User:Rana Saad/The human GABAb receptor
From Proteopedia
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
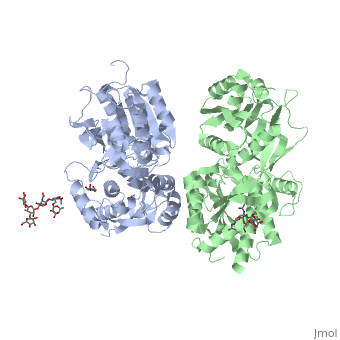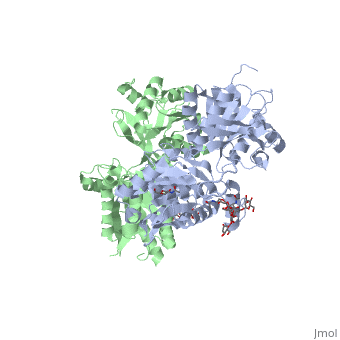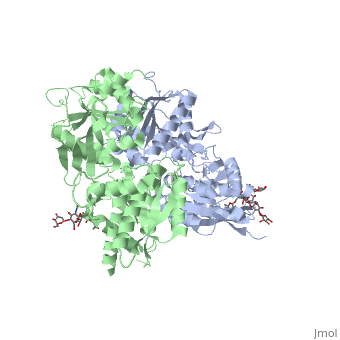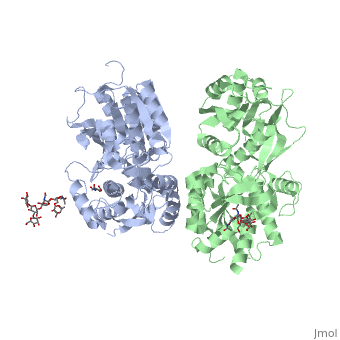
| - | <Structure load='4mqe' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Extracellular domains of human GABA | + | <Structure load='4mqe' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Extracellular domains of human GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> |
=='''''Agonist and antagonist binding'''''== | =='''''Agonist and antagonist binding'''''== | ||
Revision as of 08:26, 18 May 2015
Contents |
Introduction
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)
GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS). It plays a key role in modulating neuronal activity since it binds to specific transmembrane receptors (GABAA,GABAB and GABAC) in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal level.
GABAB receptors
Mammalian GABAB receptor is a class C G-protein coupled receptor[1]. Its structure is similar to mGluR ligand binding domain. GABAB is central to inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain and so is considered a good candidate for treatments against alcoholism, stress and number of brain diseases[2].
Function
The GABAB receptor causes the opening of the K+ channels in the postsynaptic membrane, bringing the neuron closer to the equilibrium potential of K+, producing hyperpolarization. As a result the Ca+2 channels in the presynaptic terminal close and neurotransmitter release stops. GABAB can also reduce the activity of adenylyl cyclase and decrease the cell’s conductance to Ca+2.[1].
structure
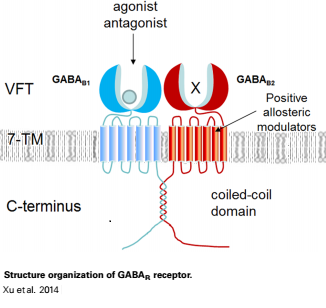
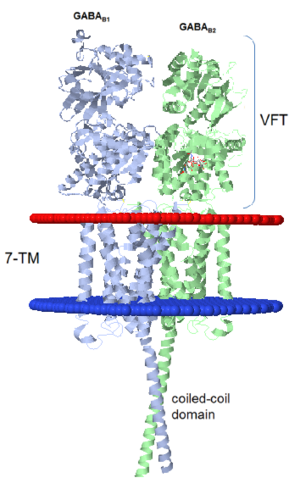
GABAB functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of GABAB1 (GBR1) and GABAB2 (GBR2). GBR1 is responsible for ligand-binding. GBR2, on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunits. The GABAB receptor is one of only a few obligate receptor heterodimers currently known.
GBR1 and GBR2 subunits structure
Each subunit is a domain of seven-transmembrane helixes, composed of a large extracellular domain - venus flytrap (VFT). VFT contains two lobe-shaped domains: LB1 and LB2, which are connected by three short loops. LB1 and LB2 are [3].
| |||||||||||