Sandbox Reserved 1068
From Proteopedia
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
1. Chi G1, Manos-Turvey A, O'Connor PD, Johnston JM, Evans GL, Baker EN, Payne RJ, Lott JS, Bulloch EM. 2012. Implications of binding mode and active site flexibility for inhibitor potency against the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry 51(24):4868-79. doi: 10.1021/bi3002067 | 1. Chi G1, Manos-Turvey A, O'Connor PD, Johnston JM, Evans GL, Baker EN, Payne RJ, Lott JS, Bulloch EM. 2012. Implications of binding mode and active site flexibility for inhibitor potency against the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry 51(24):4868-79. doi: 10.1021/bi3002067 | ||
| - | |||
| - | 5. De Voss, James J., Kerry Rutter, Benjamin G. Schroeder, Hua Su, and YaQi Zhu. The salicylate-derived mycobacterium siderophore of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are essential for growth in macrophages. "Proceedings of the National Science Academy" 97.3 (2000): 1252-57. Web. 5 Apr. 2015. | ||
| - | |||
2. Ferrer S1, Martí S, Moliner V, Tuñón I, Bertrán J. 2012 Understanding the different activities of highly promiscuous MbtI by computational methods. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 14(10):3482-9. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23149b. | 2. Ferrer S1, Martí S, Moliner V, Tuñón I, Bertrán J. 2012 Understanding the different activities of highly promiscuous MbtI by computational methods. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 14(10):3482-9. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23149b. | ||
3. Harrison AJ1, Yu M, Gårdenborg T, Middleditch M, Ramsay RJ, Baker EN, Lott JS. 2006. The structure of MbtI from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the first enzyme in the biosynthesis of the siderophore mycobactin, reveals it to be a salicylate synthase. J Bacteriol. 188(17):6081-91. | 3. Harrison AJ1, Yu M, Gårdenborg T, Middleditch M, Ramsay RJ, Baker EN, Lott JS. 2006. The structure of MbtI from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the first enzyme in the biosynthesis of the siderophore mycobactin, reveals it to be a salicylate synthase. J Bacteriol. 188(17):6081-91. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | 4. He, Ze, Kimberly D. Lavoie, Paul A. Bartlett, and Michael D. Toney. Conservation of Mechanism in Three Chorismate-Utilizing Enzymes. "Journal of American Chemistry Society" 126 (2004): 2378-85. Web. 7 Apr. 2015. PMID: 14982443 | ||
| - | |||
| - | 5. Lamb, Audrey L. "Pericyclic Reactions Catalized by Chorimsate-Utilizing Enzymes." American Chemical Society 50 (2011): 7476-83. Web. 5 Apr. 2015. | ||
4. Manos-Turvey A1, Cergol KM, Salam NK, Bulloch EM, Chi G, Pang A, Britton WJ, West NP, Baker EN, Lott JS, Payne RJ. 2012. Synthesis and evaluation of M. tuberculosis salicylate synthase (MbtI) inhibitors designed to probe plasticity in the active site. Org Biomol Chem 10(46):9223-36. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26736e. | 4. Manos-Turvey A1, Cergol KM, Salam NK, Bulloch EM, Chi G, Pang A, Britton WJ, West NP, Baker EN, Lott JS, Payne RJ. 2012. Synthesis and evaluation of M. tuberculosis salicylate synthase (MbtI) inhibitors designed to probe plasticity in the active site. Org Biomol Chem 10(46):9223-36. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26736e. | ||
| - | 5. Zwahlen J1, Kolappan S, Zhou R, Kisker C, Tonge PJ. 2007. Structure and mechanism of MbtI, the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry. 46(4):954-64. | + | 5. Zwahlen J1, Kolappan S, Zhou R, Kisker C, Tonge PJ. 2007. Structure and mechanism of MbtI, the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry. 46(4):954-64. |
Revision as of 04:20, 11 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
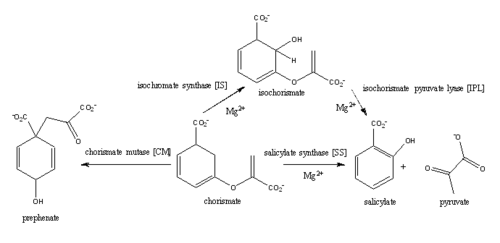
Mycobacterium tuberculosis salicylate synthase (Mbt1)
| |||||||||||
References
1. Chi G1, Manos-Turvey A, O'Connor PD, Johnston JM, Evans GL, Baker EN, Payne RJ, Lott JS, Bulloch EM. 2012. Implications of binding mode and active site flexibility for inhibitor potency against the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry 51(24):4868-79. doi: 10.1021/bi3002067
2. Ferrer S1, Martí S, Moliner V, Tuñón I, Bertrán J. 2012 Understanding the different activities of highly promiscuous MbtI by computational methods. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 14(10):3482-9. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23149b.
3. Harrison AJ1, Yu M, Gårdenborg T, Middleditch M, Ramsay RJ, Baker EN, Lott JS. 2006. The structure of MbtI from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the first enzyme in the biosynthesis of the siderophore mycobactin, reveals it to be a salicylate synthase. J Bacteriol. 188(17):6081-91.
4. Manos-Turvey A1, Cergol KM, Salam NK, Bulloch EM, Chi G, Pang A, Britton WJ, West NP, Baker EN, Lott JS, Payne RJ. 2012. Synthesis and evaluation of M. tuberculosis salicylate synthase (MbtI) inhibitors designed to probe plasticity in the active site. Org Biomol Chem 10(46):9223-36. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26736e.
5. Zwahlen J1, Kolappan S, Zhou R, Kisker C, Tonge PJ. 2007. Structure and mechanism of MbtI, the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry. 46(4):954-64.