Sandbox Reserved 1074
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==='''Substrate Binding Loop Flexibility''' === | ==='''Substrate Binding Loop Flexibility''' === | ||
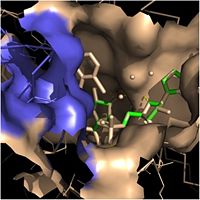
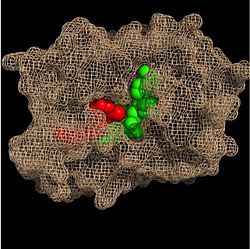
| - | In addition to the hydrogen bonding that occurs between the NADH and fatty acyl substrate within the crevice, each of these molecules is also held in place within the crevice through interactions with the side chains of surrounding <scene name='69/694241/Sbl_hydrophobic/1'>hydrophobic</scene> (purple) residues. The majority of these <scene name='69/694241/Hydrophobic_residues/1'>hydrophobic</scene> residues anchoring the substrates are found within the substrate binding loop itself, including Ala-198, Met-199, Ala-201, Ile-202, Leu-207, Ile-215, and Leu-218. Additional hydrophobic amino acids that are not a part of the substrate binding loop also play a role in positioning and stabilizing the fatty acyl chain in the crevice. Studies have found that the fatty acyl substrate adopts a u-shaped conformation to facilitate binding. As the fatty acyl substrate binds in the crevice, the substrate binding loop shifts outward toward the solvent, and the [[Tyr-158 #'''Importance of Tyr-158''']] residue is rotated to facilitate the binding of fatty acyl chains of 16 carbons or greater. During this conformational change upon substrate binding, no hydrogen bonds are broken, which supports the flexibility of the substrate binding loop. It is likely that this flexibility of the substrate binding loop provides increased freedom for the active site to accept fatty acyl substrates of varying carbon chain lengths <ref name="InhA" />. | + | In addition to the hydrogen bonding that occurs between the NADH and fatty acyl substrate within the crevice, each of these molecules is also held in place within the crevice through interactions with the side chains of surrounding <scene name='69/694241/Sbl_hydrophobic/1'>hydrophobic</scene> (purple) residues. The majority of these <scene name='69/694241/Hydrophobic_residues/1'>hydrophobic</scene> residues anchoring the substrates are found within the substrate binding loop itself, including Ala-198, Met-199, Ala-201, Ile-202, Leu-207, Ile-215, and Leu-218. Additional hydrophobic amino acids that are not a part of the substrate binding loop also play a role in positioning and stabilizing the fatty acyl chain in the crevice. Studies have found that the fatty acyl substrate adopts a u-shaped conformation to facilitate binding. As the fatty acyl substrate binds in the crevice, the substrate binding loop shifts outward toward the solvent, and the [[Tyr-158 #==='''Importance of Tyr-158'''===]] residue is rotated to facilitate the binding of fatty acyl chains of 16 carbons or greater. During this conformational change upon substrate binding, no hydrogen bonds are broken, which supports the flexibility of the substrate binding loop. It is likely that this flexibility of the substrate binding loop provides increased freedom for the active site to accept fatty acyl substrates of varying carbon chain lengths <ref name="InhA" />. |
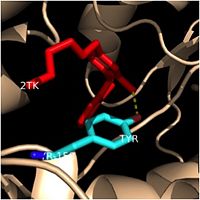
==='''Importance of Tyr-158'''=== | ==='''Importance of Tyr-158'''=== | ||
Revision as of 22:40, 8 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Enoyl-ACP Reductase InhA from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Rozwarski, D.A. (1999). Crystal Structure of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Enoyl-ACP Reductase, InhA, in Complex with NAD+ and a C16 Fatty Acyl Substrate. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274(22), 15582-15589. PMID: 10336454 DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.22.15582
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Bell, A.F. (2007). Evidence from Raman Spectroscopy That InhA , the Mycobacterial Enoyl Reductase, Modulates the Conformation of the NADH Cofactor to Promote Catalysis. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 129, 6425-6431. DOI: 10.1021/ja068219m