Regulator of G protein signaling
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== RGS4 Structural highlights == | == RGS4 Structural highlights == | ||
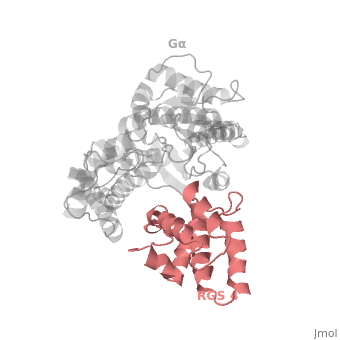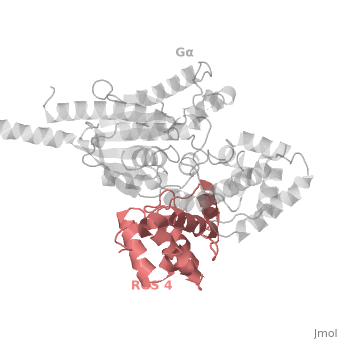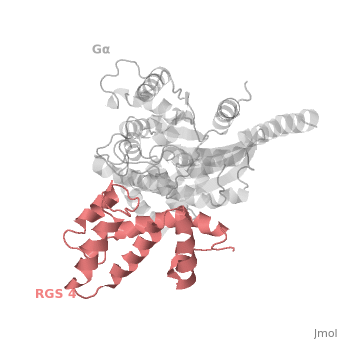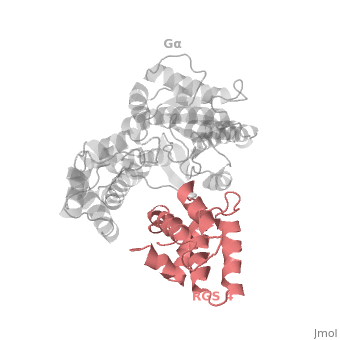
1AGR is a complex of RGS4 and Gα<sub>i1</sub> proteins defined by X-ray crystallographic analysis. | 1AGR is a complex of RGS4 and Gα<sub>i1</sub> proteins defined by X-ray crystallographic analysis. | ||
| - | <scene name='70/701447/Rgs4_monomer/5'> The RGS4 domain </scene> corresponds to an array of nine α-helices: α1, α2, α3, α4, α5 and α6 helices are colored in blue, aqua, yellow, coral, magenta and dark green respectively while helices α7, α8 and α9 are colored red. RGS4 protein fold into <scene name='70/701447/Rgs4_subdomains/1'>two small subdomains</scene>, both subdomains are required for it's GAP activity. The terminal subdomain colored magenta, contains the N and C termini of the box and is formed by α1, α2, α3, α8, and α9. The larger bundle subdomain colored cyan formed by α4, α5, α6, and α7. | + | <scene name='70/701447/Rgs4_monomer/5'> The RGS4 domain </scene> corresponds to an array of nine α-helices: α1, α2, α3, α4, α5 and α6 helices are colored in blue, aqua, yellow, coral, magenta and dark green respectively, while helices α7, α8 and α9 are colored red. RGS4 protein fold into <scene name='70/701447/Rgs4_subdomains/1'>two small subdomains</scene>, both subdomains are required for it's GAP activity. The terminal subdomain colored magenta, contains the N and C termini of the box and is formed by α1, α2, α3, α8, and α9. The larger bundle subdomain colored cyan formed by α4, α5, α6, and α7. |
== Gα<sub>i1</sub> Structural highlights == | == Gα<sub>i1</sub> Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 21:50, 10 July 2015
Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) interactions with G proteins – RGS4-Gαi as a model structure.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Milligan G, Kostenis E. Heterotrimeric G-proteins: a short history. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147 Suppl 1:S46-55. PMID:16402120 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706405
- ↑ Kosloff M, Travis AM, Bosch DE, Siderovski DP, Arshavsky VY. Integrating energy calculations with functional assays to decipher the specificity of G protein-RGS protein interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 19;18(7):846-53. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2068. PMID:21685921 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2068
- ↑ Tesmer JJ, Berman DM, Gilman AG, Sprang SR. Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF4--activated G(i alpha1): stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell. 1997 Apr 18;89(2):251-61. PMID:9108480
- ↑ Kosloff M, Travis AM, Bosch DE, Siderovski DP, Arshavsky VY. Integrating energy calculations with functional assays to decipher the specificity of G protein-RGS protein interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 19;18(7):846-53. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2068. PMID:21685921 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2068
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ali Asli, Denise Salem, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky