophobic, while the exterior is polar and predominantly acidic</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:180 rotation BON.jpg|150px]] | ||
| + | |||
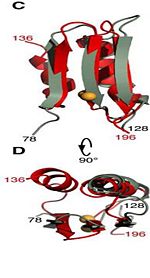
The C domain <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/1'>(residues 201-326)</scene> has homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins.The C domain of wild-type ArfA folds into four β-strands and four α-helices, arranged in the topological order αβαβαβαβ. <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/3'></scene> <scene name='61/612805/C_domain_1/1'> Three parallel (β1, β2, β3) and one antiparallel (β4) β-strands form a four-stranded β-sheet (β1–β4-β2–β3) that packs against three α-helices (α1, α2, α3), while a fourth helix (α4) extends from the N-terminus of β4. A disulfide bond </scene> between C208 and C250 connects the N-terminus of α1 to the C-terminus of α2 and stabilizes the structure. | The C domain <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/1'>(residues 201-326)</scene> has homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins.The C domain of wild-type ArfA folds into four β-strands and four α-helices, arranged in the topological order αβαβαβαβ. <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/3'></scene> <scene name='61/612805/C_domain_1/1'> Three parallel (β1, β2, β3) and one antiparallel (β4) β-strands form a four-stranded β-sheet (β1–β4-β2–β3) that packs against three α-helices (α1, α2, α3), while a fourth helix (α4) extends from the N-terminus of β4. A disulfide bond </scene> between C208 and C250 connects the N-terminus of α1 to the C-terminus of α2 and stabilizes the structure. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 55: | ||
[[Image:Rv0899 memb arch.jpg|150px]] | [[Image:Rv0899 memb arch.jpg|150px]] | ||
| - | [[Image:180 rotation BON.jpg|150px]] | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 21 January 2015
| |||||||||||