We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1063
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structural Highlights == | == Structural Highlights == | ||
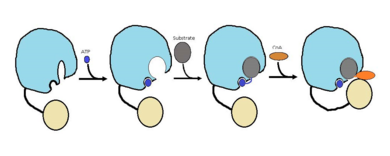
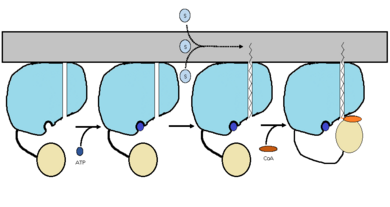
| - | FadD13 is composed of 503 amino acids which are divided into two domains. The larger of the two domains is the N-terminal domain composed of <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/8'>residues 1-395</scene> shown in blue. The smaller of the two domains is the C-terminal domain composed of <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/10'>residues 402-503</scene> shown in yellow. These two domains are held together by a flexible 6 amino acid linker (<scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/11'>residues 396-401</scene>) shown in black<ref name="Anderson 2012"/>. Research has also shown that altering V209D, D382A, and W377A effects the structual stability of FadD13. <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/18'>Val 209</scene> and <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/19'>Asp 382</scene> showed marginally reduced cytoplasmic expression, while <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/17'>Trp 377</scene> showed a noteworthy low cytosolic expression. | + | FadD13 is composed of 503 amino acids which are divided into two domains. The larger of the two domains is the N-terminal domain composed of <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/8'>residues 1-395</scene> shown in blue. The smaller of the two domains is the C-terminal domain composed of <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/10'>residues 402-503</scene> shown in yellow. These two domains are held together by a flexible 6 amino acid linker (<scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/11'>residues 396-401</scene>) shown in black<ref name="Anderson 2012"/>. Research has also shown that altering V209D, D382A, and W377A effects the structual stability of FadD13. <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/18'>Val 209</scene> and <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/19'>Asp 382</scene> showed marginally reduced cytoplasmic expression, while <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/17'>Trp 377</scene> showed a noteworthy low cytosolic expression<ref name="Khare 2009"/>. |
===Active Site=== | ===Active Site=== | ||
The active site of FadD13 is composed of an <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/12'>ATP/AMP binding region</scene>. This region is comprised of residues 164-TSGTTGHPKG173-173 shown in red which binds to the phosphate group, and residues 298-VQGYALTE-305 shown in blue which binds to the adenine group. Research has also shown that <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/16'>Ser 404</scene> plays a major role in binding of CoA. Ser 404 was shown to have a 4-fold enhancement for the Km value of CoA.<ref name="Khare 2009">DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008387</ref> | The active site of FadD13 is composed of an <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/12'>ATP/AMP binding region</scene>. This region is comprised of residues 164-TSGTTGHPKG173-173 shown in red which binds to the phosphate group, and residues 298-VQGYALTE-305 shown in blue which binds to the adenine group. Research has also shown that <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/16'>Ser 404</scene> plays a major role in binding of CoA. Ser 404 was shown to have a 4-fold enhancement for the Km value of CoA.<ref name="Khare 2009">DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008387</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 21 April 2015
FadD13
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Watkins PA, Maiguel D, Jia Z, Pevsner J. Evidence for 26 distinct acyl-coenzyme A synthetase genes in the human genome. J Lipid Res. 2007 Dec;48(12):2736-50. Epub 2007 Aug 30. PMID:17762044 doi:http://dx.doi.org/M700378-JLR200
- ↑ Kochan G, Pilka ES, von Delft F, Oppermann U, Yue WW. Structural snapshots for the conformation-dependent catalysis by human medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM2A. J Mol Biol. 2009 May 22;388(5):997-1008. Epub 2009 Apr 1. PMID:19345228 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.064
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Andersson CS, Lundgren CA, Magnusdottir A, Ge C, Wieslander A, Molina DM, Hogbom M. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: Structural Basis for Housing Lipid Substrates Longer than the Enzyme. Structure. 2012 May 2. PMID:22560731 doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.03.012
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Khare G, Gupta V, Gupta RK, Gupta R, Bhat R, Tyagi AK. Dissecting the role of critical residues and substrate preference of a Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase (FadD13) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2009 Dec 21;4(12):e8387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008387. PMID:20027301 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008387