We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1066
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== General mechanism for the activation of fatty acids == | == General mechanism for the activation of fatty acids == | ||
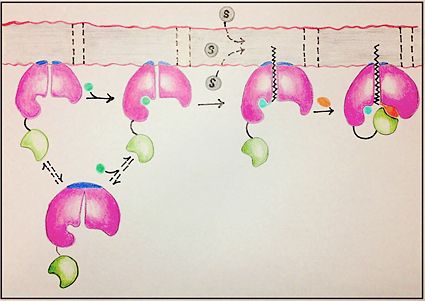
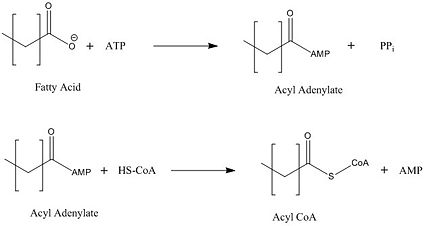
| - | FadD13 represents the first Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase of its kind to display biphasic kinetics.<ref name="residue paper"/> FadD13 first activates the fatty acid through a reaction with ATP to form an acyl adenylate intermediate and release pyrophosphate. Following a conformational change of the enzyme, coenzyme A is able to bind and reaction with the acyl adenylate intermediate forming the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl-CoA acyl CoA] product (Figure 2). | + | FadD13 represents the first Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase of its kind to display biphasic kinetics.<ref name="residue paper"/> FadD13 first activates the fatty acid through a reaction with ATP to form an acyl adenylate intermediate and release pyrophosphate. Following a conformational change of the enzyme, coenzyme A is able to bind and reaction with the acyl adenylate intermediate forming the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl-CoA acyl CoA] product (Figure 2). These activated fatty acyl-CoA thioesters have then been demonstrated to be important for the synthesis of triacyglycerols and phospholipids in the membrane of ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. <ref name="residue paper"/> |
Revision as of 01:46, 9 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Andersson CS, Lundgren CA, Magnusdottir A, Ge C, Wieslander A, Molina DM, Hogbom M. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: Structural Basis for Housing Lipid Substrates Longer than the Enzyme. Structure. 2012 May 2. PMID:22560731 doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.03.012
- ↑ Jatana N, Jangid S, Khare G, Tyagi AK, Latha N. Molecular modeling studies of Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (FadD13) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis--a potential target for the development of antitubercular drugs. J Mol Model. 2011 Feb;17(2):301-13. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3. Epub 2010 May, 8. PMID:20454815 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Khare G, Gupta V, Gupta RK, Gupta R, Bhat R, Tyagi AK. Dissecting the role of critical residues and substrate preference of a Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase (FadD13) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2009 Dec 21;4(12):e8387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008387. PMID:20027301 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008387
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Jatana N, Jangid S, Khare G, Tyagi AK, Latha N. Molecular modeling studies of Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (FadD13) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis--a potential target for the development of antitubercular drugs. J Mol Model. 2011 Feb;17(2):301-13. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3. Epub 2010 May, 8. PMID:20454815 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3
Similar Proteopedia Pages
Thioesterase Do we have anything like this?
External Resources
Tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Coenzyme A Wikipedia page
Acyl CoA Wikipedia Page
Mycolic Acid Wikipedia page