This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Vitamin D receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
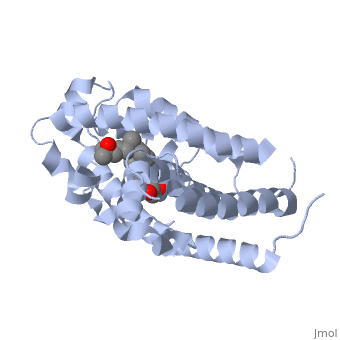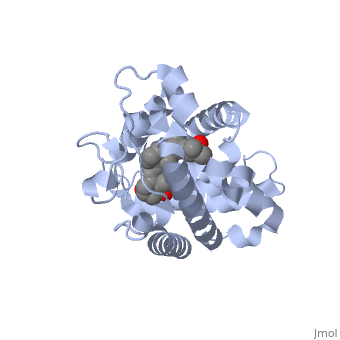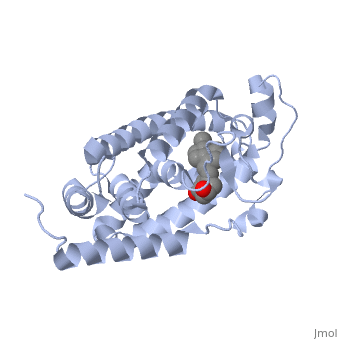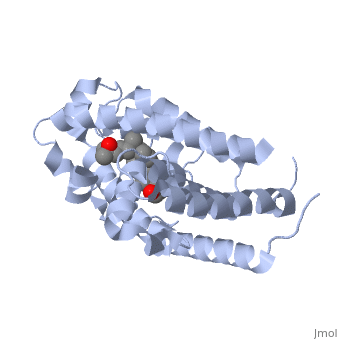
<StructureSection load='1db1' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human vitamin D receptor ligand-binding domain complex with vitamin D (PDB entry [[1db1]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1db1' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human vitamin D receptor ligand-binding domain complex with vitamin D (PDB entry [[1db1]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | == Introduction == | |
'''Vitamin D receptor''' (<scene name='56/562378/Vit_d_receptor_3m7r/3'>VDR</scene>) is a transcription factor. Upon binding to vitamin D, VDR forms a heterodimer with retinoid-X receptor and binds to hormone response receptors on DNA causing gene expression. The <scene name='56/562378/Vit_d_receptor_ligand/1'>vitamin D hormone</scene> (in green) binds to receptors in its target cells, controlling the synthesis of many different proteins involved in calcium transport and utilization. VDR contains two domains: a <scene name='56/562378/Lbd/1'>ligand binding domain (LBD)</scene> that binds to the hormone (grey) and <scene name='56/562378/Dbd/2'>DNA-binding domain (DBD)</scene> that binds to DNA. (Green and blue are two same VDR structures). It pairs up with a similar protein, 9-cis retinoic acid receptor (RXR), and together they bind to the DNA, activating synthesis in some cases and repressing it in others. | '''Vitamin D receptor''' (<scene name='56/562378/Vit_d_receptor_3m7r/3'>VDR</scene>) is a transcription factor. Upon binding to vitamin D, VDR forms a heterodimer with retinoid-X receptor and binds to hormone response receptors on DNA causing gene expression. The <scene name='56/562378/Vit_d_receptor_ligand/1'>vitamin D hormone</scene> (in green) binds to receptors in its target cells, controlling the synthesis of many different proteins involved in calcium transport and utilization. VDR contains two domains: a <scene name='56/562378/Lbd/1'>ligand binding domain (LBD)</scene> that binds to the hormone (grey) and <scene name='56/562378/Dbd/2'>DNA-binding domain (DBD)</scene> that binds to DNA. (Green and blue are two same VDR structures). It pairs up with a similar protein, 9-cis retinoic acid receptor (RXR), and together they bind to the DNA, activating synthesis in some cases and repressing it in others. | ||
Revision as of 11:01, 13 December 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of vitamin D receptor
Updated on 13-December-2016
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky, Isita Amin