Vitis vinifera Flavonoid 3-O-Glucosyltransferase (Vv3GT)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
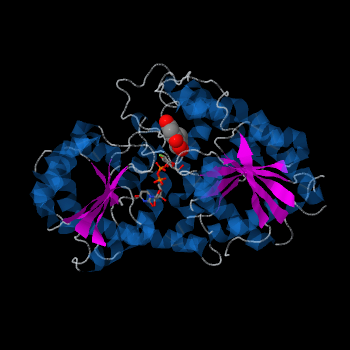
| - | Vv3GT is a GT-B enzyme. GT-B enzymes consists of two β/α/β Rossmann-like domains. The two domains are associated and face each other with the active-site lying between them. These domains are associated with the donor and acceptor substrate binding sites. | + | Plant glycosyltransferases assume one of two folds, GT-A or GT-B. Vv3GT is a GT-B enzyme. GT-B enzymes consists of two β/α/β Rossmann-like domains. The two domains are associated and face each other with the active-site lying between them. These domains are associated with the donor and acceptor substrate binding sites. |
| - | The <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_rainbow/1'>N-terminal and C-terminal domain</scene>, linked by a flexible loop and α-helix with a hinge region. The C-terminal domain is highly conserved and binds the | + | The <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_rainbow/1'>N-terminal and C-terminal domain</scene>, linked by a flexible loop and α-helix with a hinge region. The linker could be important for sugar donor binding. This linker region holds the UDP-sugar donor next to the C-terminal PSPG motif. The C-terminal domain is highly conserved and binds the UDP sugar donor (e. g. UDP-Glc). On the other hand, the N-terminal domain is not conserved it binds the substrate and provides catalytically active amino acids. |
{{Template:ColorKey_N52C3Rainbow}} | {{Template:ColorKey_N52C3Rainbow}} | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| - | The plant UGTs are characterized by sharing a highly conserved motif referred to as the | + | The plant UGTs are characterized by sharing a highly conserved 44 amino acid motif referred to as the |
| - | <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_pspg/1'>PSPG</scene> motif (Plant Secondary Product Glycosyltransferase motif). | + | <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_pspg/1'>PSPG</scene> motif (Plant Secondary Product Glycosyltransferase motif). Amino acids of the PSPG motif provide most of the interactions with the sugar donor molecule. |
Three conserved motifs involved in sugar binding are present in Vv3GT. The first, a <scene name='60/607848/2c1z_loop_n5_label/1'>loopN5</scene> motif (Thr 141; Ala 142) involved in sugar binding. The second, a <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_wns_label/1'>WNS</scene> (Trp 354; Asn 355; Ser 356) motif residues are involved in binding UDP phosphates. The third, <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_d_eq_label/1'>D/EQ</scene> motif residues also involved in sugar binding (Asp 374; Gln 375). The WNS and D/EQ motifs are part of the highly conserved PSPG region. | Three conserved motifs involved in sugar binding are present in Vv3GT. The first, a <scene name='60/607848/2c1z_loop_n5_label/1'>loopN5</scene> motif (Thr 141; Ala 142) involved in sugar binding. The second, a <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_wns_label/1'>WNS</scene> (Trp 354; Asn 355; Ser 356) motif residues are involved in binding UDP phosphates. The third, <scene name='69/692252/2c1z_d_eq_label/1'>D/EQ</scene> motif residues also involved in sugar binding (Asp 374; Gln 375). The WNS and D/EQ motifs are part of the highly conserved PSPG region. | ||
Revision as of 08:21, 25 January 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Offen W, Martinez-Fleites C, Yang M, Kiat-Lim E, Davis BG, Tarling CA, Ford CM, Bowles DJ, Davies GJ. Structure of a flavonoid glucosyltransferase reveals the basis for plant natural product modification. EMBO J. 2006 Mar 22;25(6):1396-405. Epub 2006 Feb 16. PMID:16482224