User:Rana Saad/The human GABAb receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|thumb|250px]] | [[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|thumb|250px]] | ||
=='''''Structure'''''== | =='''''Structure'''''== | ||
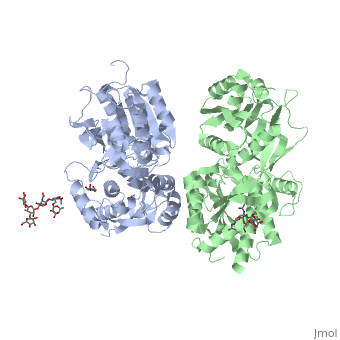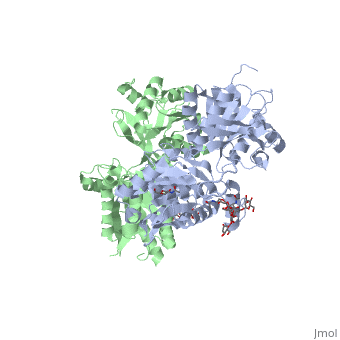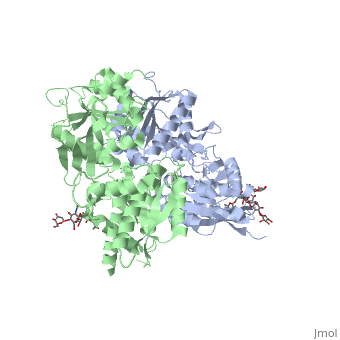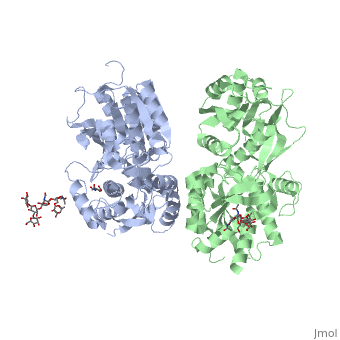
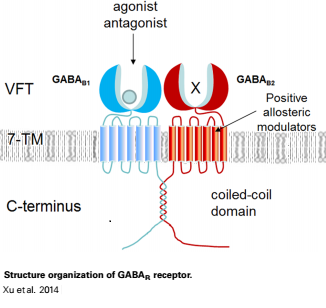
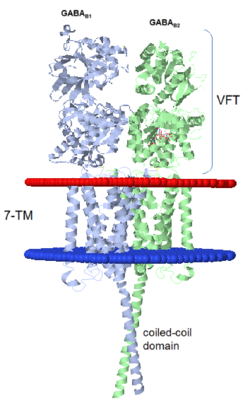
| - | GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of GABA<sub>B1</sub> (GBR1) and GABA<sub>B2</sub> (GBR2). GBR1 (blue) is responsible for ligand-binding (chain A). GBR2 (green), on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunit (chain B). The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of only a few obligate receptor heterodimer currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete receptor since it have extracellular and inter cellular regions. | + | GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of '''GABA<sub>B1</sub>''' (GBR1) and '''GABA<sub>B2</sub>''' (GBR2). '''GBR1''' (blue) is responsible for ligand-binding (chain A). '''GBR2''' (green), on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunit (chain B). The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of only a few obligate receptor heterodimer currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete receptor since it have extracellular and inter cellular regions in addition to there 7 trans membrane helices. |
| - | Each subunit, GBR1 and GBR2, is a domain of seven-transmembrane | + | Each subunit, GBR1 and GBR2, is a domain of seven-transmembrane helices, composed of a large extracellular domain - venus flytrap (VFT), it is called like this because it is like the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus_flytrap venus flytrap] while binding agonist and antagonist, and intercellular domain which important for the dimerzation. |
| + | ==='''The extracellular domain'''=== | ||
VFT contains two lobe-shaped domains: LB1 and LB2, which are connected by three short loops. | VFT contains two lobe-shaped domains: LB1 and LB2, which are connected by three short loops. | ||
LB1 and LB2 are <scene name='70/701448/Gbr2_subunit/1'>αβ-folds composed of central β sheet flanked by an α helix</scene><ref>PMID:24305054</ref>. | LB1 and LB2 are <scene name='70/701448/Gbr2_subunit/1'>αβ-folds composed of central β sheet flanked by an α helix</scene><ref>PMID:24305054</ref>. | ||
| - | + | ===='''''Agonist and antagonist binding'''''==== | |
| - | =='''''Agonist and antagonist binding'''''== | + | |
All of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agonist agonists] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_antagonist antagonists] bind the '''extracellular VFT module situated at the crevice between the LB1 and LB2 domains of the GBR1 subunit'''. | All of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agonist agonists] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_antagonist antagonists] bind the '''extracellular VFT module situated at the crevice between the LB1 and LB2 domains of the GBR1 subunit'''. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP54626</scene> (PDB 4MR7). | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP54626</scene> (PDB 4MR7). | ||
[[ Image:GABAb bound to antagonist2.jpg|center|450px]] | [[ Image:GABAb bound to antagonist2.jpg|center|450px]] | ||
| - | ==''''' | + | ==='''''The intercellular dimerization motif'''''=== |
When the GBR1 subunit is expressed alone, it is trapped in vesicles within the cell, whereas the GBR2 alone is expressed on the cell surface, but cannot bind GABA or activate G proteins. When both receptor subunits are expressed in the same cell, the receptor interact through <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/1'>coiled-coil domain</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref><ref>PMID:12209124</ref> (PDB 4PAS) in their carboxyl tails. They are then expressed on the cell surface, bind GABA and activate G proteins. | When the GBR1 subunit is expressed alone, it is trapped in vesicles within the cell, whereas the GBR2 alone is expressed on the cell surface, but cannot bind GABA or activate G proteins. When both receptor subunits are expressed in the same cell, the receptor interact through <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/1'>coiled-coil domain</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref><ref>PMID:12209124</ref> (PDB 4PAS) in their carboxyl tails. They are then expressed on the cell surface, bind GABA and activate G proteins. | ||
This domain is shaped by <scene name='70/701448/Coild-coil_domain/1'>polar interactions within the hydrophobic core</scene> and is stabilized by <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/3'>hydrogen-bonding interactions</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref>. | This domain is shaped by <scene name='70/701448/Coild-coil_domain/1'>polar interactions within the hydrophobic core</scene> and is stabilized by <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/3'>hydrogen-bonding interactions</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 06:56, 9 July 2015
| |||||||||||