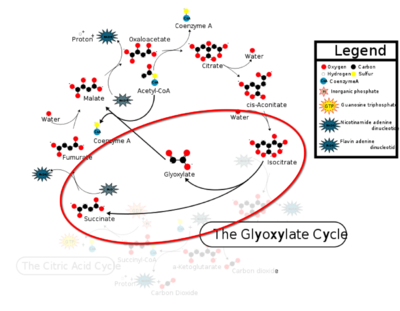
Figure 1: ICL mediated glyoxylate shunt pathway of the Citric Acid Cycle
Isocitrate Lyase (ICL) is a metabolic enzyme that converts the metabolite isocitrate into glyoxylate and succinate. ICL is a homotetramer with each monomer being composed of 14 alpha helices, 14 beta sheets, and a magnesium ion cofactor. ICL has shown clinical relevance in the disease state Tuberculosis where it is responsible for the persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis during the chronic stage of infection[1] This survival strategy mediated by ICL is characterized by a metabolic shortcut within the Citric Acid Cycle. ICL creates this shunt pathway by converting isocitrate to succinate and glyoxylate, diverting acetyl-CoA from the beta-oxidation of fatty acids[2][3].
Structure
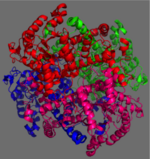
Figure 2: 222 Symmetry of the homotetramer isocitrate lyase
The ICL homotetramer possesses 222 symmetry, with an axis of rotation at x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis of the enzyme. Two individual subunits off ICL are held together by a characteristic between three alpha helices formed by residues 370-384, 349-367, and 399-409 on neighboring monomers[2]. The interlocking mechanism created by these helices provides additional strength to hold the two monomeric subunits together, allowing ICL to essentially be composed of two dimerized subunits[3]. This interaction will bury approximately 18% of the surface of each subunit, and will help to shield the interior binding site from hydration.
Active Site
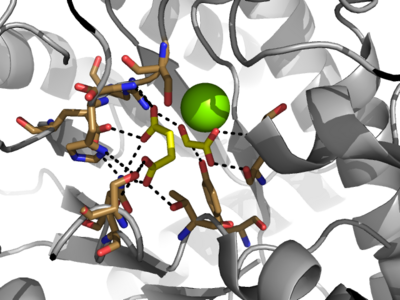
Figure 3: Highly ordered hydrogen bonding network within the active site of ICL
The of isocitrate lyase lies near the C-terminal ends of the Beta-strands of the active site[3]. The glyoxylate substrate is held into place by a network of hydrogen bonds with Ser 91, Gly 92, Trp 93, and Arg 228[2]. The magnesium ion serves to stabilize the partial negative charge placed on the carbonyl oxygens of the glyoxylate. The other substrate, succinate, contains two carboxyl groups and possesses a similar network of hydrogen bonding that holds the ligand in place within the active site. One carboxylate group is hydrogen bound to Asn 313, Glu 295, Arg 228, and Gly 192. The second carboxylate is hydrogen bound to Thr 347, Asn 313, Ser 315, Ser 317, and His 193[2]. The ordered hydrogen bonding within the active site orients the succinate molecule such that the alpha carbon is only 3.2 angstroms away from the deprotonated thiol group of Cys 191[2][4].
Catalytic Loop
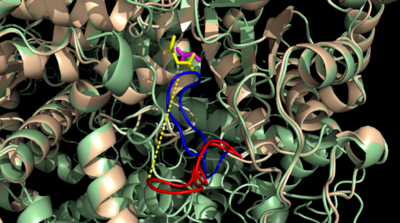
Figure 3: Highly ordered hydrogen bonding network within the active site of ICL
The of the Isocitrate Lyase enzyme is composed of residues 185-196, and can exist in both the open and closed conformation. In the open conformation, the catalytic loop is oriented such that the catalytic CYS191 residue is located far from the active site, allowing for solvent accessibility and substrate binding.[5] Upon substrate binding, the catalytic loop adopts a closed conformation, moving between ten and fifteen angstroms[2]. This closed conformation will cause the binding site to become inaccessible to the solvent. The loop closure is triggered by the movement of the Mg2+ ion that occurs upon binding of the succinate. This movement of the Mg2+ ion results in electrostatic interactions at LYS189, causing the loop to close.
Mechanism
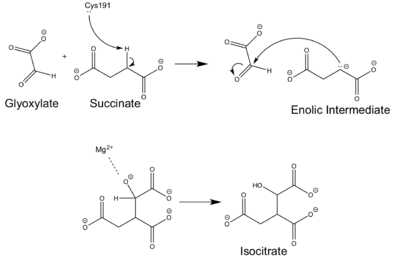
Figure 4: Chemical Mechanism of Isocitrate Lyase
Isocitrate lyase catalyzes a reversible aldol condensation, converting isocitrate to glyoxylate and succinate via the breaking of a C-C bond[4]. Within the active site of ICL the HIS193 residue deprotonates the CYS191 residue of the active site in order to increase its basicity[2][4]. The Cys 191 residue then deprotonates the alpha carbon adjacent to one of the carbonyl groups of succinate, thus forming the enolic intermediate[4]. The negatively charged alpha carbon atom of the enolic intermediate acts as a nucleophile that attacks the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde of glyoxylate. The nucleophilic attack will place a negative charge on the oxygen atom oxygen at the former carbonyl oxygen of the aldehyde, which will be stabilized by positive charges of the Mg2+ ion, ARG228 and HIS180[2]. The protonation of this species will yield the final product. It is important to note that this reaction is entirely reversible; the breakdown of isocitrate into glyoxylate and succinate occurs using a similar mechanism.
Elucidation of ICL Structure Using Inhibitors
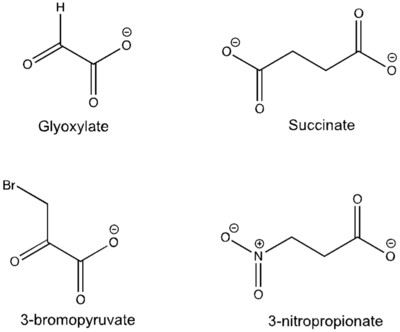
Figure 5: Substrate inhibitors of Isocitrate Lyase
The two inhibitors used to elucidate the structure of ICL were 3-nitropropionate and 3-bromopyruvate. The 3-nitropropionate was used to mimic the succinate, while the 3-bromopyruvate is used to mimic the glyoxylate. These two inhibitors have also been shown to be good inhibitors of isocitrate lyase in M. avium indicating that their inhibitory capacity is conserved across multiple species. A mutant isocitrate lyase C191S, in conjunction with the aforementioned substrate mimics, was used to elucidate the first high resolution crystal structure of ICL. Dehalogenated 3-nitropropionate works to inhibit isocitrate lyase by forming a covalent bond with the SER191 residue in the active site. This 3-nitropropionate occupies the same site that the succinate would occupy. The C191S mutant adopts a conformation almost identical to the CYS191 residue in the wild type indicating that this is an accurate depiction of the conformation.






