We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Connexin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
=Structure:= | =Structure:= | ||
==Connexin structure== | ==Connexin structure== | ||
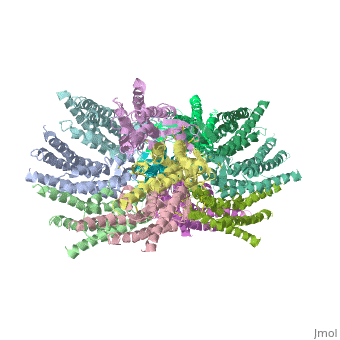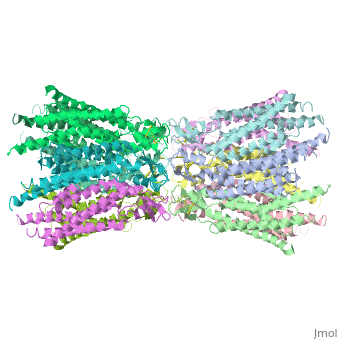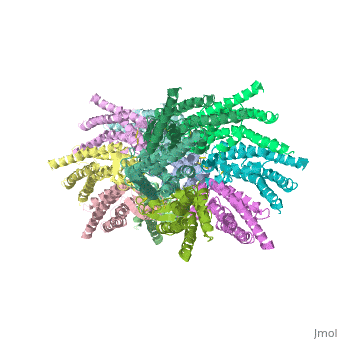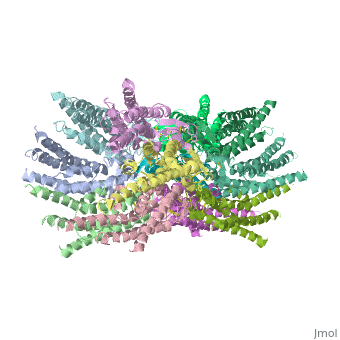
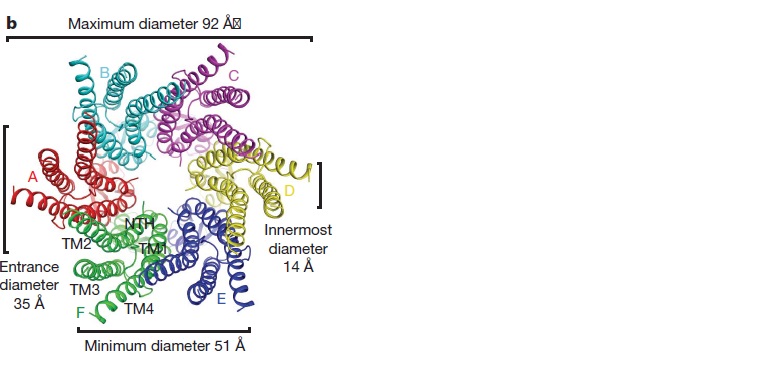
| - | + | <scene name='70/701426/Connexons_secondary_structure/1'>connexins</scene>are integral α-hellical transmembrane proteins that form intercellular channels in vertebrates . Six connexins form a hexamerical assembly, known as <scene name='70/701426/Connexin_26_basic_structure/2'>Connexon</scene> connexon or hemichannel , which delineates an aqueous pore with a minimum diameter of ∼1.2 nm. When two hemichannels from adjacent cells dock and join, leaving a gap of ∼2–3 nm, they may form an intercellular [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P29033 gap junction channel] which spans the two pαlasma membranes and allows the exchange of cytoplasmic molecules with size up to ∼1 kDa. | |
The height of the modelled structure of the gap junction channel without disordered cytoplasmic loop and C-terminal segment is approximately 155Å. The transmembrane region and membrane surfaces were deduced from the distribution of hydrophobic and aromatic amino acid residues along the noncrystallographic six-fold axis It is a tsuzumi shape, a traditional Japanese drum.<ref name='Structure'/> [[Image:distances a.jpg]] | The height of the modelled structure of the gap junction channel without disordered cytoplasmic loop and C-terminal segment is approximately 155Å. The transmembrane region and membrane surfaces were deduced from the distribution of hydrophobic and aromatic amino acid residues along the noncrystallographic six-fold axis It is a tsuzumi shape, a traditional Japanese drum.<ref name='Structure'/> [[Image:distances a.jpg]] | ||
The protomers in each hexameric connexon are related by a sixfold non-crystallographic symmetry (NCS) axis perpendicular to the membrane plane . The transmembrane region of the channel is 38Å thick.TM2 extends about 19Å from the membrane surface into the cytoplasm. The extracellular region of the connexon extends 23Å from the membrane surface and interdigitates to the opposite connexon by 6Å, resulting in the intercellular ‘gap’ of 40Å. The extracellular lobes are not protruding so much, as indicated by the structural analyses of split gap junction channels with atomic force microscopy and electron microscopy. The relatively flat lobes could be attributed to the conformational change of the extracellular region induced by the docking of two connexons. The diameter of the connexon is biggest at the cytoplasmic side | The protomers in each hexameric connexon are related by a sixfold non-crystallographic symmetry (NCS) axis perpendicular to the membrane plane . The transmembrane region of the channel is 38Å thick.TM2 extends about 19Å from the membrane surface into the cytoplasm. The extracellular region of the connexon extends 23Å from the membrane surface and interdigitates to the opposite connexon by 6Å, resulting in the intercellular ‘gap’ of 40Å. The extracellular lobes are not protruding so much, as indicated by the structural analyses of split gap junction channels with atomic force microscopy and electron microscopy. The relatively flat lobes could be attributed to the conformational change of the extracellular region induced by the docking of two connexons. The diameter of the connexon is biggest at the cytoplasmic side | ||
Revision as of 11:44, 17 May 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Zonta F, Buratto D, Cassini C, Bortolozzi M, Mammano F. Molecular dynamics simulations highlight structural and functional alterations in deafness-related M34T mutation of connexin 26. Front Physiol. 2014 Mar 4;5:85. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00085. eCollection 2014. PMID:24624091 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00085
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Suga M, Maeda S, Nakagawa S, Yamashita E, Tsukihara T. A description of the structural determination procedures of a gap junction channel at 3.5 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009 Aug;65(Pt 8):758-66. Epub 2009, Jul 10. PMID:19622859 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0907444909014711
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Connexin
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Ambrosi C, Walker AE, Depriest AD, Cone AC, Lu C, Badger J, Skerrett IM, Sosinsky GE. Analysis of trafficking, stability and function of human connexin 26 gap junction channels with deafness-causing mutations in the fourth transmembrane helix. PLoS One. 2013 Aug 15;8(8):e70916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070916. eCollection, 2013. PMID:23967136 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070916
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Oshima A, Tani K, Toloue MM, Hiroaki Y, Smock A, Inukai S, Cone A, Nicholson BJ, Sosinsky GE, Fujiyoshi Y. Asymmetric Configurations and N-terminal Rearrangements in Connexin26 Gap Junction Channels. J Mol Biol. 2011 Jan 21;405(3):724-35. Epub 2010 Nov 20. PMID:21094651 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.10.032
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Safaa Salah Hussiesy, Michal Harel, Doaa Naffaa, Jaime Prilusky