We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1066
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase == | == ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase == | ||
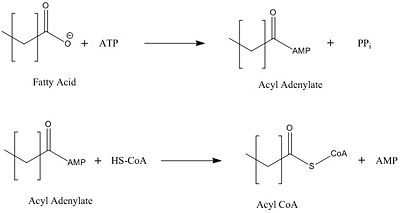
| - | ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase, also known as FadD13, is unique within its class in regards to its ability to house lipid substrates longer than itself. Most FadD class proteins exist as integral membrane proteins involved in lipid transport into the cell. FadD13 is unique structurally in that it exists as a peripheral protein on the inside of the cell membrane. This feature is key in the mechanistic basis for FadD13's transport of fatty acids of length C24-C26. | + | ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase, also known as FadD13, is unique within its class in regards to its ability to house lipid substrates longer than itself. Most FadD class proteins exist as integral membrane proteins involved in lipid transport into the cell. FadD13 is unique structurally in that it exists as a peripheral protein on the inside of the cell membrane. This feature is key in the mechanistic basis for FadD13's transport of fatty acids of length C24-C26.<ref name="Our Paper">PMID: 22560731</ref> |
FadD13 may be important in the virulence of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tuberculosis tuberculosis] and has emerged as possible target for therapeutic agents. | FadD13 may be important in the virulence of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tuberculosis tuberculosis] and has emerged as possible target for therapeutic agents. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
This is the <scene name='69/698726/Overall_structure_cartoon/1'>overall structure of FadD13</scene> | This is the <scene name='69/698726/Overall_structure_cartoon/1'>overall structure of FadD13</scene> | ||
| - | FadD13 is composed of 503 amino acid residues divided into three main regions: The <scene name='69/694233/Domains/1'>N-terminal domain</scene> (residues 1-395) and <scene name='69/694233/C-terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> (residues 402-503) which are connected via a flexible linker (residues 396-401). | + | FadD13 is composed of 503 amino acid residues divided into three main regions: The <scene name='69/694233/Domains/1'>N-terminal domain</scene> (residues 1-395) and <scene name='69/694233/C-terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> (residues 402-503) which are connected via a flexible linker (residues 396-401).<ref name="OUR PAPER"/> |
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
== Hydrophobic Tunnel == | == Hydrophobic Tunnel == | ||
| - | The hydrophobic tunnel of FadD13 is essential to the transport and accommodation of very long fatty acids from the membrane into the cell. This | + | The hydrophobic tunnel of FadD13 is essential to the transport and accommodation of very long fatty acids from the membrane into the cell. This tunnel runs through the middle of FadD13 from the arginine rich lid loop to the ATP binding site and is situated between the and alpha helices α8-α9 and parallel beta sheet β9- β14.<ref name="OUR PAPER"/> |
== Active Site == | == Active Site == | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 3 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Andersson CS, Lundgren CA, Magnusdottir A, Ge C, Wieslander A, Molina DM, Hogbom M. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: Structural Basis for Housing Lipid Substrates Longer than the Enzyme. Structure. 2012 May 2. PMID:22560731 doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.03.012
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedOUR_PAPER
Similar Proteopedia Pages
Thioesterase Do we have anything like this?
External Resources
Tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Acyl-CoA Wikipedia page
Mycolic Acid Wikipedia page