Sandbox Reserved 1068
From Proteopedia
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
==Molecular Mechanism== | ==Molecular Mechanism== | ||
| + | '''Magnesium cation effect''' | ||
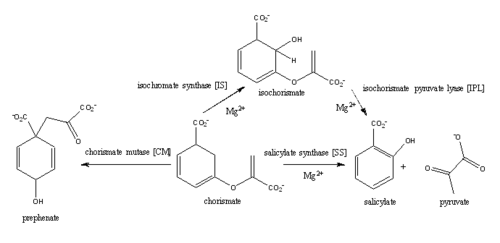
| + | The coordination shell of the magnesium cation in the active site of MbtI is composed of two water molecules, Glu434, Glu294, and the two oxygen atoms of the C1 carboxylate group of chorismate. | ||
'''Isochorismate pyruvae lyase (IPL)''' | '''Isochorismate pyruvae lyase (IPL)''' | ||
| - | For IPL activity, a proposed histidine residue (his334) acts as a base, abstracting the C2 proton of isochorismate through a second order elimination mechanism. The C9 atom of isochorismate is then protonated, leading to the elimination of pyruvate and formation of salicylate. At pH values below 7.5 the histidine residue is protonated and therefore | + | For IPL activity, a proposed histidine residue (his334) acts as a base, abstracting the C2 proton of isochorismate through a second order elimination mechanism. The C9 atom of isochorismate is then protonated, leading to the elimination of pyruvate and formation of salicylate. At pH values below 7.5 the histidine residue is protonated and therefore not able to act as a base in the mechanism, causing an accumulation of isochorismate. |
| - | + | ||
| + | '''Isochorismate synthast (IS)''' | ||
| + | The C1 carboxylate group of chorismate binds to the magnesium cation within the active site. | ||
| + | Currently, isochorismate is believed to be formed from chorismate through a proposed Sn2 mechanism involving nucleophilic attack of an activated water molecule to the C2 center followed by either a concerted or stepwise elimination of the C4 hydroxyl group'''(He et al.)'''. Lys205 has been proposed to act as the catalytic base, activating a water molecule in the active site by abstracting one of its protons. A glutamic residue (Gly252) could then protonate the C4 leaving hydroxyl group. However, mutational analysis of Lys205 suggested that the lysine reside is not the sole determinant in the activation of a water molecule for nucleophilic attack of the C2 center. | ||
| + | '''isochorismate pyruvate lyase (IPL)''' | ||
| + | '''salicylate synthase (SS)''' | ||
| + | '''chorismate mutase (CM)''' | ||
A magnesium ion in the active site orients the C1 carboxyl group of chorismate. A lysine residue then serves as a general base for the activation of a water molecule to attack at C2 | A magnesium ion in the active site orients the C1 carboxyl group of chorismate. A lysine residue then serves as a general base for the activation of a water molecule to attack at C2 | ||
Revision as of 23:47, 10 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis salicylate synthase (Mbt1)
| |||||||||||
References
1. Chi G1, Manos-Turvey A, O'Connor PD, Johnston JM, Evans GL, Baker EN, Payne RJ, Lott JS, Bulloch EM. 2012. Implications of binding mode and active site flexibility for inhibitor potency against the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry 51(24):4868-79. doi: 10.1021/bi3002067
2. Ferrer S1, Martí S, Moliner V, Tuñón I, Bertrán J. 2012 Understanding the different activities of highly promiscuous MbtI by computational methods. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 14(10):3482-9. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23149b.
3. Harrison AJ1, Yu M, Gårdenborg T, Middleditch M, Ramsay RJ, Baker EN, Lott JS. 2006. The structure of MbtI from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the first enzyme in the biosynthesis of the siderophore mycobactin, reveals it to be a salicylate synthase. J Bacteriol. 188(17):6081-91.
4. Manos-Turvey A1, Cergol KM, Salam NK, Bulloch EM, Chi G, Pang A, Britton WJ, West NP, Baker EN, Lott JS, Payne RJ. 2012. Synthesis and evaluation of M. tuberculosis salicylate synthase (MbtI) inhibitors designed to probe plasticity in the active site. Org Biomol Chem 10(46):9223-36. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26736e.
5. Zwahlen J1, Kolappan S, Zhou R, Kisker C, Tonge PJ. 2007. Structure and mechanism of MbtI, the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry. 46(4):954-64.