This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis ArfA Rv0899
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
1. Acquisition of Zn(2+) ions by {{Template:ColorKey Composition Ligand}} <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>L82, D96, F97, H125, D127 and V129</scene> <ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref>. | 1. Acquisition of Zn(2+) ions by {{Template:ColorKey Composition Ligand}} <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>L82, D96, F97, H125, D127 and V129</scene> <ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref>. | ||
| - | 2. Bacterium's adaptation to the acidic environment of the phagosome during infection | + | 2. Bacterium's adaptation to the acidic environment of the phagosome during infection by: |
| - | + | a)deamidation of the amino acid pair <scene name='61/612805/Asn111_and_gly112/1'> Asn111-Gly112 </scene>, located at the end of α1 and preceding L3, a pH-dependent reaction whereby Asn is converted to Asp and ammonia is released. Asparagine residues preceding glycine, and situated in conformationally flexible regions of proteins, are frequently deamidated, with potentially significant consequences for protein regulation and function <ref>PMID: 20199110</ref> [[Image:Asparaginase-reaction.jpg|250px]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | It exhibits pH-dependent conformational dynamics 232, 225, 240, 244, 281, 285 <scene name='61/612805/D236_before_mutation/1'>in neutral pH (D236) </scene> and a more ordered structure at <scene name='61/612805/D236a_after_mut/3'>acidic pH (D236A) </scene>, which could be related to its acid stress response. | + | 3. It exhibits pH-dependent conformational dynamics 232, 225, 240, 244, 281, 285 <scene name='61/612805/D236_before_mutation/1'>in neutral pH (D236) </scene> and a more ordered structure at <scene name='61/612805/D236a_after_mut/3'>acidic pH (D236A) </scene>, which could be related to its acid stress response. |
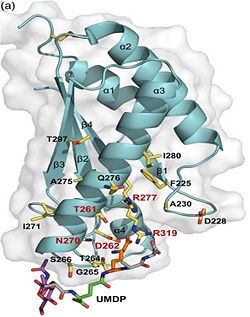
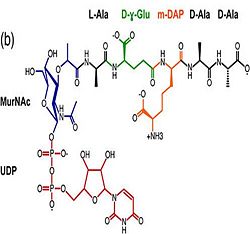
Its functions in acid stress protection and [peptidoglycan][http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peptidoglycan] binding site <scene name='61/612805/Peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>(R277, R319, T261, D262, N270)</scene> suggest a link between the acid stress response and the physicochemical properties of the mycobacterial cell wall. These residues are strictly conserved in the OmpA -like family <ref>PMID: 22206986 </ref>. | Its functions in acid stress protection and [peptidoglycan][http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peptidoglycan] binding site <scene name='61/612805/Peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>(R277, R319, T261, D262, N270)</scene> suggest a link between the acid stress response and the physicochemical properties of the mycobacterial cell wall. These residues are strictly conserved in the OmpA -like family <ref>PMID: 22206986 </ref>. | ||
Revision as of 22:16, 23 January 2015
| |||||||||||