We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1056
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
==Elucidation of ICL Structure Using Inhibitors== | ==Elucidation of ICL Structure Using Inhibitors== | ||
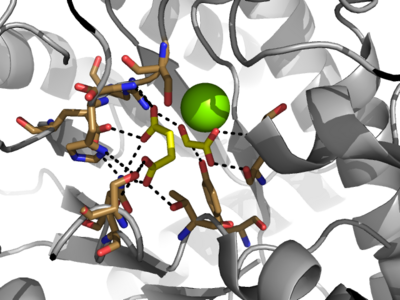
[[Image:Inhibitors57.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 5: Substrate inhibitors of Isocitrate Lyase]] | [[Image:Inhibitors57.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 5: Substrate inhibitors of Isocitrate Lyase]] | ||
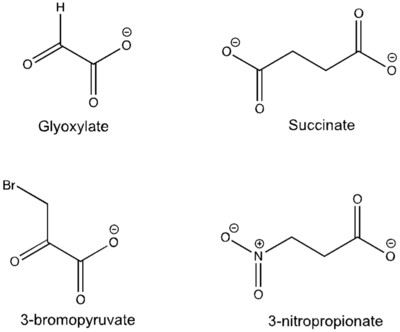
| - | The two inhibitors used to elucidate the structure of ICL were 3-nitropropionate and 3-bromopyruvate. The 3-nitropropionate was used to mimic the succinate, while the 3-bromopyruvate is used to mimic the glyoxylate. These two inhibitors have also been shown to be good inhibitors of isocitrate lyase in ''M. avium'' indicating that their inhibitory capacity is conserved across multiple species<ref name="ICL">PMID:10932251</ref>. A mutant isocitrate lyase C191S, in conjunction with the aforementioned substrate mimics, was used to elucidate the first high resolution crystal structure of ICL <ref name="ICL">PMID:10932251</ref>. Dehalogenated 3-bromopyruvate works to inhibit isocitrate lyase by forming a covalent bond with the | + | The two inhibitors used to elucidate the structure of ICL were 3-nitropropionate and 3-bromopyruvate. The 3-nitropropionate was used to mimic the succinate, while the 3-bromopyruvate is used to mimic the glyoxylate. These two inhibitors have also been shown to be good inhibitors of isocitrate lyase in ''M. avium'' indicating that their inhibitory capacity is conserved across multiple species<ref name="ICL">PMID:10932251</ref>. A mutant isocitrate lyase C191S, in conjunction with the aforementioned substrate mimics, was used to elucidate the first high resolution crystal structure of ICL <ref name="ICL">PMID:10932251</ref>. Dehalogenated 3-bromopyruvate works to inhibit isocitrate lyase by forming a covalent bond with the Ser191 in the active site. This 3-bromopyruvate occupies the same site that the succinate would occupy. The C191S mutant adopts a conformation almost identical to the CYS191 residue in the wild type indicating that this is an accurate depiction of the conformation. |
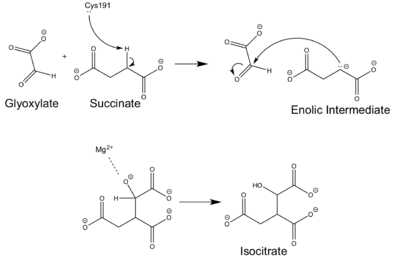
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 17 April 2015
Isocitrate Lyase from Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Isocitrate Lyase
Updated on 17-April-2015
- ICL from other bacteria
References
- ↑ Srivastava V, Jain A, Srivastava BS, Srivastava R. Selection of genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis upregulated during residence in lungs of infected mice. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2008 May;88(3):171-7. Epub 2007 Dec 3. PMID:18054522 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2007.10.002
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 Sharma V, Sharma S, Hoener zu Bentrup K, McKinney JD, Russell DG, Jacobs WR Jr, Sacchettini JC. Structure of isocitrate lyase, a persistence factor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Struct Biol. 2000 Aug;7(8):663-8. PMID:10932251 doi:10.1038/77964
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Beeching JR. High sequence conservation between isocitrate lyase from Escherichia coli and Ricinus communis. Protein Seq Data Anal. 1989 Dec;2(6):463-6. PMID:2696959
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Masamune et al. Bio-Claisen condensation catalyzed by thiolase from Zoogloea ramigera. Active site cysteine residues. "Journal of the American Chemical Society" 111: 1879-1881 (1989). DOI: 10.1021/ja00187a053
- ↑ Connely, M. L. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids "Science" 221:709-713 (1983). DOI: 10.1126/science.6879170