This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
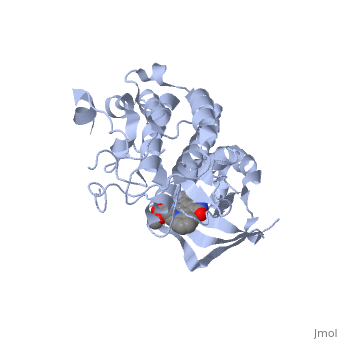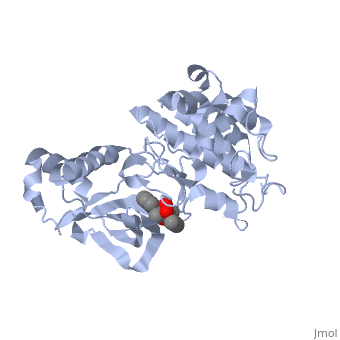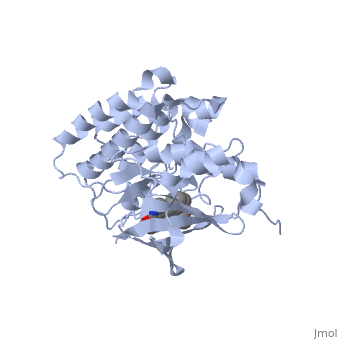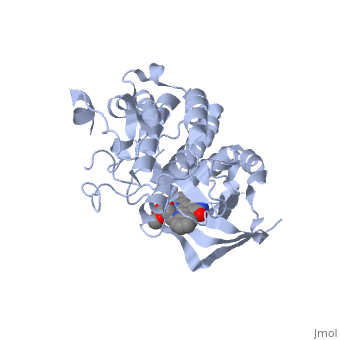
This receptor follows the typical structure of a protein kinase, with a bilobal structure. The N-terminal contains <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/Beta_sheets/1'>β-sheets</scene> and is linked through a hinge to the C lobe, which is full of α helices. This particular kinase domain is very similar to the domains of the insulin receptor kinase and fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase.<ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> | This receptor follows the typical structure of a protein kinase, with a bilobal structure. The N-terminal contains <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/Beta_sheets/1'>β-sheets</scene> and is linked through a hinge to the C lobe, which is full of α helices. This particular kinase domain is very similar to the domains of the insulin receptor kinase and fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase.<ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> | ||
| - | =Helices= | + | ==Helices== |
This structure is made up of many α helical structures that move in the transformation from inactive to active kinase. Some of these helices are conserved in many different tyrosine kinases. C-met does show a divergence from other tyrosine kinases (such as IRK and FGFRK) in the helix formed at the N-terminus, before the core kinase domain, in residues <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/1060-1069/1'>1060-1069</scene>. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> The αA is in contact with αC and so causes αC to be in a slightly different orientation than in FGFRK and IRK. Residues Leu-1062, Val-1066, and Val-1069 of αA <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/A_and_c_intercalating/1'>intercalate</scene> with with residues Leu-1125 and Ile-1129 of αC. There is another <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/A_and_c_intercalating/2'>interaction</scene> between the residues Ile-1053, Leu-1055 and Leu-1058 of αA and Ile-1118 and Val-1121 of αC. Because of the movement of αC during activation of the kinase, it is an assumption that αA is also part of the kinase activation upon ligand binding. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> | This structure is made up of many α helical structures that move in the transformation from inactive to active kinase. Some of these helices are conserved in many different tyrosine kinases. C-met does show a divergence from other tyrosine kinases (such as IRK and FGFRK) in the helix formed at the N-terminus, before the core kinase domain, in residues <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/1060-1069/1'>1060-1069</scene>. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> The αA is in contact with αC and so causes αC to be in a slightly different orientation than in FGFRK and IRK. Residues Leu-1062, Val-1066, and Val-1069 of αA <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/A_and_c_intercalating/1'>intercalate</scene> with with residues Leu-1125 and Ile-1129 of αC. There is another <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/A_and_c_intercalating/2'>interaction</scene> between the residues Ile-1053, Leu-1055 and Leu-1058 of αA and Ile-1118 and Val-1121 of αC. Because of the movement of αC during activation of the kinase, it is an assumption that αA is also part of the kinase activation upon ligand binding. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
<scene name='User:Juliette_Personius/sandbox_1/1234_and_1235_mutations/1'>tyr1234 and tyr1235</scene> are replaced by a phenylalanine and aspartate, respectively. This mutation normally causes the receptor to be constitutively active, and is found in HNSC (Head, Neck squamous cell) carcinoma. Although there is no longer phosphorylation at these sites, it is believed that the negative charge of the aspartate resembles the negative phosphate that would normally cause activation, and therefore keeps the protein in its active form. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> There is a third mutation at Tyr-1194 which is substituted for a <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/1194/1'>phenylalanine</scene>. This is shown to point into the <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/1198/1'>pocket</scene> formed by Lys-1198 and Leu-1195 from αE. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> This structure is conserved in the wild type protein, suggesting that the mutation at residue 1149 is not changing the structure at this position. | <scene name='User:Juliette_Personius/sandbox_1/1234_and_1235_mutations/1'>tyr1234 and tyr1235</scene> are replaced by a phenylalanine and aspartate, respectively. This mutation normally causes the receptor to be constitutively active, and is found in HNSC (Head, Neck squamous cell) carcinoma. Although there is no longer phosphorylation at these sites, it is believed that the negative charge of the aspartate resembles the negative phosphate that would normally cause activation, and therefore keeps the protein in its active form. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> There is a third mutation at Tyr-1194 which is substituted for a <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/1194/1'>phenylalanine</scene>. This is shown to point into the <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/1198/1'>pocket</scene> formed by Lys-1198 and Leu-1195 from αE. <ref>PMID: 14559966</ref> This structure is conserved in the wild type protein, suggesting that the mutation at residue 1149 is not changing the structure at this position. | ||
| - | =K-252a= | + | ==K-252a== |
<scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/K-252a/1'>K-252a</scene> is a staurosporine analog. Staurosporine is an inhibitor of many Ser/Thr Kinases, and has been shown to also inhibit c-Met activation by inhibiting its autophosphorylation. The structures of K-252a and staurosporine are very similar, with the main difference being that K-252a has a furanose instead of a pyranose structure. The binding of K-252a causes the c-Met to adopt an inhibitory conformation of the A-loop, specifically with residues <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/Residues1231-1244/1'>1231-1244</scene> . This segment blocks the place where the substrate tyrosine side chain would bind, if the protein were in an active conformation. Residues | <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/K-252a/1'>K-252a</scene> is a staurosporine analog. Staurosporine is an inhibitor of many Ser/Thr Kinases, and has been shown to also inhibit c-Met activation by inhibiting its autophosphorylation. The structures of K-252a and staurosporine are very similar, with the main difference being that K-252a has a furanose instead of a pyranose structure. The binding of K-252a causes the c-Met to adopt an inhibitory conformation of the A-loop, specifically with residues <scene name='Hepatocyte_growth_factor_receptor/Residues1231-1244/1'>1231-1244</scene> . This segment blocks the place where the substrate tyrosine side chain would bind, if the protein were in an active conformation. Residues | ||
Revision as of 10:00, 8 February 2016
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of hepatocyte growth factor receptor
Updated on 08-February-2016
References
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C-Met
- ↑ Maina F, Casagranda F, Audero E, Simeone A, Comoglio PM, Klein R, Ponzetto C. Uncoupling of Grb2 from the Met receptor in vivo reveals complex roles in muscle development. Cell. 1996 Nov 1;87(3):531-42. PMID:8898205
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100