This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Ubc9
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
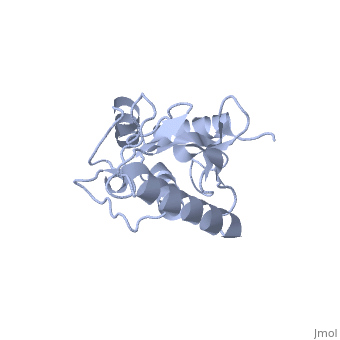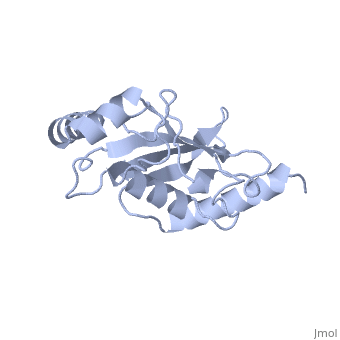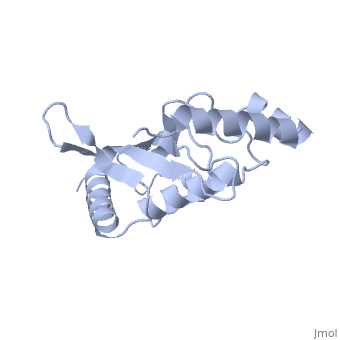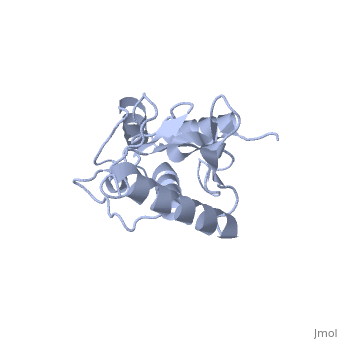
| - | Murine/human ''Ubc9'' exhibits a single domain structure consisting of both alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets (PDB: 1U9A). <scene name='69/694804/Cys93/6'>Cys93</scene> has been identified as the active residue and is located on a loop of amino acids (78-108) between beta sheet four and alpha helix two <ref name="crystal"/>. Crystal structure of the <scene name='69/694804/Noncovalent_ubc9_sumo1/1'>noncovalent interaction between | + | Murine/human ''Ubc9'' exhibits a single domain structure consisting of both alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets (PDB: 1U9A). <scene name='69/694804/Cys93/6'>Cys93</scene> has been identified as the active residue and is located on a loop of amino acids (78-108) between beta sheet four and alpha helix two <ref name="crystal"/>. Crystal structure of the <scene name='69/694804/Noncovalent_ubc9_sumo1/1'>noncovalent interaction between Ubc9 and SUMO1</scene> have shown that the Ubc9 residues involved in this interaction are located at the end of helix one, on beta strand one, and along the following loop. These residues were shown to interact with the beta sheet of SUMO1 <ref name="ubcsumocomplex">PMID:17491593</ref>. |
Revision as of 02:22, 25 February 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tong H, Hateboer G, Perrakis A, Bernards R, Sixma TK. Crystal structure of murine/human Ubc9 provides insight into the variability of the ubiquitin-conjugating system. J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 22;272(34):21381-7. PMID:9261152
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Knipscheer P, van Dijk WJ, Olsen JV, Mann M, Sixma TK. Noncovalent interaction between Ubc9 and SUMO promotes SUMO chain formation. EMBO J. 2007 Jun 6;26(11):2797-807. Epub 2007 May 10. PMID:17491593